NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science - Control and Coordination - Free PDF Download
The free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 - Control and Coordination is available which is solved by expert Science teachers on Vedantu.com. The solutions of the Chapter 7 - Control and Coordination exercise are well presented to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations. The NCERT Solutions are always useful for the exam preparation and as well as for the revision. The solutions of Vedantu are well curated by master teachers. Science Students who are looking for Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions find these solutions very beneficial.
To understand the concepts better of class 10 Science NCERT Exemplar, students should first start off their preparation by studying from NCERT by underlining each important definition or name and then solving the NCERT book. After this, they can move on to the NCERT Exemplar to solve more questions. If a problem arises in any question then they should look up the solutions and then keep the practice from the NCERT Exemplar and other related important questions. This way, students of Class 10 can understand the NCERT Exemplar.
There are a total of 52 questions in the NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 - Control and Coordination which are important for each student of class 10 to understand and solve. There are Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) type questions, Short Answer Type Questions and Long Answer Type Questions. All these questions can be answered by a student who has studied the NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 7- Control and Coordination in depth. This helps a student to ace the Class 10 Science Examination.
Access NCERT Exemplar Solution for Class 10 Science(Biology) Chapter 7- Control and Coordination
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. Which of the following statements is correct about receptors?
(a) Gustatory receptors detect taste while olfactory receptors detect smell
(b) Both gustatory and olfactory receptors detect smell
(c) Auditory receptors detect smell and olfactory receptors detect taste
(d) Olfactory receptors detect taste and gustatory receptors smell
Ans: (a) Gustatory receptors detect taste while olfactory receptors detect smell. Gustatory receptors are present on the tongue, while olfactory receptors are present in the back of the nasal cavity and hence detect smell. Auditory receptors do not sense smell rather sense sound waves.
2. Electrical impulse travels in a neuron from
(a) Dendrite→ axon →axonal end →cell body
(b) Cell body →dendrite →axon →axonal end
(c) Dendrite →cell body →axon →axonal end
(d) Axonal end →axon →cell body →dendrite
Ans: (c) Dendrite → cell body → axon → axonal end
Explanation: Dendrites of a neuron receive electrical impulse from the axonal end of another neuron. After that, electrical impulse travels through the cell body, axon; to the axonal end.
3. In a synapse, chemical signal is transmitted from
(a) dendritic end of one end of another neuron
(b) axon to cell body of the same neuron
(c) cell body to axonal end of the same neuron
(d) axonal end of one neuron to dendritic end of another neuron
Ans: (d) axonal end of one neuron to dendritic end of another neuron
Explanation: The electric impulses travel from the axon to the dendrite of another neuron through a synaptic gap which consists of SYNAPSE. The electric impulse or the neurotransmitter translates from the presynaptic neuron to the synaptic cleft and then finally the next neuron. In this way a chain of electric impulses is carried out.
4. In a neuron, conversion of electrical signal to a chemical signal occurs at/in
(a) cell body
(b) axonal end
(c) dendritic end
(d) axon
Ans: (b) Axonal end
Explanation: At the axonal end, electrical impulse sets off the release of some chemicals; called neurotransmitters. These chemicals are then received by the dendrites of another neuron. This region is also known as synapse and electrical signals are converted into chemical signals.
5. Which is the correct sequence of the components of a reflex arc?
(a) Receptors→ Muscles→ Sensory neuron→ Motor neuron→ Spinal cord
(b) Receptors→ Motor neuron →Spinal cord →Sensory neuron →Muscle
(c) Receptors →Spinal cord →Sensory neuron →Motor neuron →Muscle
(d) Receptors →Sensory neuron →Spinal cord →Motor neuron →Muscle
Ans: (d) Receptors →Sensory neuron →Spinal cord →Motor neuron →Muscle
Explanation: In a reflex arc, sensory neurons pick signals from receptors such as skin, muscles, or organs. These signals are then sent to the spinal cord; from where they go to muscle via motor neuron and finally the signals are sent to the effector which are either muscles, glands, or both. It helps in performing the action in response to the stimuli.
6. Which of the following statements are true?
(i) Sudden action in response to something in the environment is called reflex action
(ii) Sensory neurons carry signals from spinal cord to muscles
(iii) Motor neurons carry signals from receptors to spinal cord
(iv) The path through which signals are transmitted from a receptor to a muscle or a gland is called reflex arc
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Ans: (c) (i) and (iv)
Explanation: Sensory neurons carry signals from muscles to spinal cord, while motor neurons carry the signals from spinal cord to the muscles, hence statements (ii) and (iii) are incorrect. And on the other hand, reflex arc is the path from effector to the muscles in response to the stimuli, hence option (i) and (iv) correct.
