
Write the complete structural formula, condensed structural formula and bond line formula of iso-octane.
Answer
513.9k+ views
Hint :Electrons reside outside of the nucleus of an atom and are found in major energy levels with only a limited amount of electrons. The valence level is the outermost main energy level that contains electrons, and it contains valence electrons. Lewis symbols are diagrams that illustrate the number of valence electrons in a certain element together with lone pairs represented by dots.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The chemical molecule 2,2,4-trimethylpentane, sometimes known as iso octane or iso-octane, has the formula $ {\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)_3}{\text{CC}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CH}}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)_2} $ . It's one of numerous octane isomers ( $ {C_8}{H_{18}} $ ). On the octane rating scale, this isomer is the typical 100 point (the zero point is n-heptane). It is a significant component of gasoline, and it is typically used in rather high amounts to improve the fuel's knock resistance.
A way of writing organic structures in a line of text is known as a condensed structural formula. All atoms are visible, but the vertical bonds and most or all horizontal single bonds are missing. It uses parentheses to indicate that polyatomic groups in a formula are connected to the non-hydrogen atom on the left. Covalent bonds are represented with one line for each degree of bond order in a bond-line structure, which is a depiction of molecular structure. A chemical compound's structural formula is a pictorial depiction of the molecular structure, indicating how the atoms could be placed in three-dimensional space.
Complete structural formula:
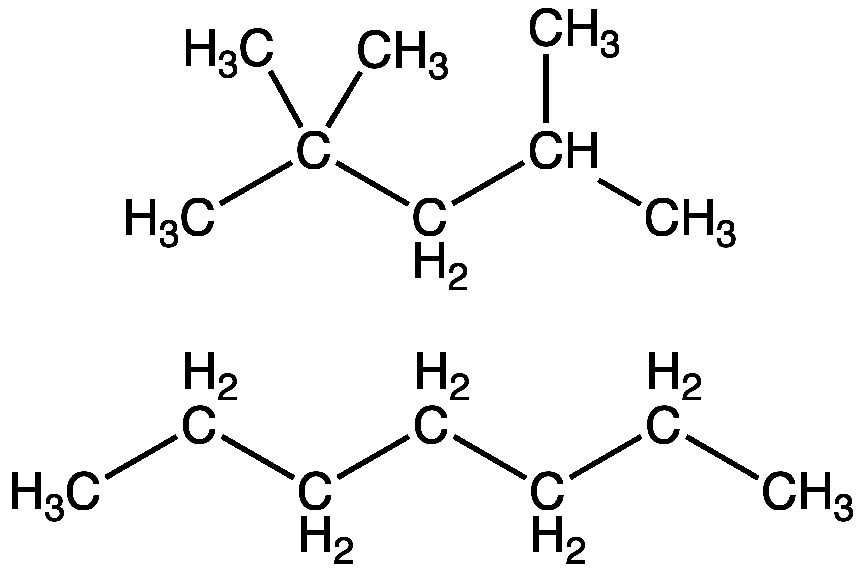
Bond line formula:
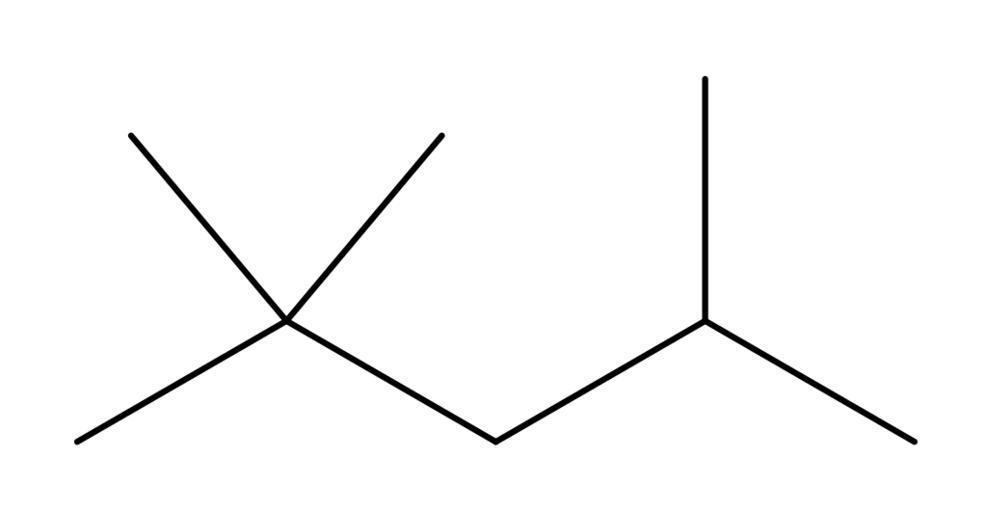
Condensed formula: $ {\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)_3}{\text{CC}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CH}}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)_2} $ .
Note :
Engine knocking is an undesired phenomenon that can occur in internal combustion engines with high compression ratios. In 1926, Graham Edgar experimented with varying quantities of n-heptane and 2,2,4-trimethylpentane in gasoline and discovered that when 2,2,4-trimethylpentane was introduced, the knocking ceased. The octane rating scale was born out of this research.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The chemical molecule 2,2,4-trimethylpentane, sometimes known as iso octane or iso-octane, has the formula $ {\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)_3}{\text{CC}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CH}}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)_2} $ . It's one of numerous octane isomers ( $ {C_8}{H_{18}} $ ). On the octane rating scale, this isomer is the typical 100 point (the zero point is n-heptane). It is a significant component of gasoline, and it is typically used in rather high amounts to improve the fuel's knock resistance.
A way of writing organic structures in a line of text is known as a condensed structural formula. All atoms are visible, but the vertical bonds and most or all horizontal single bonds are missing. It uses parentheses to indicate that polyatomic groups in a formula are connected to the non-hydrogen atom on the left. Covalent bonds are represented with one line for each degree of bond order in a bond-line structure, which is a depiction of molecular structure. A chemical compound's structural formula is a pictorial depiction of the molecular structure, indicating how the atoms could be placed in three-dimensional space.
Complete structural formula:

Bond line formula:

Condensed formula: $ {\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)_3}{\text{CC}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CH}}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)_2} $ .
Note :
Engine knocking is an undesired phenomenon that can occur in internal combustion engines with high compression ratios. In 1926, Graham Edgar experimented with varying quantities of n-heptane and 2,2,4-trimethylpentane in gasoline and discovered that when 2,2,4-trimethylpentane was introduced, the knocking ceased. The octane rating scale was born out of this research.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




