
Which isomerism is present in n-butyl, alcohol and isobutyl alcohol?
(A) Position
(B) Chain
(C) Optical
(D) Geometrical
Answer
515.1k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, we first need to understand what isomerism is. The phenomenon of isomerism occurs when two or more compounds have the same chemical formula but distinct chemical structures. Isomers are chemical compounds with identical chemical formulas but differ in characteristics and atom arrangement in the molecule.
Complete answer:
Positional isomers - Positional isomers are constitutional isomers that have the identical carbon skeleton and functional groups but differ in where the functional groups are located on or in the carbon chain. They both have a bromine atom as a functional group.
Chain isomers - A change in the atomic arrangement of the carbon to the carbon chain of a molecule is known as chain isomerism. Chain isomerism is a feature that occurs when two or more compounds have the same sort of chemical formula but different primary chains.
Optical isomers - Optical isomers are two compounds with the same number and kinds of atoms, bonds (i.e., atom connectivity), and distinct spatial arrangements of the atoms, but non-superimposable mirror images. An enantiomer is a non-superimposable mirror image structure.
Geometrical isomers - Chemical species with the same type and number of atoms as another species but a distinct geometric structure is known as geometric isomers. On either side of a chemical bond or ring structure, atoms or groups have different spatial configurations.
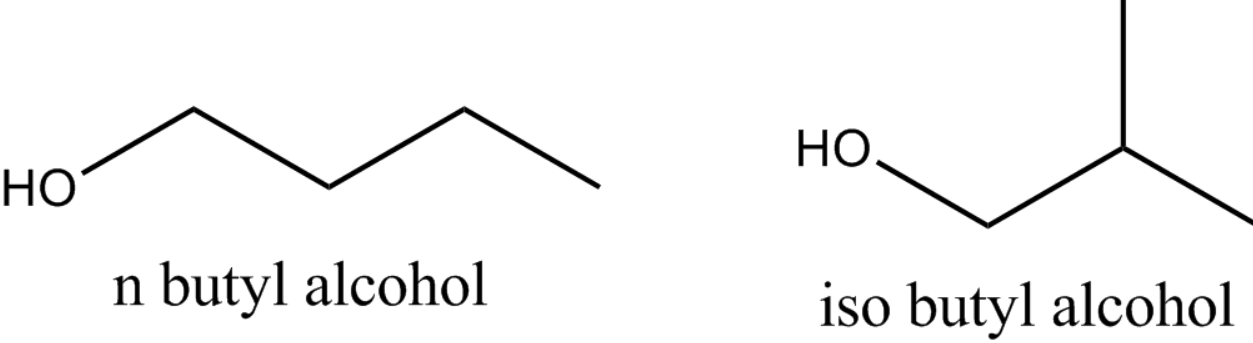
N-butyl alcohol and isobutyl alcohol both have chain isomerism.
Components of the (typically carbon) skeleton are differentially re-ordered to generate different structures in chain isomerism, also known as skeletal isomerism.
So, the final answer is option (B) Chain.
Note:
The phenomenon of isomerism occurs when two or more compounds have the same chemical formula but distinct chemical structures. Isomers are chemical compounds with identical chemical formulas but differ in characteristics and atom arrangement in the molecule.
Complete answer:
Positional isomers - Positional isomers are constitutional isomers that have the identical carbon skeleton and functional groups but differ in where the functional groups are located on or in the carbon chain. They both have a bromine atom as a functional group.
Chain isomers - A change in the atomic arrangement of the carbon to the carbon chain of a molecule is known as chain isomerism. Chain isomerism is a feature that occurs when two or more compounds have the same sort of chemical formula but different primary chains.
Optical isomers - Optical isomers are two compounds with the same number and kinds of atoms, bonds (i.e., atom connectivity), and distinct spatial arrangements of the atoms, but non-superimposable mirror images. An enantiomer is a non-superimposable mirror image structure.
Geometrical isomers - Chemical species with the same type and number of atoms as another species but a distinct geometric structure is known as geometric isomers. On either side of a chemical bond or ring structure, atoms or groups have different spatial configurations.

N-butyl alcohol and isobutyl alcohol both have chain isomerism.
Components of the (typically carbon) skeleton are differentially re-ordered to generate different structures in chain isomerism, also known as skeletal isomerism.
So, the final answer is option (B) Chain.
Note:
The phenomenon of isomerism occurs when two or more compounds have the same chemical formula but distinct chemical structures. Isomers are chemical compounds with identical chemical formulas but differ in characteristics and atom arrangement in the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




