
What is the function of a polysome?
Answer
570.6k+ views
Hint: Polysome is a thread-like structure that is a group of ribosomes that are bound to a messenger RNA molecule. It constitutes a complex of an mRNA and ribosomes which help to translate mRNA into polypeptides.
Complete step by step answer:
Ribosomes can translate mRNA and form polysomes. If more than one ribosome translates an mRNA it forms many polypeptides from a single mRNA. When the ribosomes and elongation factor synthesize the encoded polypeptide, polysomes are formed. It is created by the coding region of mRNA which is moved by multiple ribosomes. This ability of multiple ribosomes in the functioning of an mRNA explains the abundance of mRNA in the cells. The structure of polyribosomes is different in prokaryotic polysomes, eukaryotic polysomes, and membrane-bound polysomes. The level of gene expression through a technique is measured by polysome activity and is known as polysomal profiling. Polysomal profiling is used to arrest translation and sucrose gradient for the separation of resulting cells to be extracted by centrifugation. The increase in the number of ribosomes is associated with the corresponding mRNA. It is applied to cultured cells and tissues which track the translational status of identified mRNA and measure ribosome density.
Additional information:
In prokaryotic cells, the bacterial polysomes are in the form of double row structures and the ribosome is contacting each other within smaller subunits. In eukaryotic cells, the densely packed 3D helices and double row polysomes which are planar are found, which are similar to that of prokaryotic polysomes. They are bound to the membrane by a two-dimensional space and the restriction of inter ribosomal contacts that arrange ribosomes along with the mRNA form a smooth pathway. The polysomal profiling is used to investigate the effect of vesicular stomatitis virus. It shows that the host mRNAs are outcompeted by the viral mRNA which decreases the translation of host mRNA with increasing in the translation of viral mRNA.
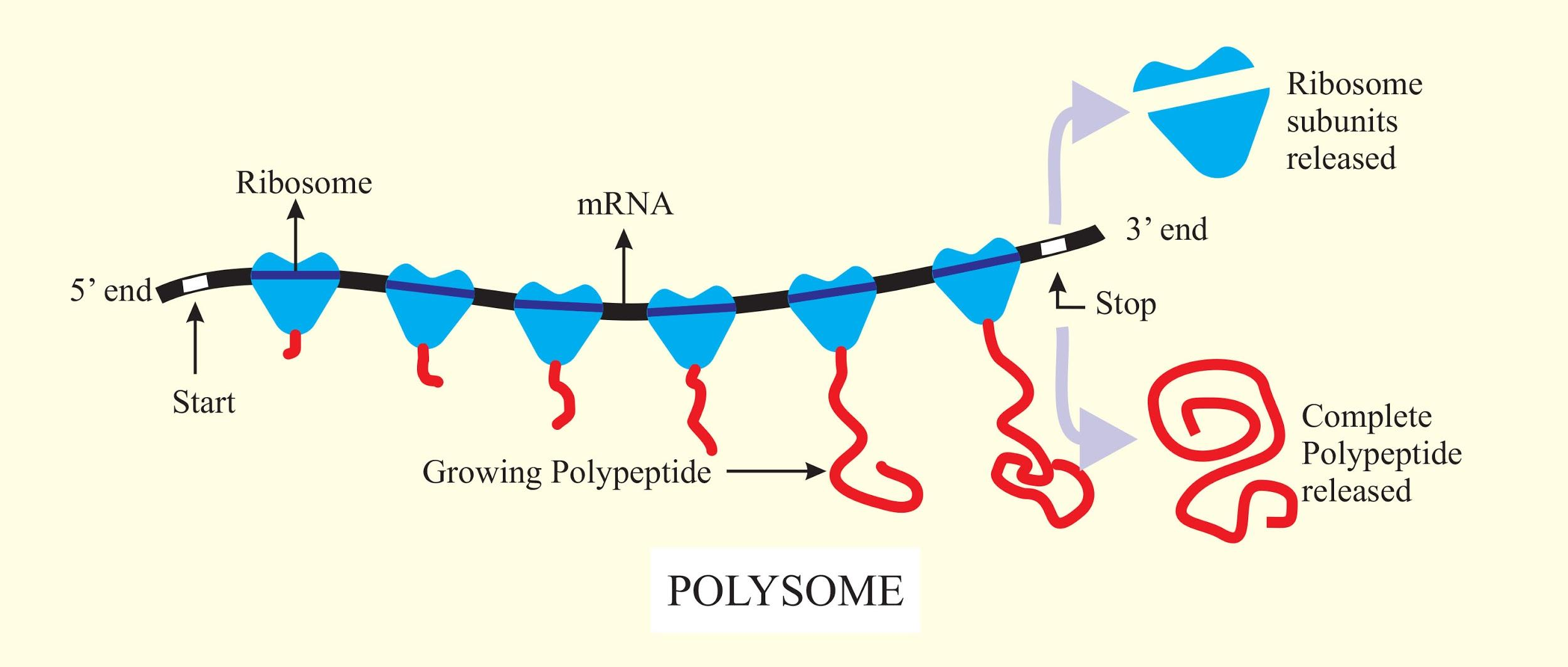
Note: Ribosomes are present in eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells and can be found in human beings. They are free-floating in the cytoplasm and are found attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. They are transported inside the nucleolus as the raw materials are produced outside the nucleus.
Complete step by step answer:
Ribosomes can translate mRNA and form polysomes. If more than one ribosome translates an mRNA it forms many polypeptides from a single mRNA. When the ribosomes and elongation factor synthesize the encoded polypeptide, polysomes are formed. It is created by the coding region of mRNA which is moved by multiple ribosomes. This ability of multiple ribosomes in the functioning of an mRNA explains the abundance of mRNA in the cells. The structure of polyribosomes is different in prokaryotic polysomes, eukaryotic polysomes, and membrane-bound polysomes. The level of gene expression through a technique is measured by polysome activity and is known as polysomal profiling. Polysomal profiling is used to arrest translation and sucrose gradient for the separation of resulting cells to be extracted by centrifugation. The increase in the number of ribosomes is associated with the corresponding mRNA. It is applied to cultured cells and tissues which track the translational status of identified mRNA and measure ribosome density.
Additional information:
In prokaryotic cells, the bacterial polysomes are in the form of double row structures and the ribosome is contacting each other within smaller subunits. In eukaryotic cells, the densely packed 3D helices and double row polysomes which are planar are found, which are similar to that of prokaryotic polysomes. They are bound to the membrane by a two-dimensional space and the restriction of inter ribosomal contacts that arrange ribosomes along with the mRNA form a smooth pathway. The polysomal profiling is used to investigate the effect of vesicular stomatitis virus. It shows that the host mRNAs are outcompeted by the viral mRNA which decreases the translation of host mRNA with increasing in the translation of viral mRNA.

Note: Ribosomes are present in eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells and can be found in human beings. They are free-floating in the cytoplasm and are found attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. They are transported inside the nucleolus as the raw materials are produced outside the nucleus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




