
While studying the saponification reaction what do you observe when you mix an equal amount of colourless vegetable oil and 20 % aqueous solution of NaOH in a beaker?
A) The colour of the mixture has become dark brown.
B) A brisk effervescence is taking place in the beaker.
C) The outer surface of the beaker has become hot.
D) The outer surface of the beaker has become cold.
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: The conversion of lipid fat into the soap and alcohol by the action of a heat in the presence of aqueous alkali is called a saponification process. Saponification method is ideal for producing soaps that are derived from single fatty acid, which leads to soaps with predictable physical properties.
Complete answer:
When equal amounts of colourless vegetable oil and 20 % aqueous solution of NaOH is mixed in the beaker. The alkaline hydrolysis gives the formation of sodium salt of fatty acid. To boil this solution under reflux to speed up the reaction and move it to completion. Reflux stops volatile components from escaping. The ethanol content is removed by distillation. The residue left is excess NaOH, glycerol and soap dissolved in minimum hot water, once cooled then poured into the concentrated solution of NaCl on stirring and allowed to cool as well. Glycerol and NaOH dissolve in brine (solution of NaCl) but soap does not dissolve in brine and forms at the top of liquid. Water, brine and glycerol is removed by a filtration. Soap is rinsed with ice cold water to reduce its amount, lost by dissolving.
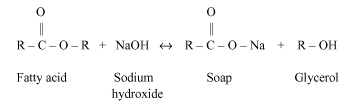
From the above information by adding 20 % of aqueous solution of NaOH in a beaker, the beaker becomes hot. This is because saponification is an exothermic reaction. By this process, the outer surface of the beaker has become hot.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: The reaction of fatty acids with base is the main method of saponification. In this case, the reaction involves neutralization of carboxylic acid. The neutralization method is used to produce industrial soap such as those derived from magnesium, transition metals and aluminum.
Complete answer:
When equal amounts of colourless vegetable oil and 20 % aqueous solution of NaOH is mixed in the beaker. The alkaline hydrolysis gives the formation of sodium salt of fatty acid. To boil this solution under reflux to speed up the reaction and move it to completion. Reflux stops volatile components from escaping. The ethanol content is removed by distillation. The residue left is excess NaOH, glycerol and soap dissolved in minimum hot water, once cooled then poured into the concentrated solution of NaCl on stirring and allowed to cool as well. Glycerol and NaOH dissolve in brine (solution of NaCl) but soap does not dissolve in brine and forms at the top of liquid. Water, brine and glycerol is removed by a filtration. Soap is rinsed with ice cold water to reduce its amount, lost by dissolving.

From the above information by adding 20 % of aqueous solution of NaOH in a beaker, the beaker becomes hot. This is because saponification is an exothermic reaction. By this process, the outer surface of the beaker has become hot.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: The reaction of fatty acids with base is the main method of saponification. In this case, the reaction involves neutralization of carboxylic acid. The neutralization method is used to produce industrial soap such as those derived from magnesium, transition metals and aluminum.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