7. Which of the following statements are true about the brain?
(i) The main thinking part of brain is hind brain
(ii) Centres of hearing, smell, memory, sight etc are located in fore brain.
(iii) Involuntary actions like salivation, vomiting, blood pressure are controlled by the medulla in the hind brain
(iv) Cerebellum does not control posture and balance of the body
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans: (c) (ii) and (iii)
Explanation: The main thinking part of the brain is the forebrain and hence statement (i) is incorrect. The cerebellum controls posture and balance of the body and hence statement (iv) is incorrect. Option (ii) and (iii) are correct.
8. Posture and balance of the body is controlled by
(a) cerebrum
(b) cerebellum
(c) medulla
(d) pons
Ans: (b) Cerebellum
Explanation: Cerebrum helps in maintaining processes of learning, memory, language, and speech. While Medulla Oblongata controls heartbeat, breathing rhythm, and other vital functions. Pons maintain a connection between the spinal cord and the brain. Cerebellum controls posture and balance of the body
9. Spinal cord originates from
(a) cerebrum
(b) medulla
(c) pons
(d) cerebellum
Ans: (b) medulla, Medulla Oblongata connects brain and spinal cord and is the origin for the spinal cord. It runs from the brain down to the backbone. Together the brain and spinal cord form the central nervous system.
10. The movement of shoot towards light is
(a) geotropism
(b) hydrotropism
(c) chemotropism
(d) phototropism
Ans: (d) phototropism
Explanation: The term ‘phototropism’ is composed of two terms. ‘Photo’ means light and ‘tropism’ means growth. Therefore, movement towards the light is associated with phototropism which is one of the movements towards the external stimuli like water and gravity. Therefore, the correct option is A.
11. The main function of abscisic acid in plants is to
(a) increase the length of cells
(b) promote cell division
(c) inhibit growth
(d) promote growth of stem
Ans: (c) Inhibit growth
Explanation: Abscisic acid is a stress related hormone which helps in closing of stomata. It is a plant growth inhibitor and allows seed morbidity at the time of turbulence. It also inhibits plant metabolism and hinders seed germination.
12. Which of the following is not associated with growth of plant?
(a) Auxin
(b) Gibberellins
(c) Cytokinins
(d) Abscisic acid
Ans: (d) Abscisic acid
Explanation: Abscisic acid is a plant growth inhibitor. Its functions include wilting of leaves, inhibition of seed germination and seed dormancy under the required conditions. Rest other hormones mentioned above are related with plant growth.
13. Iodine is necessary for the synthesis of which hormone?
(a) Adrenaline
(b) Thyroxin
(c) Auxin
(d) Insulin
Ans: (b) Thyroxin
Explanation: Thyroxine is produced by the thyroid gland. And iodine is required for its production. For rest other hormones iodine is not required for the production. This is the reason, deficiency of iodine results in hypothyroidism.
14. Choose the incorrect statement about insulin
(a) It is produced from pancreas
(b) It regulates growth and development of the body
(c) It regulates blood sugar level
(d) Insufficient secretion of insulin will cause diabetes
Ans: (b) It regulates growth and development of the body
Explanation: Insulin is produced by cells present in pancreas. It helps in maintaining blood sugar levels. Deficiency of Insulin causes a disease called Diabetes, in which blood sugars are not maintained. Insulin has no role to play in growth and development of the body.
15. Select the mis-matched pair
(a) Adrenaline: Pituitary gland
(b) Testosterone: Testes
(c) Estrogen: Ovary
(d) Thyroxin: Thyroid gland
Ans: (a) Adrenaline: Pituitary gland
Explanation: Adrenaline is secreted by adrenal glands. And the pituitary gland secretes GSH, TSH and FSH. Rest other pairs are correctly matched as Testosterone is secreted by Testes, Estrogen is secreted by ovaries and Thyroxine is secreted by Thyroxine gland.
16. The shape of guard cells changes due to change in the
(a) protein composition of cells
(b) temperature of cells
(c) amount of water in cells
(d) position of nucleus in the cells
Ans: (c) Amount of water in cells
Explanation: Opening and closing of stomata is regulated by guard cells. Excess amount of water results in guard cells becoming turgid and it allows stomata to open, while lack of water results in flaccidity of guard cells and stomata closes in that condition.
