
The solubility of alcohols in water gradually increases with molecular weight.
(A) True
(B) False
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: The increasing molecular weight of the alcohol involving the addition of methylene group which has a tendency to partially donate its electron towards the adjacent carbon atom to the hydroxyl group in alcohols has an impact on its solubility.
Complete step by step solution:
In order to determine the solubility of the alcohols in water, the hydroxyl group present in alcohol plays an important role. As the alcohol consists of the hydrocarbon chain which is non-polar in nature and the hydroxyl group which is polar in nature due to the presence of the electronegative oxygen atom which forms the hydrogen-bond with the water molecule.
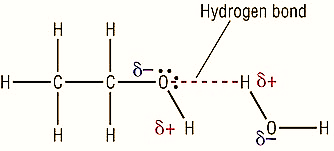
But as the length of the hydrocarbon chain increases, more than four carbon atoms, that is, with the increase in the molecular weight of the alcohol, there is a significant decrease in the solubility of the alcohols in water. Also, beyond, seven carbon atoms chain, the alcohols become immiscible and the mixture forms. This is because of the increase inductive effect by the methylene $(-C{{H}_{2}}-)$ and methyl $(-C{{H}_{3}})$ group present, which causes a positive inductive effect $(+I)$, increasing the electron density over the electronegative oxygen atom. Thus, making the formation of hydrogen bonds difficult. Thereby, decreasing the solubility of the higher or heavier alcohols in water.
Therefore, the solubility of alcohols in water gradually increases with molecular weight is option (B)- False.
Note: The nonpolar hydrocarbon chains in alcohol are hydrophobic or water-repelling in nature whereas, the hydroxyl group is hydrophilic in nature as it bonds with the water molecule. So, the dominance of either the hydrophobic part of the hydrophilic part determines the solubility of the alcohol as their molecular weight increases.
Complete step by step solution:
In order to determine the solubility of the alcohols in water, the hydroxyl group present in alcohol plays an important role. As the alcohol consists of the hydrocarbon chain which is non-polar in nature and the hydroxyl group which is polar in nature due to the presence of the electronegative oxygen atom which forms the hydrogen-bond with the water molecule.

But as the length of the hydrocarbon chain increases, more than four carbon atoms, that is, with the increase in the molecular weight of the alcohol, there is a significant decrease in the solubility of the alcohols in water. Also, beyond, seven carbon atoms chain, the alcohols become immiscible and the mixture forms. This is because of the increase inductive effect by the methylene $(-C{{H}_{2}}-)$ and methyl $(-C{{H}_{3}})$ group present, which causes a positive inductive effect $(+I)$, increasing the electron density over the electronegative oxygen atom. Thus, making the formation of hydrogen bonds difficult. Thereby, decreasing the solubility of the higher or heavier alcohols in water.
Therefore, the solubility of alcohols in water gradually increases with molecular weight is option (B)- False.
Note: The nonpolar hydrocarbon chains in alcohol are hydrophobic or water-repelling in nature whereas, the hydroxyl group is hydrophilic in nature as it bonds with the water molecule. So, the dominance of either the hydrophobic part of the hydrophilic part determines the solubility of the alcohol as their molecular weight increases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




