
Which is S-lactic acid among the two isomers?
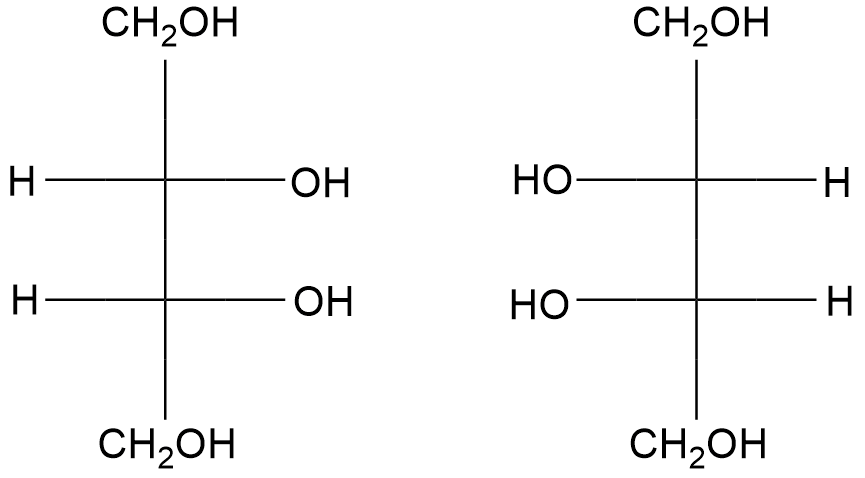
(A)- a
(B)- b
(C)- Both a and b
(D)- None of the above

Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint:. This question is based on the configuration of two isomers. An absolute configuration refers to the spatial arrangement of the atoms of a chiral molecular entity and its stereochemical description i.e. R and S.
Complete step by step answer:
Lactic acid is a chiral compound, consisting of two optical isomers. One is known as L-lactic acid or (S)−lactic acid and the other, its mirror image, is D−lactic acid or(R)-lactic acid.
There are so many terms which you might not know. Let's talk about them first.
- R and S configuration: R- and S-notation used for the assignment of the absolute configuration around a stereocenter.
To find it first we should assign priorities to each bonded group surrounding the stereocenter (1 for highest to 4 for lowest).
Second, imagine the lowest priority (4) atom away from you. Follow the direction of the remaining 3 priorities from highest to lowest priority.
A counterclockwise direction is called S (sinister, Latin for left) configuration. A clockwise direction is called R (rectus, Latin for right) configuration.
- D and L configuration: An optical isomer can be named by the configuration of its atoms. The d by l system (named after Latin dexter and laevus which is known as right and left), not to be confused with the d- and l-system. The d by l labeling is unrelated to (+) by (−) i.e. it does not indicate which enantiomer is dextrorotatory and which is levorotatory. Rather, it indicates the compound's stereochemistry relative to that of the d by l (dextrorotatory or levorotatory).
D- and L- notation provides a quick shorthand for designating the enantiomers. For example, D-Glucose is the enantiomer of L-Glucose as L-Alanine is the enantiomer of D-Alanine.
In the Fischer projection form, if the OH on the bottom chiral center points to the right, it is referred as D whereas if the OH on the bottom chiral center points to the left, it is referred as L.
Based on other discussion, So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: D and L configuration works well for sugars since they can be built up so systematically (like the binary system). The key point is you just have to look at the bottom stereocenter while it’s drawn in the Fischer projection and you can easily judge D for right and L for left.
Complete step by step answer:
Lactic acid is a chiral compound, consisting of two optical isomers. One is known as L-lactic acid or (S)−lactic acid and the other, its mirror image, is D−lactic acid or(R)-lactic acid.
There are so many terms which you might not know. Let's talk about them first.
- R and S configuration: R- and S-notation used for the assignment of the absolute configuration around a stereocenter.
To find it first we should assign priorities to each bonded group surrounding the stereocenter (1 for highest to 4 for lowest).
Second, imagine the lowest priority (4) atom away from you. Follow the direction of the remaining 3 priorities from highest to lowest priority.
A counterclockwise direction is called S (sinister, Latin for left) configuration. A clockwise direction is called R (rectus, Latin for right) configuration.
- D and L configuration: An optical isomer can be named by the configuration of its atoms. The d by l system (named after Latin dexter and laevus which is known as right and left), not to be confused with the d- and l-system. The d by l labeling is unrelated to (+) by (−) i.e. it does not indicate which enantiomer is dextrorotatory and which is levorotatory. Rather, it indicates the compound's stereochemistry relative to that of the d by l (dextrorotatory or levorotatory).
D- and L- notation provides a quick shorthand for designating the enantiomers. For example, D-Glucose is the enantiomer of L-Glucose as L-Alanine is the enantiomer of D-Alanine.
In the Fischer projection form, if the OH on the bottom chiral center points to the right, it is referred as D whereas if the OH on the bottom chiral center points to the left, it is referred as L.
Based on other discussion, So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: D and L configuration works well for sugars since they can be built up so systematically (like the binary system). The key point is you just have to look at the bottom stereocenter while it’s drawn in the Fischer projection and you can easily judge D for right and L for left.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