17. The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to
(a) effect of light
(b) effect of gravity
(c) rapid cell divisions in tendrillar cells that are away from the support
(d) rapid cell divisions in tendrillar cells in contact with the support
Ans: (c) rapid cell divisions in tendrillar cells that are away from the support
Explanation: Tendrils help the vines to grow upwards with support to climb. Due to this, there is more growth on the portion away from support. This results in tendrils getting twined around the support. It is a modified shoot. When tendrils meet a surface for support it coils itself around that area and growth becomes faster.
18. The growth of pollen tubes towards ovules is due to
(a) hydrotropism
(b) chemotropism
(c) geotropism
(d) phototropism
Ans: (b) chemotropism
Explanation: Ovules release certain chemicals which stimulate the growth of pollen tubes towards ovules and hence since it is related with chemicals this movement is known as chemotropism. Rest other movements are related to water, gravity, and light respectively.
19. The movement of sunflower in accordance with the path of sun is due to
(a) phototropism
(b) geotropism
(c) chemotropism
(d) hydrotropism
Ans: (a) phototropism
Explanation: Phototropism is the response of the plants towards light. Thus, the sunflower moves in accordance with the path of the sun. It is one of the movements associated with external stimuli like gravity, water, and chemicals.
20. The substance that triggers the fall of mature leaves and fruits from plants is due to
(a) auxin
(b) gibberellin
(c) abscisic acid
(d) cytokinin
Ans: (c) abscisic acid
Explanation: Abscisic acid is a growth-inhibiting hormone. It is responsible for seed dormancy, inhibition of seed growth, and closing of stomata. Other hormones like auxin is growth hormone, Gibberellin promotes shoot elongation, flowering, and germination, Cytokinin is a growth promoter and hormone that stimulates cell division.
21. Which of the following statements about the transmission of nerve impulse is incorrect?
(a) Nerve impulse travels from dendritic end towards axonal end
(b) At the dendritic end electrical impulses bring about the release of some chemicals which generate an electrical impulse at the axonal end of another neuron
(c) The chemicals released from the axonal end of one neuron cross the synapse and generate a similar electrical impulse in a dendrite of another neuron
(d) A neuron transmits electrical impulses not only to another neuron but also to muscle and gland cells
Ans: (b) At the dendritic end electrical impulses bring about the release of some chemicals which generate an electrical impulse at the axonal end of another neuron.
Explanation: Chemicals are released from the axonal end and not from the dendritic end. Chemicals released by the axonal end convert the electric signals into chemical signals. These chemicals are also known as Neurotransmitters. The junction between the axonal end and dendrites of adjacent neurons is known as Synapse.
22. Involuntary actions in the body are controlled by
(a) medulla in fore brain
(b) medulla in mid brain
(c) medulla in hind brain
(d) medulla in spinal cord
Ans: (c) Medulla in hindbrain
Explanation: Medulla is a part of hindbrain. Medulla is responsible for controlling involuntary actions and reflex responses. Since it is part of the hind brain, the correct answer is C.
23. Which of the following is not an involuntary action?
(a) Vomiting
(b) Salivation
(c) Heartbeat
(d) Chewing
Ans: (d) Chewing
Involuntary actions are the actions which are not governed by our own wish, for example our heartbeat, Salivation and Vomiting. Even if we don’t want it to not happen, even then these processes occur. It is regulated by Medulla Oblongata. But Chewing is a voluntary action, it will only happen according to our will and is controlled by cerebrum.
24. When a person is suffering from severe cold, he or she cannot
(a) differentiate the taste of an apple from that of an ice cream
(b) differentiate the smell of a perfume from that of an agarbatti
(c) differentiate red light from green light
(d) differentiate a hot object from a cold object
Ans: (b) differentiate the smell of a perfume from that of an agarbatti
Explanation: When a person is suffering from a severe cold, his olfactory receptors are blocked. Due to this, the sense of smell is compromised because of clogging of the nose. Since other sense receptors like photoreceptors and taste receptors known as gustatory receptors work fine, these senses are not lost.
