
Why do two types of chromatin exist?
Answer
478.8k+ views
Hint: Chromatin is a DNA-protein complex found in eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to compress and densify long DNA molecules into smaller, more compact structures. This keeps the strands from tangling, and it also helps to reinforce the DNA during cell division, prevent DNA damage, and regulate gene expression and DNA replication.
Complete answer:
Chromatin aids proper chromosome segregation in anaphase during mitosis and meiosis; the distinctive shapes of chromosomes visible during this stage are the result of DNA being coiled into highly condensed chromatin.
During the cell cycle, chromatin undergoes various structural changes. Histone proteins are the basic chromatin packers and arrangers, and they can be altered through various post-translational modifications to change chromatin packing (histone modification). The majority of histone modifications take place on histone tails. The impact on chromatin accessibility and compaction is determined by the modified amino acid as well as the type of modification.
There are two types of chromatin:
1. Euchromatin
2. Heterochromatin
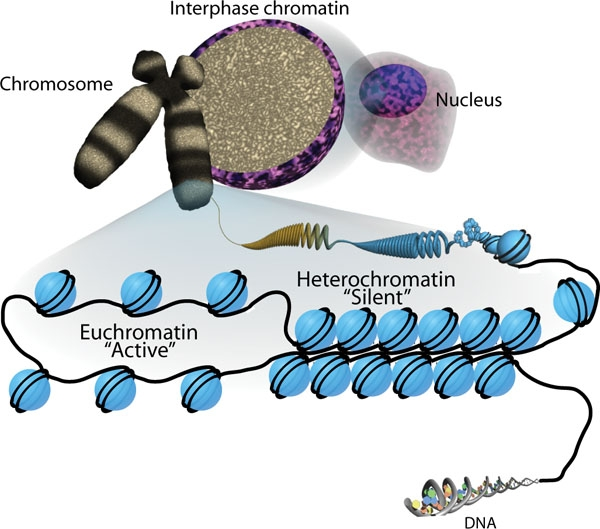
These are distinguished primarily by histological staining and appearance during the interphase.
The majority of chromatin takes up light stains during interphase, but a small amount of chromatin in the eukaryotic nucleus appears very dark under the microscope. Euchromatin is found in the light areas, while heterochromatin is found in the dark patches.
Euchromatin is thought to be more hydrated and loosely arranged than heterochromatin. This also means that the DNA in these areas is actively transcribed.
Heterochromatin is obviously tightly packed, and the DNA in this area replicates slowly in nature. (Because constitutive heterochromatin is made up of repetitive sequences, the areas may be devoid of genes, whereas facultative heterochromatin is not).
Note:
Transcription is the process of genetic information being transferred from DNA to proteins. After that, the information is transcribed into RNA. The translation of RNA into functional proteins is the final step. Chromatin regulates the transcription process. The transcription will halt if chromatin is strengthened and access to read the proteins is restricted.
Complete answer:
Chromatin aids proper chromosome segregation in anaphase during mitosis and meiosis; the distinctive shapes of chromosomes visible during this stage are the result of DNA being coiled into highly condensed chromatin.
During the cell cycle, chromatin undergoes various structural changes. Histone proteins are the basic chromatin packers and arrangers, and they can be altered through various post-translational modifications to change chromatin packing (histone modification). The majority of histone modifications take place on histone tails. The impact on chromatin accessibility and compaction is determined by the modified amino acid as well as the type of modification.
There are two types of chromatin:
1. Euchromatin
2. Heterochromatin

These are distinguished primarily by histological staining and appearance during the interphase.
The majority of chromatin takes up light stains during interphase, but a small amount of chromatin in the eukaryotic nucleus appears very dark under the microscope. Euchromatin is found in the light areas, while heterochromatin is found in the dark patches.
Euchromatin is thought to be more hydrated and loosely arranged than heterochromatin. This also means that the DNA in these areas is actively transcribed.
Heterochromatin is obviously tightly packed, and the DNA in this area replicates slowly in nature. (Because constitutive heterochromatin is made up of repetitive sequences, the areas may be devoid of genes, whereas facultative heterochromatin is not).
Note:
Transcription is the process of genetic information being transferred from DNA to proteins. After that, the information is transcribed into RNA. The translation of RNA into functional proteins is the final step. Chromatin regulates the transcription process. The transcription will halt if chromatin is strengthened and access to read the proteins is restricted.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




