
The hypoblast (inner germ layer of gastrula) forms the
A. Ectoderm
B. Mesoderm
C. Endoderm
D. None of the above.
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: The endoderm is a prominent germ layer which is formed during the period of animal embryogenesis. It is essentially derived from the hypoblast.
Complete answer: The hypoblast is an important transient structure which greatly contributes to the development of the extraembryonic mesoderm along with the yolk sac and plays a crucial role in signaling to establish the characteristic axial patterning in the embryo itself.
The inner cell mass (ICM) segregates into a bilaminar embryonic disc (i.e. bilaminar blastoderm) which again consists of two epithelial layers, each having a distinct lineage: the external epiblast (it is present dorsally) and the internal hypoblast (it is present ventrally). During the period of gastrulation, the process in which the three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and the endoderm) of the trilaminar embryonic disc are formed, cells from the epiblast migrate, through the primitive streak, into the inside part of the embryo, in a process which is better known as ingression.
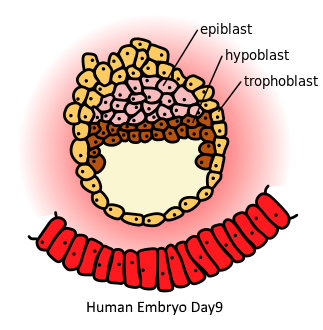
Additional information: Ingression is the process which involves cellular epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT).
The initial wave of these migrating cells streams through the primitive streak, thus displacing the hypoblast cells to become the definitive endoderm, which eventually produces the future gut derivatives and gut linings.
So, the correct answer is C. Endoderm.
Note: The hypoblast is located beneath the epiblast and is made up of small cuboidal cells. The cells of the hypoblast ultimately form the endoderm, which in turn gives rise to the development and formation of the respiratory and digestive tracts.
Complete answer: The hypoblast is an important transient structure which greatly contributes to the development of the extraembryonic mesoderm along with the yolk sac and plays a crucial role in signaling to establish the characteristic axial patterning in the embryo itself.
The inner cell mass (ICM) segregates into a bilaminar embryonic disc (i.e. bilaminar blastoderm) which again consists of two epithelial layers, each having a distinct lineage: the external epiblast (it is present dorsally) and the internal hypoblast (it is present ventrally). During the period of gastrulation, the process in which the three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and the endoderm) of the trilaminar embryonic disc are formed, cells from the epiblast migrate, through the primitive streak, into the inside part of the embryo, in a process which is better known as ingression.

Additional information: Ingression is the process which involves cellular epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT).
The initial wave of these migrating cells streams through the primitive streak, thus displacing the hypoblast cells to become the definitive endoderm, which eventually produces the future gut derivatives and gut linings.
So, the correct answer is C. Endoderm.
Note: The hypoblast is located beneath the epiblast and is made up of small cuboidal cells. The cells of the hypoblast ultimately form the endoderm, which in turn gives rise to the development and formation of the respiratory and digestive tracts.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




