
What type of isomers are glucose and fructose?
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: Glucose and fructose two examples of monosaccharide isomers. Isomers would have the same chemical formula but different molecular structure. From the structures it's clear that fructose is a ketone whereas glucose is an aldehyde. Both of them differ in the functional group.
Complete step by step solution:
- As we know, isomers are those two molecules which have the same molecular formula but structurally different. Thus, they contain the same number of atoms for each element, but will have different atomic arrangement. These differences will result in the change of physical and chemical properties of molecules.
- There are mainly two types of isomerism which is named as structural isomerism and stereoisomerism. Structural isomers differ with respect to the specific attachment of functional groups and atoms. There are different types of structural isomers such as chain isomers, functional isomers, position isomers, skeletal isomers etc.
- Similarly, stereoisomerism corresponds to isomerism in terms of the geometric position of the atoms and functional groups. It generally consists of conformational isomers, diastereomers and enantiomers.
- As we are aware, fructose and glucose are monosaccharides with the general molecular formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}$.The carbohydrates play an important role in the sustainment of life through its various functions such as the source of energy in animals, structural material to plants metabolic materials in plants and as components of biomolecules.
- Both glucose and fructose cycle structures and open chain are assigned to them. A part of the properties of these molecules can be explained by cyclic structures and some properties by the open chain structure.
- These both cyclic and open chain structures are shown below,
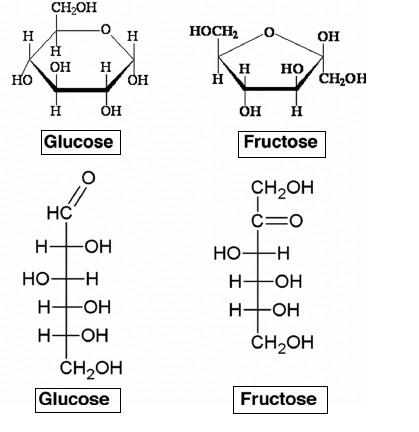
- From the above diagram, it's clear that glucose is an aldohexose (containing aldehyde group) and fructose is a ketohexose (containing ketone). Thus, glucose and fructose have the same molecular formula with different functional groups and hence its an example of functional isomerism.
Therefore, we can say that glucose and fructose are functional isomers.
Note: It should be noted that another monosaccharide galactose also has the same chemical formula of glucose and fructose ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}$. The molecule galactose and glucose are stereoisomers. Even though their atoms are bonded together in the same order, they have a different three-dimensional organization of atoms around one of their asymmetric carbon atoms Thus we can say that fructose is a structural isomer of galactose and glucose and galactose is a stereoisomer of glucose.
Complete step by step solution:
- As we know, isomers are those two molecules which have the same molecular formula but structurally different. Thus, they contain the same number of atoms for each element, but will have different atomic arrangement. These differences will result in the change of physical and chemical properties of molecules.
- There are mainly two types of isomerism which is named as structural isomerism and stereoisomerism. Structural isomers differ with respect to the specific attachment of functional groups and atoms. There are different types of structural isomers such as chain isomers, functional isomers, position isomers, skeletal isomers etc.
- Similarly, stereoisomerism corresponds to isomerism in terms of the geometric position of the atoms and functional groups. It generally consists of conformational isomers, diastereomers and enantiomers.
- As we are aware, fructose and glucose are monosaccharides with the general molecular formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}$.The carbohydrates play an important role in the sustainment of life through its various functions such as the source of energy in animals, structural material to plants metabolic materials in plants and as components of biomolecules.
- Both glucose and fructose cycle structures and open chain are assigned to them. A part of the properties of these molecules can be explained by cyclic structures and some properties by the open chain structure.
- These both cyclic and open chain structures are shown below,

- From the above diagram, it's clear that glucose is an aldohexose (containing aldehyde group) and fructose is a ketohexose (containing ketone). Thus, glucose and fructose have the same molecular formula with different functional groups and hence its an example of functional isomerism.
Therefore, we can say that glucose and fructose are functional isomers.
Note: It should be noted that another monosaccharide galactose also has the same chemical formula of glucose and fructose ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}$. The molecule galactose and glucose are stereoisomers. Even though their atoms are bonded together in the same order, they have a different three-dimensional organization of atoms around one of their asymmetric carbon atoms Thus we can say that fructose is a structural isomer of galactose and glucose and galactose is a stereoisomer of glucose.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




