
The type of isomerism observed in benzaldoxime is:
(A) Optical
(B) Functional
(C) Geometrical
(D) Tautomerism
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Draw the structure of the organic compound benzaldoxime. Try to understand the types of isomerism given in the options with an example to understand how the isomerism works. Benzaldoxime does have a double bond outside the benzene ring however a chiral carbon centre is absent as well.
Complete step by step answer:
As suggested in the hint we will draw the structure of the organic compound benzaldoxime:
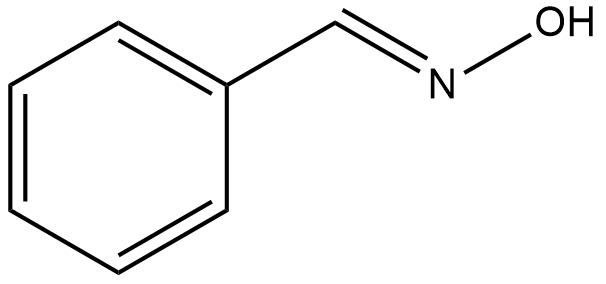
From the above structure we can make the following observations:
No chiral centre present, No change is functional group,
Presence of double bond, but cis-trans isomers not possible.
Due to the above observations, it is clear that benzaldoxime does not show optical, geometrical, functional isomerism.
The reaction involving simple proton transfer in an intramolecular fashion is called tautomerism.
Tautomers are a pair of compounds which differ only in the position of the protons and electrons. The carbon skeleton of the compound remains the same.
The tautomer of benzaldoxime is given below:

Hence the type of isomerism shown by benzaldoxime is tautomerism.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: It is important to know that tautomerism occurs only when two isomers exist in mobile equilibrium with each other. Isomers are molecules having the same molecular formula and composition. Tautomers are constitutional isomers of two compounds that readily interconvert between one another.
Complete step by step answer:
As suggested in the hint we will draw the structure of the organic compound benzaldoxime:

From the above structure we can make the following observations:
No chiral centre present, No change is functional group,
Presence of double bond, but cis-trans isomers not possible.
Due to the above observations, it is clear that benzaldoxime does not show optical, geometrical, functional isomerism.
The reaction involving simple proton transfer in an intramolecular fashion is called tautomerism.
Tautomers are a pair of compounds which differ only in the position of the protons and electrons. The carbon skeleton of the compound remains the same.
The tautomer of benzaldoxime is given below:

Hence the type of isomerism shown by benzaldoxime is tautomerism.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: It is important to know that tautomerism occurs only when two isomers exist in mobile equilibrium with each other. Isomers are molecules having the same molecular formula and composition. Tautomers are constitutional isomers of two compounds that readily interconvert between one another.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