25. What is the correct direction of the flow of electrical impulses?
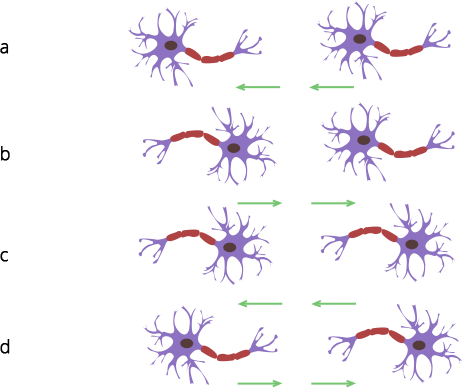
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Dendrites of a neuron receive electrical impulse from the axonal end of another neuron. After that, electrical impulse travels through the cell body, axon; to the axonal end. The transmission of nerve impulse is in the order - Axon end – synapse - dendrites - axon body - axon end.
26. Which statement is not true about thyroxin?
(a) Iron is essential for the synthesis of thyroxin
(b) It regulates carbohydrates, protein, and fat metabolism in the body
(c) Thyroid gland requires iodine to synthesize thyroxin
(d) Thyroxin is also called thyroid hormone
Ans: (a) Iron is essential for the synthesis of thyroxine
Explanation: It is iodine which is essential for the synthesis of thyroxine and not iron. It regulates the fat metabolism in the body. Thyroxine, which is also called thyroid hormone, is produced by the thyroid gland. Therefore, option A is incorrect.
27. Dwarfism results due to
(a) Excess secretion of thyroxin
(b) Less secretion of growth hormone
(c) Less secretion of adrenaline
(d) Excess secretion of growth hormone
Ans: (b) Less secretion of growth hormone
Explanation: As the name suggests, growth hormone is responsible for proper growth in a person. Hence, lack of production of growth hormone would result in dwarfism. It is specifically due to the underproduction of somatotropin.
28. Dramatic changes of body features associated with puberty are mainly because of secretion of
(a) oestrogen from testes and testosterone from ovary
(b) estrogen from adrenal gland and testosterone from pituitary gland
(c) testosterone from testes and estrogen from ovary
(d) testosterone from thyroid gland and estrogen from pituitary gland
Ans: (c) testosterone from testes and estrogen from ovary
Explanation: These are called sex hormones and are secreted from gonads. Testosterone is secreted in males and oestrogen is secreted in females. They regulate the sexual characters in both males and females at the time of puberty.
29. A doctor advised a person to take an injection of insulin because
(a) his blood pressure was low
(b) his heart was beating slowly
(c) he was suffering from goiter
(d) his sugar level in blood was high
Ans: (d) his sugar level in blood was high
Explanation: Insulin maintains the blood sugar levels. Lack of insulin production causes diabetes. Hence, a person suffering from diabetes needs to take insulin artificially. If a person is suffering from diabetes, then his blood sugar level may become high. This disease is managed in some patients by administering insulin injection.
30. The hormone which increases the fertility in males is called
(a) oestrogen
(b) testosterone
(c) insulin
(d) growth hormone
Ans: (b) Testosterone
Explanation: Testosterone is secreted by testes, and it promotes spermatogenesis, the process of production of sperms. It is also responsible for sexual characteristics such as body hair growth and sexual desires.
31. Which of the following endocrine glands is unpaired?
(a) Adrenal
(b) Testes
(c) Pituitary
(d) Ovary
Ans: C) Pituitary Gland
Explanation: Adrenal gland is a paired gland and is present one on the top of each kidney. Testes are also paired and produce male sex hormone. Ovaries are also present in pairs on both sides of the female reproductive system. Pituitary gland is not a paired gland and is present just below the brain.
32. Junction between two neurons is called
(a) cell junction
(b) neuromuscular junction
(c) neural joint
(d) synapse
Ans: Synapse
Explanation: The synapse is the junction between two neurons. The synapse is the site of transmission of electric signals being carried forward from the dendrites to the axon, to the axonal end, to the synapse and then to the adjacent neuron. It is also known as neuromuscular junction.
33. In humans, the life processes are controlled and regulated by
(a) reproductive and endocrine systems
(b) respiratory and nervous systems
(c) endocrine and digestive systems
(d) nervous and endocrine systems
Ans: Nervous and endocrine Systems
Explanation: Neurons which form the nervous system tend to be the main aspect for communication of the body. Signals move through the neurons. Apart from the nervous system, the endocrine system is also necessary for the metabolism of life processes. Endocrine system is formed of the glands which secrete the hormones for the metabolism. Therefore, the correct option is D.
