
What is isoelectric point?
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: We will try to recall the pH point where molecules do not show any charge or can be called neutral.In order to look for the neutrality, we will check the charges on the respective molecules and in different pH media.
Complete step by step solution:
- The isoelectric point is defined as the pH at which the molecules are considered to be electrically neutral or will carry no units of positive or negative charge.
- But it is important to understand that net charge of any molecules is solely affected by the gain or loss of protons.
- However,the net charge is governed by the pH of the surrounding medium.
-Let us try to cite the example of amino acids and try to understand the concept of isoelectric point(IP)
An amino acid contains an amine group and a carboxyl group. At physiological pH ,amino acids show isoelectricity with a net charge of zero.
In aqueous solution, the carboxyl group can lose a proton,and the amino group can gain a proton, forming a dipolar ion, known as zwitterion.
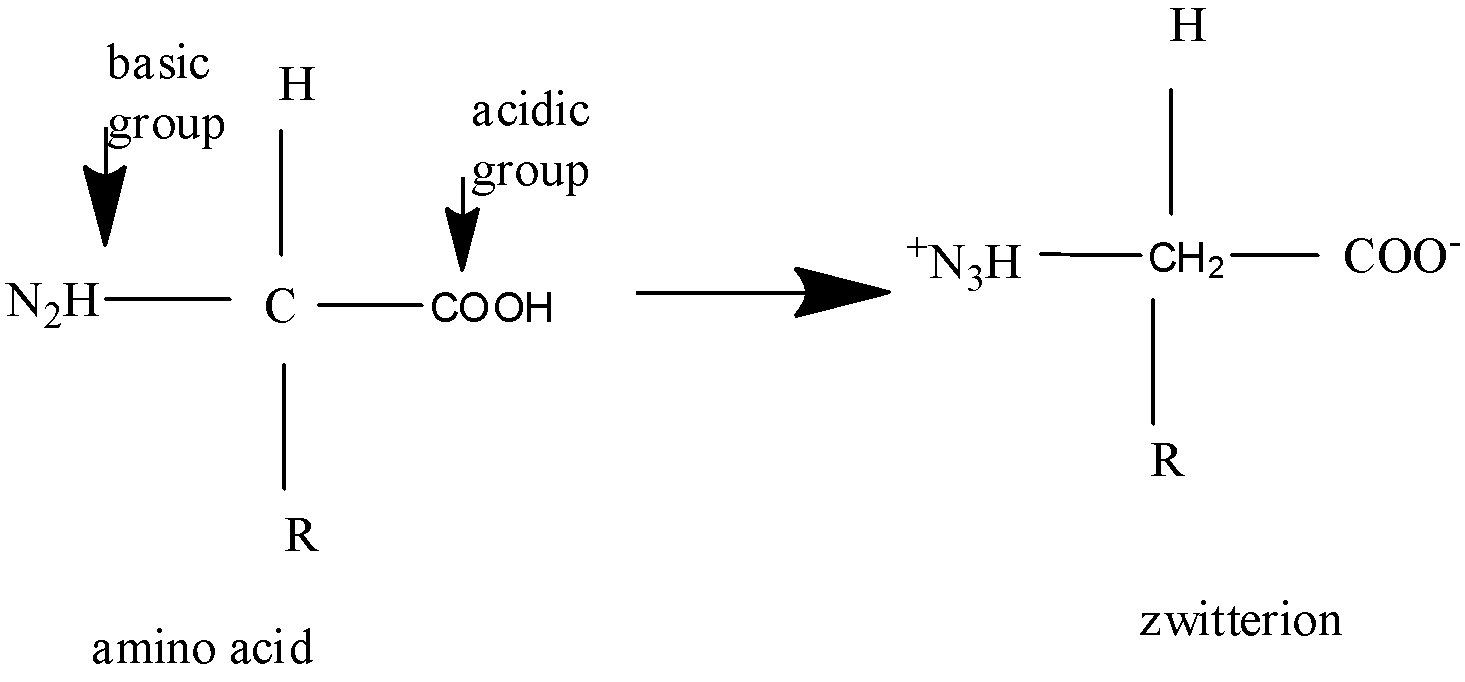
Now contains both positive and negative charges, thus balancing each other and showing neutrality, thus showing isoelectric point.
Glycine, the simplest amino acid, has an IP of 6.0 , where it exists as a positively charged species.
- In order to calculate the PI of simple amino acids, it is given by the average of pKa ‘s of carboxyl group and the ammonium group. The formula is given by:
PI= ${\text{pka1+pka2}}/{\text{2}}\;$
-So from the given formula we can calculate IP of acids.
Note: Always remember to check for the overall neutrality of an ion, in order to calculate the Isoelectric point.The formation of zwitterion is a classic example of Isoelectric point and we should try to check the pH of it in different mediums.
Complete step by step solution:
- The isoelectric point is defined as the pH at which the molecules are considered to be electrically neutral or will carry no units of positive or negative charge.
- But it is important to understand that net charge of any molecules is solely affected by the gain or loss of protons.
- However,the net charge is governed by the pH of the surrounding medium.
-Let us try to cite the example of amino acids and try to understand the concept of isoelectric point(IP)
An amino acid contains an amine group and a carboxyl group. At physiological pH ,amino acids show isoelectricity with a net charge of zero.
In aqueous solution, the carboxyl group can lose a proton,and the amino group can gain a proton, forming a dipolar ion, known as zwitterion.

Now contains both positive and negative charges, thus balancing each other and showing neutrality, thus showing isoelectric point.
Glycine, the simplest amino acid, has an IP of 6.0 , where it exists as a positively charged species.
- In order to calculate the PI of simple amino acids, it is given by the average of pKa ‘s of carboxyl group and the ammonium group. The formula is given by:
PI= ${\text{pka1+pka2}}/{\text{2}}\;$
-So from the given formula we can calculate IP of acids.
Note: Always remember to check for the overall neutrality of an ion, in order to calculate the Isoelectric point.The formation of zwitterion is a classic example of Isoelectric point and we should try to check the pH of it in different mediums.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




