
Write the structures of nucleoside and nucleotide.
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: The phosphate esters of nucleosides are called nucleotides. Nucleotides are monomeric units of the nucleic acids i.e.; they bond to each other by phosphodiester bonds and form the long strands of nucleic acids such as ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid..
Complete step by step answer:
Structure of Nucleoside: Nucleosides can be defined as glycosylamines that consist of a pentose sugar joined to a nitrogenous base such as adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, or uracil by a glycosidic bond. They are similar to nucleotides in structure but lack the phosphate group.
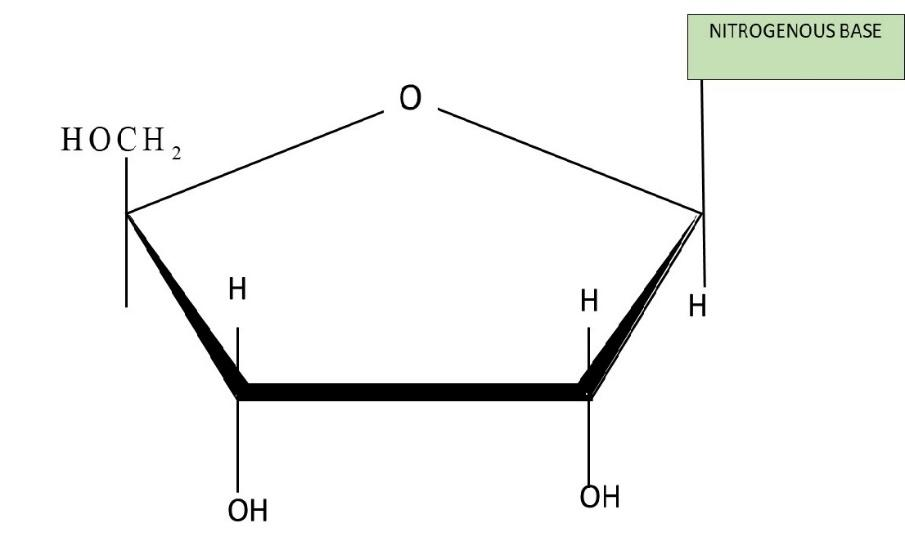
Nucleosides occur in two different conformations; syn and anti. These conformations are possible due to the ability of the nitrogenous base to rotate around the glycosidic bond. Pyrimidines are prone to attain anti conformation while purines can attain either of the two.
Structure of Nucleotide: Nucleosides from nucleotides when a phosphate group gets attached to it at the C5 position. Nucleotides can have one or more phosphate groups attached in chains. The nucleotides get linked to each other by phosphodiester bonds and form a long nucleic acid strand.
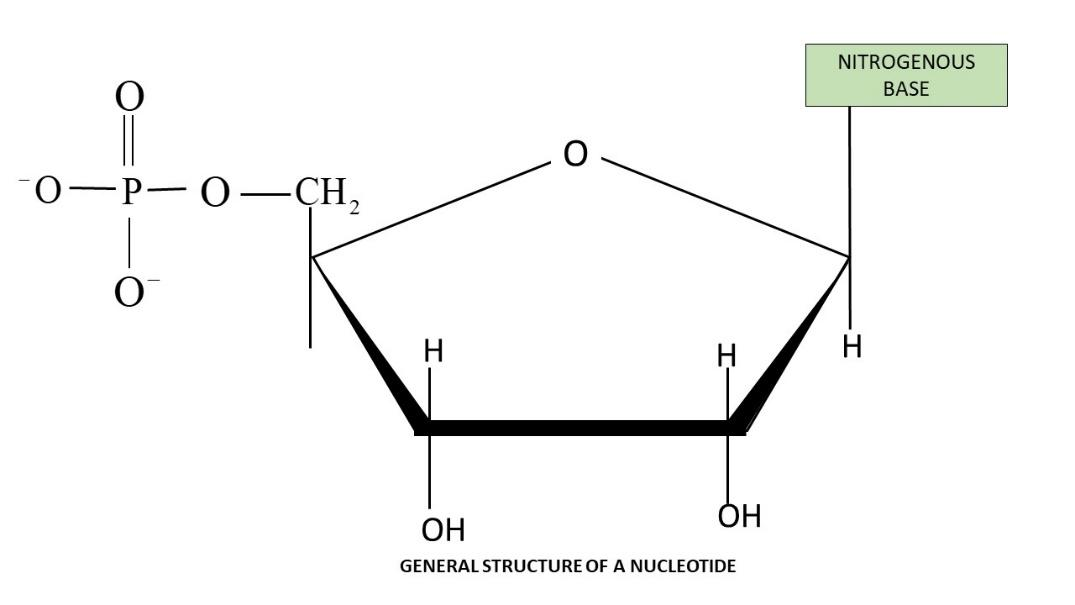
Other than acting as monomeric units of nucleic acids, they participate in the formation of energy-rich molecules like ATP, GTP. They serve as precursors to activate secondary messengers such as cAMP, cGMP. Even several coenzymes too require nucleotides as their precursor.
Note:
A nucleotide that acts as the monomeric unit of the nucleic acid has three main components. They include a base with a nitrogen atom, a five-carbon (pentose) sugar, and anion of phosphoric acid. Naturally occurring nucleic acids have only two types of pentose sugars: ribose and deoxyribose. These are known to exhibit D-stereoisomeric configuration. The nitrogenous bases that involve information of nucleosides or nucleotides are categorized into two groups: purines and pyrimidines.
Complete step by step answer:
Structure of Nucleoside: Nucleosides can be defined as glycosylamines that consist of a pentose sugar joined to a nitrogenous base such as adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, or uracil by a glycosidic bond. They are similar to nucleotides in structure but lack the phosphate group.

Nucleosides occur in two different conformations; syn and anti. These conformations are possible due to the ability of the nitrogenous base to rotate around the glycosidic bond. Pyrimidines are prone to attain anti conformation while purines can attain either of the two.
Structure of Nucleotide: Nucleosides from nucleotides when a phosphate group gets attached to it at the C5 position. Nucleotides can have one or more phosphate groups attached in chains. The nucleotides get linked to each other by phosphodiester bonds and form a long nucleic acid strand.

Other than acting as monomeric units of nucleic acids, they participate in the formation of energy-rich molecules like ATP, GTP. They serve as precursors to activate secondary messengers such as cAMP, cGMP. Even several coenzymes too require nucleotides as their precursor.
Note:
A nucleotide that acts as the monomeric unit of the nucleic acid has three main components. They include a base with a nitrogen atom, a five-carbon (pentose) sugar, and anion of phosphoric acid. Naturally occurring nucleic acids have only two types of pentose sugars: ribose and deoxyribose. These are known to exhibit D-stereoisomeric configuration. The nitrogenous bases that involve information of nucleosides or nucleotides are categorized into two groups: purines and pyrimidines.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