Short Answer Questions
34. Label the parts (a), (b), (c) and (d) and show the direction of flow of electrical signals in Figure 7.2.
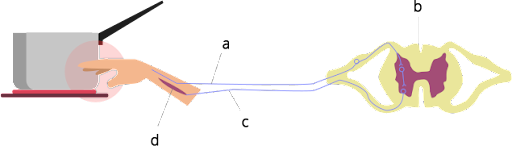
Ans: (a) Sensory neuron (b) Spinal cord (c) Motor neuron (d) Muscle
Sensory Neurons carry the information to the spinal cord, from the spinal cord the signals are transferred to the motor neuron and from the motor neuron transferred to the muscle, which performs the specific function.
The transmission of nerve impulse is in the order - Axon end – synapse - dendrites - axon body - axon end.
35. Name the plant hormones responsible for the following
(a) elongation of cells
Ans: Auxin
Auxin is a growth hormone and helps in the elongation and growth of the cells.
(b) growth of stem
Ans: Giberellins
Giberellins, are the growth hormone and help in the growth of stem and shoot.
(c) promotion of cell division
Ans: Cytokinin
Cytokinin are the growth hormones which help in cell division of the cell.
(d) falling of senescent leaves.
Ans: Abscisic Acid
Abscisic Acid is growth inhibiting hormone and causes wilting of leaves and seed dormancy.
36. Label the endocrine glands in Figure 7.3.
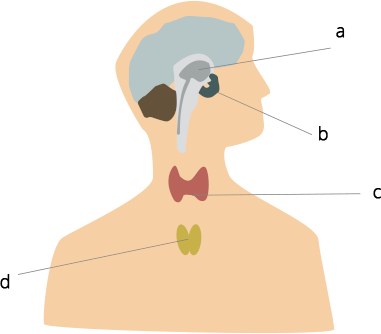
Ans: (a) Pineal gland (b) Pituitary gland (c) Thyroid gland (d) Thymus
37. In Figure 7.4 (a), (b) and (c), which appears more accurate and why?

Ans: Figure ‘a’ appears more accurate. In this figure roots are showing positive geotropism, while shoot is showing negative geotropism and positive phototropism. As shoots need to grow in the direction of sunlight it has to show positive phototropism, but the same shoot needs to move upwards away from the gravity and therefore, it shows negative geotropism.
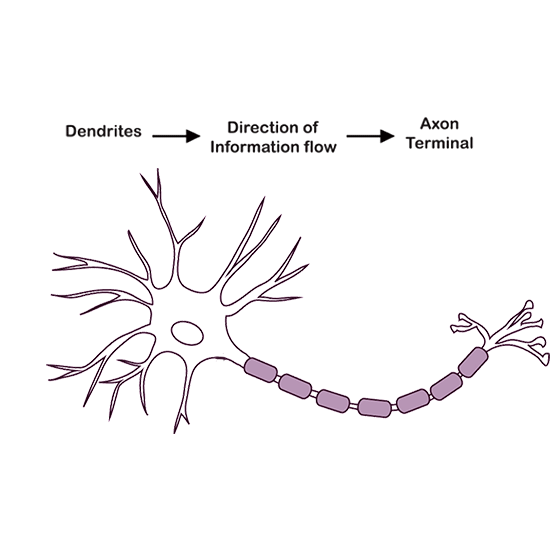
38. Label the parts of a neuron in Figure 7.5
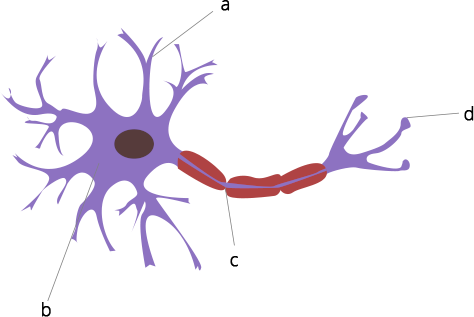
Ans: (a) Dendrite
(b) Cell body
(c) Axon
(d) Axon terminal
39. Match the terms of Column (A) with those of Column (B)
Column A | Column B |
(a) Olfactory receptors | (i) Tongue |
(b) Thermoreceptors (temperature receptors) | (ii) Eye |
(c) Gustatoreceptors | (iii) Nose |
(d) Photoreceptors | (iv) Skin |
Ans:
Column A | Column B |
(a) Olfactory receptors | (iii) Nose |
(b) Thermoreceptors (temperature receptors) | (iv) Skin |
(c) Gustatoreceptors | (i) Tongue |
(d) Photoreceptors | (ii) Eye |
40. What is a tropic movement? Explain with an example.
Ans: The movements which are in a particular direction in relation to the stimulus are called tropic movements. Tropic movements happen because of growth of a plant in a particular direction. There are four types of tropic movements, viz. geotropic, phototrophic, hydrotropic and thermotropic.
