
Which one of these is a sedimentary cycle?
(a). Phosphorus
(b). Hydrogen
(c). Oxygen
(d). Nitrogen
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: It is the biogeochemical cycle that includes the element with atomic number 15 and describes the movement of that cycle through the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere. The cycle should be viewed from the whole Earth system and then specifically focused on the cycle in terrestrial and aquatic systems.
Complete answer
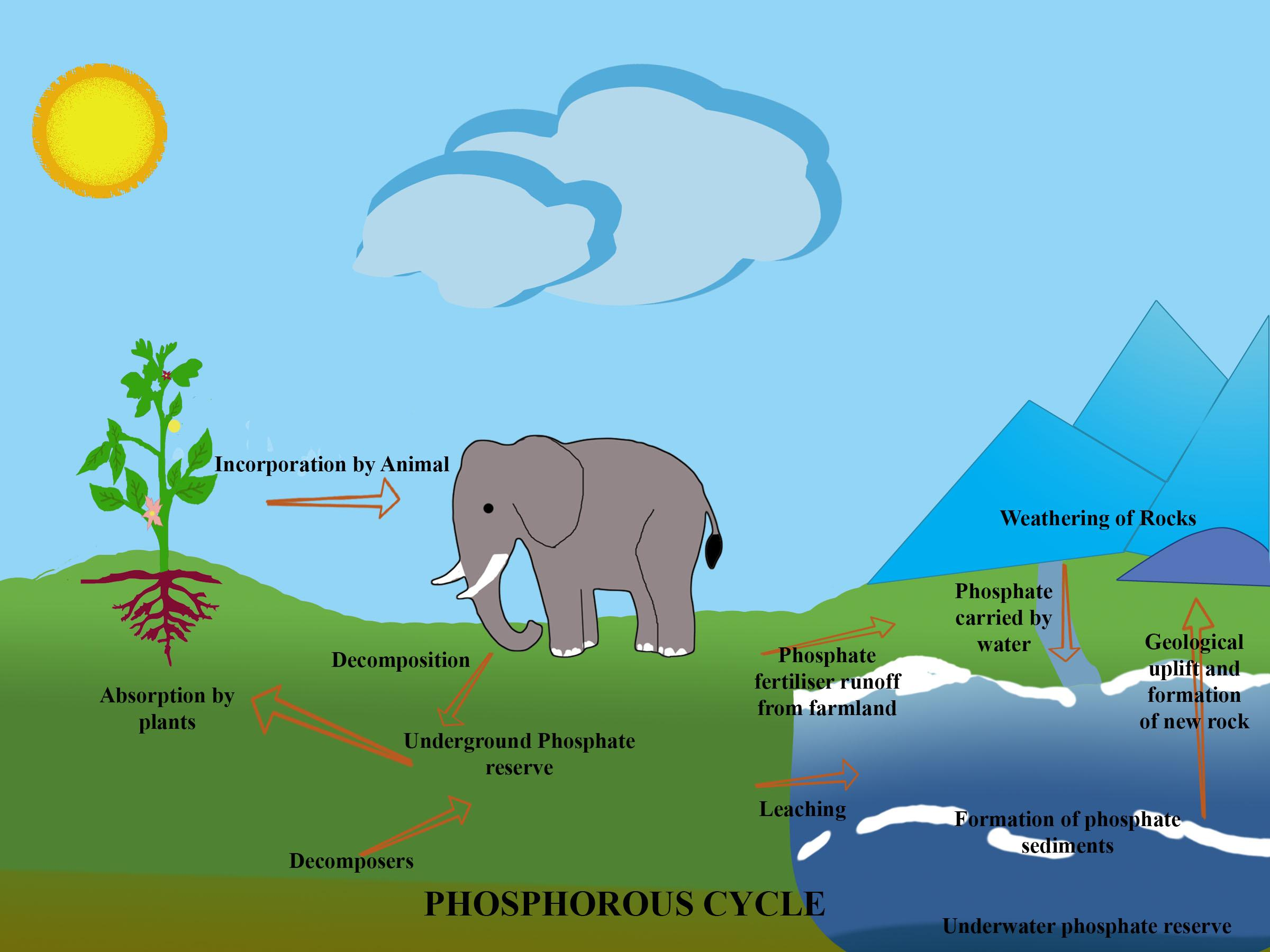
In sedimentary cycles, it incorporates the weathering of rocks and erosion of minerals alongside its flow in the climate and back to the earth’s crust. It also includes those of iron, calcium, phosphorus, and other more earthbound elements. The phosphorus cycle is also a type of sedimentary cycle. It is due to the sedimentary rocks, also because the cycling of phosphorus from the abiotic to the biotic and back will occur due to the other sort of rocks on weathering.
