
Which of the following is Lewis acid?
A. $B{F_3}$
B. $C{l^ - }$
C. ${H_2}O$
D. $N{H_3}$
Answer
579.6k+ views
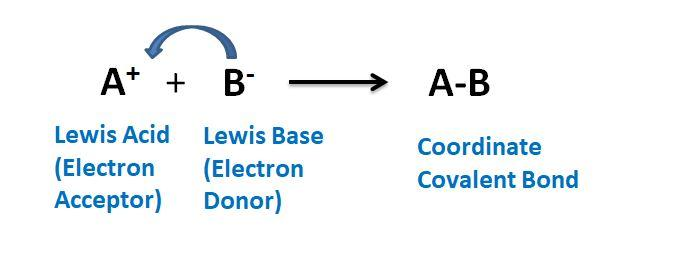
Hint: A Lewis acid is the one which can accept a pair of electrons from the non- bonding electrons. Thus it is an electron acceptor. Whereas the Lewis base is the one which can donate a pair of electrons to the non- bonding electrons and is regarded as the electron donors.
Complete step by step answer:
A molecule with an incomplete octet of electrons can accept electrons and all the cations are Lewis acids since they accept the electrons as they are electron deficient whereas all anions are Lewis bases since they donate the electrons as they are electron rich.
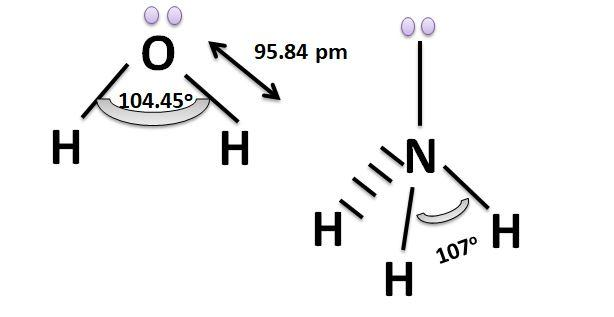
$Cl^-$ is an anion and it can donate the pair of electrons thus it is a Lewis base in nature. Similarly H2O also has a lone pair of electrons which it can donate during the bond formation and $NH_3$ molecule also has the lone pair of electrons so these all are Lewis bases in nature. The structures of Water and Ammonia molecule are shown below:
Thus the option A that is $BF_3$ is the Lewis Acid as it can accept the electrons since it is electron deficient in nature.
Based on this concept Lewis gave his theory known as the Lewis Theory and thus the number of the acids increased based on his concept which in turn increases the number of acid base reactions. Thus it also satisfies the oxidation and reduction reactions where electrons are transferred during the bond formation. The classic example of the Lewis acid- base reaction is:
$A{l^{3 + }}(aq) + 6{H_2}O(l) \rightleftharpoons Al{({H_2}O)_6}^{3 + }(aq)$
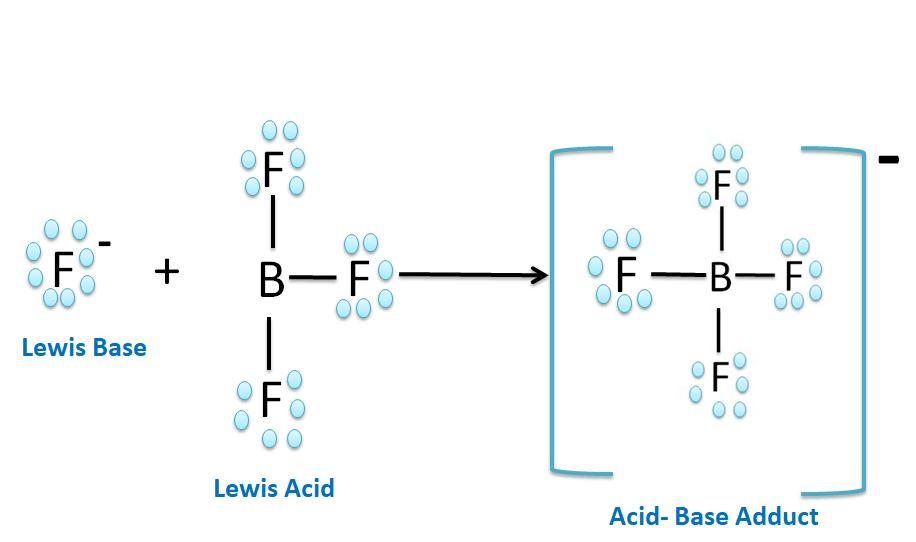
$BF_3$ is a trigonal-planar molecule because electrons can be found in only three places in the valence shell of the boron atom. As a result, the boron atom is $sp^2$ hybridized, which leaves an empty $2p_z$ orbital on the boron atom. $BF_3$ can therefore act as an electron-pair acceptor, or Lewis acid. It can use the empty $2p_z$ orbital to pick up a pair of nonbonding electrons from a Lewis base to form a covalent bond. $BF_3$ therefore reacts with Lewis bases such as $NH_3$ to form acid-base complexes in which all of the atoms have a filled shell of valence electrons, as shown in the figure below
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Note:
The shape of the molecule $BF_3$ molecule is trigonal –planar and is depicted by the VSEPR theory and is abbreviated as VSPER theory and based on the assumption that that there is repulsion between the pairs of valence electrons in all atoms, and the atoms will always tend to arrange themselves in a manner in which this electron pair repulsion is minimized. This theory helps to predict the geometry of the molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
A molecule with an incomplete octet of electrons can accept electrons and all the cations are Lewis acids since they accept the electrons as they are electron deficient whereas all anions are Lewis bases since they donate the electrons as they are electron rich.

$Cl^-$ is an anion and it can donate the pair of electrons thus it is a Lewis base in nature. Similarly H2O also has a lone pair of electrons which it can donate during the bond formation and $NH_3$ molecule also has the lone pair of electrons so these all are Lewis bases in nature. The structures of Water and Ammonia molecule are shown below:

Thus the option A that is $BF_3$ is the Lewis Acid as it can accept the electrons since it is electron deficient in nature.

Based on this concept Lewis gave his theory known as the Lewis Theory and thus the number of the acids increased based on his concept which in turn increases the number of acid base reactions. Thus it also satisfies the oxidation and reduction reactions where electrons are transferred during the bond formation. The classic example of the Lewis acid- base reaction is:
$A{l^{3 + }}(aq) + 6{H_2}O(l) \rightleftharpoons Al{({H_2}O)_6}^{3 + }(aq)$
$BF_3$ is a trigonal-planar molecule because electrons can be found in only three places in the valence shell of the boron atom. As a result, the boron atom is $sp^2$ hybridized, which leaves an empty $2p_z$ orbital on the boron atom. $BF_3$ can therefore act as an electron-pair acceptor, or Lewis acid. It can use the empty $2p_z$ orbital to pick up a pair of nonbonding electrons from a Lewis base to form a covalent bond. $BF_3$ therefore reacts with Lewis bases such as $NH_3$ to form acid-base complexes in which all of the atoms have a filled shell of valence electrons, as shown in the figure below
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Note:
The shape of the molecule $BF_3$ molecule is trigonal –planar and is depicted by the VSEPR theory and is abbreviated as VSPER theory and based on the assumption that that there is repulsion between the pairs of valence electrons in all atoms, and the atoms will always tend to arrange themselves in a manner in which this electron pair repulsion is minimized. This theory helps to predict the geometry of the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