Example: Roots usually show positive geotropic movement, i.e., they grow in the direction of the gravity. Stems usually show negative geotropic movement.
41. What will happen if the intake of iodine in our diet is low?
Ans: Iodine is essential for the manufacture of thyroxin or thyroid hormone in the body. If intake of iodine in our diet is low, it will reduce the production of thyroxine by the thyroid gland. This can result in hypothyroidism. It can even result in goiter.
42. What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
Ans: The junction between two neurons is called the synapse. When an electrical impulse reaches the axonal end of a neuron, it sets off the release of neurotransmitters in the synapse. These neurotransmitters enter the dendrite of another neuron to set off electrical signals in that neuron. That is how an electrical impulse travels from one neuron to another.
43. Answer the following:
(a) Which hormone is responsible for the changes noticed in females at puberty?
Ans: Oestrogen
Explanation: Estrogen or Oestrogen is female sex hormone, and it is responsible for development of female sexual characteristics. It maintains the reproductive system of the females.
(b) Dwarfism results due to deficiency of which hormone?
Ans: Growth hormone
Explanation: Growth hormones are produced by the pituitary gland and are responsible for growth and development of the body, excessive production of growth hormones causes gigantism and less production causes dwarfism.
(c) Blood sugar level rises due to deficiency of which hormone?
Ans: Insulin
Explanation: Insulin maintains the blood sugar level by absorbing glucose, produced by the cells of the pancreas it metabolizes fats, carbohydrates, and proteins.
(d) Iodine is necessary for the synthesis of which hormone?
Ans: Thyroxin
Explanation: Also known as thyroid hormone, Thyroxine is produced by the thyroid gland. For the synthesis of thyroid hormone iodine is required, which is not produced by our body and needs to be consumed through the diet. Deficiency of iodine causes Goiter.
44. Answer the following:
(a) Name the endocrine gland associated with brain?
Ans: Pituitary
(b) Which gland secretes digestive enzymes as well as hormones?
Ans: Pancreas
(c) Name the endocrine gland associated with kidneys?
Ans: Adrenal gland
(d) Which endocrine gland is present in males but not in females?
Ans: Testis
Long Answer Questions
45. Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its function.
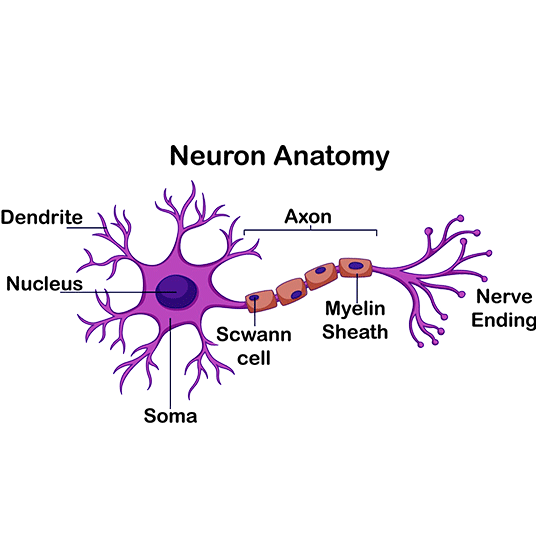
Ans: Neuron is a highly specialized cell which is responsible for transmission of nerve impulses. The neuron consists of the following parts: Cyton or cell body: The cell body or cyton has many hairlike structures protruding out of the margin. These hair-like structures are called dendrites. Dendrites receive the nerve impulses and carry it forward to the axon. Axon: This is the tail of the neuron. It ends in several hair-like structures; called axon terminals. The axon terminals relay nerve impulses. Myelin Sheath: There is an insulator cover around the axon. This is called myelin sheath. The myelin sheath insulates the axon against nerve impulses from the surroundings. The nerve impulse is thus carried from the dendrites to the axonal end and transmitted to adjacent neurons. The axonal end also releases some chemicals known as Neurotransmitters which convert electrical signals into chemical signals which are passed onto the next neuron.