Additional information
Phosphorus is a significant supplement for plants and creatures. Phosphorus is a restricting supplement for aquatic creatures. Phosphorus structures portions of significant life-continuing atoms that are very regular inside the biosphere. Phosphorus enters the environment in limited quantities when the residue is broken up in water and seaspray yet remains absolutely land and in rock and soil minerals. The vast majority of the mined phosphorus is utilized to form composts. Phosphates from composts, sewage, and cleansers can cause contamination in lakes and streams. Over-enrichment of phosphate in both fresh and inshore marine waters can cause massive algae blooms which once they die and decay results in eutrophication of freshwaters only. An example of this is often the Canadian Experimental Lakes Area. These freshwater algal blooms shouldn't be confused with those in saltwater environments.
So the correct answer is ‘Phosphorus’.
Note: The overall phosphorus cycle incorporates four significant cycles: (a) structural elevate and introduction of phosphorus-bearing rocks like apatite to surface enduring; (b) actual disintegration, and substance and natural enduring of phosphorus-bearing rocks to supply dissolved and particulate phosphorus to soils, lakes, and rivers; (c) riverine and subsurface transportation of phosphorus to varied lakes and run-off to the ocean; (d) sedimentation of particulate phosphorus (e.g., phosphorus related to organic matter and oxide/carbonate minerals) and eventual burial in marine sediments (this process also can occur in lakes and rivers)
Complete answer
In sedimentary cycles, it incorporates the weathering of rocks and erosion of minerals alongside its flow in the climate and back to the earth’s crust. It also includes those of iron, calcium, phosphorus, and other more earthbound elements. The phosphorus cycle is also a type of sedimentary cycle. It is due to the sedimentary rocks, also because the cycling of phosphorus from the abiotic to the biotic and back will occur due to the other sort of rocks on weathering.
Additional information
Phosphorus is a significant supplement for plants and creatures. Phosphorus is a restricting supplement for aquatic creatures. Phosphorus structures portions of significant life-continuing atoms that are very regular inside the biosphere. Phosphorus enters the environment in limited quantities when the residue is broken up in water and seaspray yet remains absolutely land and in rock and soil minerals. The vast majority of the mined phosphorus is utilized to form composts. Phosphates from composts, sewage, and cleansers can cause contamination in lakes and streams. Over-enrichment of phosphate in both fresh and inshore marine waters can cause massive algae blooms which once they die and decay results in eutrophication of freshwaters only. An example of this is often the Canadian Experimental Lakes Area. These freshwater algal blooms shouldn't be confused with those in saltwater environments.

So the correct answer is ‘Phosphorus’.
Note: The overall phosphorus cycle incorporates four significant cycles: (a) structural elevate and introduction of phosphorus-bearing rocks like apatite to surface enduring; (b) actual disintegration, and substance and natural enduring of phosphorus-bearing rocks to supply dissolved and particulate phosphorus to soils, lakes, and rivers; (c) riverine and subsurface transportation of phosphorus to varied lakes and run-off to the ocean; (d) sedimentation of particulate phosphorus (e.g., phosphorus related to organic matter and oxide/carbonate minerals) and eventual burial in marine sediments (this process also can occur in lakes and rivers)
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




