
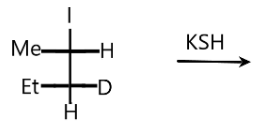
The product of following reactant is:
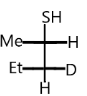
A.
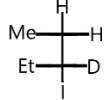
B.
C.
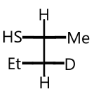
D.
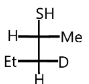





Answer
548.1k+ views
Hint: Potassium hydrosulphide is an inorganic compound. It is colorless salt. It is made up of cation ${K^ + }$ and bisulfide anion $S{H^ - }$. It will act as a nucleophile in this reaction. To find out the product of the above reactant first, we will identify whether it is primary or secondary or tertiary chiral carbon. After that we will see the role of KSH.
Complete step-by-step answer:As we know that the secondary and tertiary chiral carbon forms the product through ${S_{{N^2}}}$ mechanism. The reagent KSH acts as a nucleophile then it will displace the halogen in the compound. During ${S_{{N^2}}}$ mechanism no carbocation is formed but transition state is formed. They occur in one step. During the reaction nucleophile attacks from the back side. Since the nucleophile attacks from the back side, we get a product having configuration opposite to the reactant i.e. inversion of configuration takes place in ${S_{{N^2}}}$ reaction which is also said to be Walden inversion (complete inversion occurs).
According to the above conditions, let us see our problem. When the reactant reacts with potassium hydrosulfide, the halogen that is iodine is replaced by the $S{H^ - }$ ion. Elimination of potassium iodide will take place. The potassium hydrosulphide will split into anion and cation as:
$KSH \to {K^ + } + {\left[ {SH} \right]^ - }$
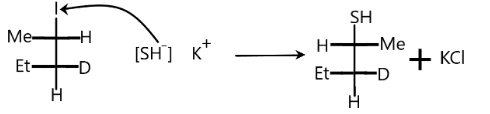
Nucleophile attacks from the back side, therefore we get products with opposite configurations to the reactant.
So, option (D) is correct.
Note: Keep in mind that only a strong nucleophile has the ability to displace the weaker nucleophile from the compound. Whenever any nucleophile attacks from the back side, the configuration of the product will be opposite to the reactant. Don’t confuse yourself with the electrophilic and nucleophilic.
Complete step-by-step answer:As we know that the secondary and tertiary chiral carbon forms the product through ${S_{{N^2}}}$ mechanism. The reagent KSH acts as a nucleophile then it will displace the halogen in the compound. During ${S_{{N^2}}}$ mechanism no carbocation is formed but transition state is formed. They occur in one step. During the reaction nucleophile attacks from the back side. Since the nucleophile attacks from the back side, we get a product having configuration opposite to the reactant i.e. inversion of configuration takes place in ${S_{{N^2}}}$ reaction which is also said to be Walden inversion (complete inversion occurs).
According to the above conditions, let us see our problem. When the reactant reacts with potassium hydrosulfide, the halogen that is iodine is replaced by the $S{H^ - }$ ion. Elimination of potassium iodide will take place. The potassium hydrosulphide will split into anion and cation as:
$KSH \to {K^ + } + {\left[ {SH} \right]^ - }$

Nucleophile attacks from the back side, therefore we get products with opposite configurations to the reactant.
So, option (D) is correct.
Note: Keep in mind that only a strong nucleophile has the ability to displace the weaker nucleophile from the compound. Whenever any nucleophile attacks from the back side, the configuration of the product will be opposite to the reactant. Don’t confuse yourself with the electrophilic and nucleophilic.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