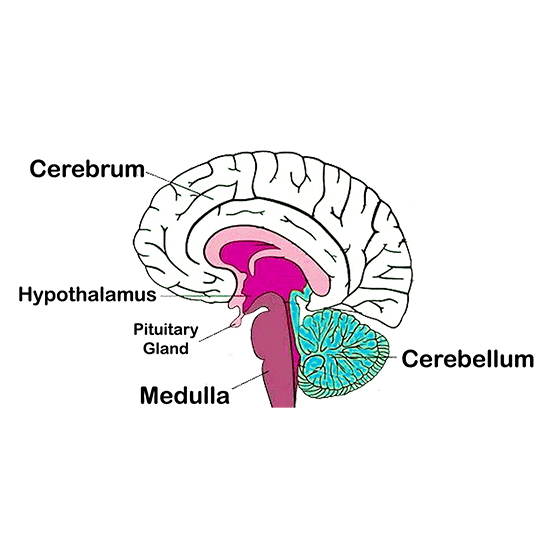
46. What are the major parts of the brain? Mention the functions of different parts.
Ans: The brain is covered by a three-layered system of membranes; called meninges. Cerebrospinal fluid is filled between the meninges. The CSF provides a cushion to the brain against mechanical shocks. The brain is located inside the skull for maximum protection. The human brain can be divided into three regions, viz. forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. Some main structures of the human brain are explained below.
Cerebrum: The cerebrum is the largest part in the human brain. It is divided into two hemispheres; called cerebral hemispheres.
Functions of the cerebrum: The cerebrum controls voluntary motor actions. It is the site of sensory perceptions, like tactile and auditory perceptions. It is the seat of learning and memory.
Hypothalamus: The hypothalamus lies at the base of the cerebrum. It controls the sleep and wake cycle (circadian rhythm) of the body. It also controls the urges for eating and drinking.
Cerebellum: Cerebellum lies below the cerebrum and at the back of the whole structure. It coordinates the motor functions. When you are riding your bicycle; the perfect coordination between your pedaling and steering control is achieved by the cerebellum.
Medulla: The medulla forms the brain stem; along with the pons. It lies at the base of the brain and continues into the spinal cord. The medulla controls various involuntary functions; like heartbeat, respiration, etc.
47. What constitutes the central and peripheral nervous systems? How are the components of central nervous system protected?
Ans: Central nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral nervous system is composed of nerves which are present outside the spinal cord.
Central nervous system has a well-developed system for protection. Brain is enclosed in skull for protection and the skull is hard and bony. Spinal cord is enclosed in vertebral column for protection. Additionally, the cerebrospinal fluid provides a cushion against mechanical shocks.
48. Mention one function for each of these hormones:
(a) Thyroxin
Ans: Thyroxin is also known as thyroid hormone which is produced by thyroid gland. Too much production or too less production of thyroid hormone causes thyroid disease. It functions includes digestion, heart and muscle function and maintenance and development of bones. Iodine is necessary and is required to produce thyroid hormone.
(b) Insulin
Ans: Insulin is peptide hormone produced by cells of pancreas. It regulates metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Main function of insulin is to regulate blood sugar levels. Insulin promotes absorption of glucose. Absence of insulin causes a disease called diabetes, in which blood sugar level are not maintained.
(c) Adrenaline
Ans: Adrenaline is a hormone released from the adrenal gland and its major function is fight or flight. It is released in the condition of stress and excitement. It is the hormone released when the body is in danger and senses threat. It is also known by name epinephrine. It helps body to response to the stress.
(d) Growth hormone
Ans: Growth hormones are released by pituitary glands and control the growth of an individual. Growth hormones regulate the height of an individual, bone length and muscle growth. Excessive release of growth hormones causes gigantism and deficiency of growth hormones causes dwarfism.
(e) Testosterone
Ans: Testosterone is male sex hormone which is released by testes. Testosterone regulates the secondary sexual characters in males. It helps in the fat distribution, regulates the sexual desires, helps in hair growth. It also helps in the production of sperm which is required for the fertilization at the time of sexual intercourse.
49. Name various plant hormones. Also give their physiological effects on plant growth and development.
Ans: Plant hormones help in growth and development of the plants. There are four types of plant hormones. These are auxin, gibberellins, cytokinin and abscisic acid.
