
Why is Primase Needed?
Answer
492.9k+ views
Hint: As we already know that genes are nothing but small sequences of DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid compact in long strands of DNA. Many strands of DNA form chromosomes and they are tightly packed with proteins inside a cell. Genes contain all the information which is being carried out from generation to generation. Primase is an enzyme which synthesizes RNA primer for DNA replication and the nucleotides get attached to new nucleotides for extending strands.
Complete answer:
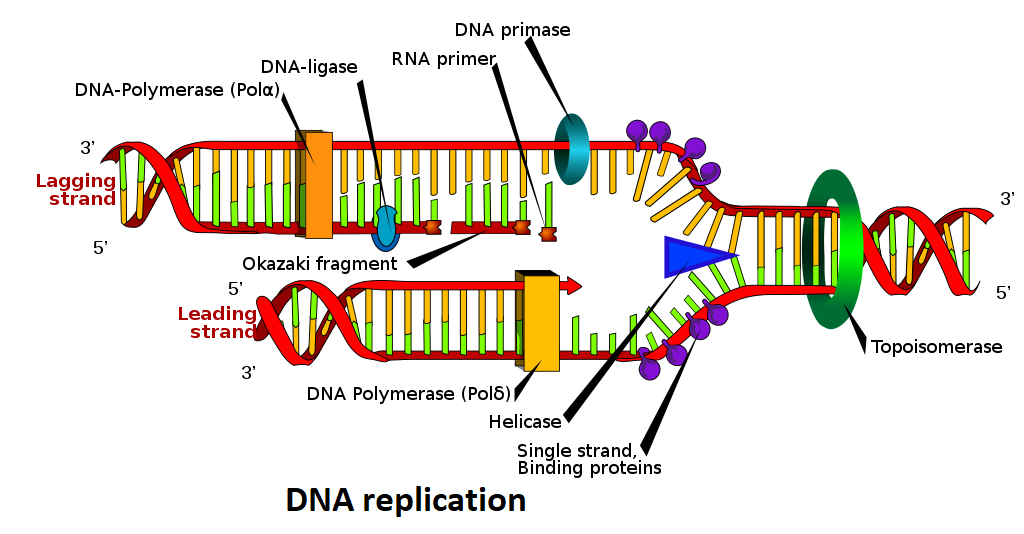
Primase is needed as it is required for the formation of RNA primers which are further required for DNA polymerisation. DNA replication is a term used for the process in which two separated strands of DNA emerge from a single parent DNA molecule. Replication models are of three types- Conservative, Semi-Conservative and dispersive. Conservative replication can be defined as a helix or strand entirely evolved from old DNA and the other helix is evolved from new DNA. Conservative mode is totally the combination of one old and one new DNA strand.
Primer is synthesized to fit into the initiating strand from DNA synthesis and repeatedly on the lagging strand to initiate Okazaki fragments. In the lagging strand the primase plays an important role. Primase synthesizes primers which code for the RNA as well as DNA polymerase.
DNA primases show continual activity at the replication fork. Primers are ribonucleoside rings from four to fifteen nucleotides long. If primase is not present the replication process won’t start. DNA polymerase cannot start the process as they can only add nucleotides.
Note:
Hence, DNA is a complex structure carrying different piles of genes in a compact globule structure. DNA is inherited from one generation to another generation by sexual reproduction. As organisms, especially mammals undergo sexual reproduction and offspring are born having sex chromosomes and genes from both their parents.
Complete answer:
Primase is needed as it is required for the formation of RNA primers which are further required for DNA polymerisation. DNA replication is a term used for the process in which two separated strands of DNA emerge from a single parent DNA molecule. Replication models are of three types- Conservative, Semi-Conservative and dispersive. Conservative replication can be defined as a helix or strand entirely evolved from old DNA and the other helix is evolved from new DNA. Conservative mode is totally the combination of one old and one new DNA strand.
Primer is synthesized to fit into the initiating strand from DNA synthesis and repeatedly on the lagging strand to initiate Okazaki fragments. In the lagging strand the primase plays an important role. Primase synthesizes primers which code for the RNA as well as DNA polymerase.
DNA primases show continual activity at the replication fork. Primers are ribonucleoside rings from four to fifteen nucleotides long. If primase is not present the replication process won’t start. DNA polymerase cannot start the process as they can only add nucleotides.

Note:
Hence, DNA is a complex structure carrying different piles of genes in a compact globule structure. DNA is inherited from one generation to another generation by sexual reproduction. As organisms, especially mammals undergo sexual reproduction and offspring are born having sex chromosomes and genes from both their parents.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