Auxin: Auxin is a growth hormone; it helps in elongation of the cells and hence the growth of the plants.
Gibberellins: Gibberellins are also growth hormones, and it helps in elongation of the shoot and stem.
Cytokinin: Cytokinin are types of growth hormones which help in cell division and thus promotes the overall growth of the plant.
Abscisic Acid: It is not a growth hormone rather a growth inhibiting hormone. Abscisic acid is responsible for closing of stomata, wilting of leaves and dormancy of seeds.
50. What are reflex actions? Give two examples. Explain a reflex arc.
Ans: The sudden involuntary movement in a voluntary organ; in response to a stimulus; is called reflex action.
Examples of reflex action: (a) Moving your hand away from a hot iron plate (b) Blinking of eyes Reflex Arc: The path of electrical impulse during a reflex action is called reflex arc.
A reflex arc is composed of a sensory neuron, spinal cord, motor neuron and muscle. It involves following steps: The sensory neuron picks signals from the stimulus and carries the signals to the spinal cord. Spinal cord processes the signals and sends messages through the motor neuron. Motor neurons transmit the signals to the effector muscle so that the muscle can take immediate action.
51. “Nervous and hormonal systems together perform the function of control and coordination in human beings.” Justify the statement.
Ans: Control and coordination of functioning of various systems is under the direct control of the nervous system. It is the nervous system which governs the way a particular organ or organ system must work. This control is achieved by a complex network of neurons which carry signals in the form of electric impulses, to and from the brain. The hormonal system, on the other hand, coordinates the functioning of the nervous system. The hormonal system has somewhat indirect control on various functions. It tells a system to either slow down or pace, according to the situation. Nervous and hormonal systems are complementary to each other. Thus, it can be said that the nervous and hormonal system together perform the function of control and coordination in human beings.
52. How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
Ans: Hormones facilitate chemical control in animals. Hormones are chemicals which are directly released in the bloodstream. A particular hormone reaches the target site through blood. Hormone tells the target tissue to behave in a particular manner. To understand this, let us take the example of adrenalin. Adrenaline is secreted by the adrenal gland. It reaches the heart and lungs and to the GI tract. Heart speeds up its pumping action so that more blood could be supplied to the limbs and facial muscles. But activity of the GI tract is slowed down to ensure better blood supply in limbs. Thus, adrenaline prepares the body for a fight or flight situation.
53. Why is the flow of signals in a synapse from axonal end of one neuron to dendritic end of another neuron but not the reverse?
Ans: Electrical impulse travels through a neuron. But to be transmitted to another neuron, it needs to pass in the form of neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are specialized chemicals. These can enter a neuron only through specialized channels. Such channels are present in dendrites but not in axon and Neurotransmitters are only produced at the axonal end and can enter a dendrite. Due to this, the flow of signals in a synapse is from the axonal end of one neuron to the dendritic end of another neuron but not the reverse.
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 - Control and Coordination (Book Solutions)
1. Where can I find the best NCERT Exemplar study material for Class 10 Science?
At Vedantu, we provide the best study material for a class 10 student whether it is science or any other subject. These study materials can be downloaded in PDFs and the student can study them any way they want whether it is offline, online, in hard copy or soft copy. The PDFs of NCERT Exemplar are easily accessible to each student via the Vedantu website or app. A student can download these in a blink of an eye just by signing in.
The concepts discussed in class 10 Science NCERT for Chapter-7 Control and Coordination are the nervous system- animals, what happens in reflex actions, the human brain in detail, how does the nervous tissue cause action, details about Coordination in plants and Hormones in animals. All the concepts that are discussed in NCERT should be well attended to by a class 10 student as the board question paper for class 10 comes mostly from NCERT and preparing from NCERT for biology helps you to get a better understanding in higher classes if you pursue biology.
In NCERT Exemplar Science Class 10 Chapter 7 Control and Coordination, students should be clear about the CNS(Central Nervous System) and PNS(Peripheral Nervous System). The brain and the spinal cord constitute the Central Nervous System. The peripheral Nervous system is composed of nerves that are outside the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System is very well-developed for protection. The brain is enclosed in the skull. The spinal cord is protected by a vertebral column. Additionally, the cerebrospinal fluid provides a cushion against mechanical shocks.






































