




Computer Memory
A computer is a digital electronic machine that can be programmed to carry out any specific sequences of arithmetic or logical operations on its own. Modern computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These programs are specific codes which form the base of computer functioning as they enable computers to perform a wide range of different tasks, from very simple tasks like performing certain calculations to some tedious tasks like browsing the web and sharing information across the world.
The computer also has the ability to store and recall all the information and programs fed into it, which enables it to reuse the same set of instructions over and over again when required.
Computer Memory System
The Computer Memory System consists of small bits (0 or 1).
Some units to measure memory are;
Bits: 1 or 0
Nibble: 1 Nibble = 4 bits
Bytes; 1 Byte = 8 bits
KiloByte: 1KB = 1024 bits
MegaBytes: 1MB=1024 KB
GigaByte: 1 GB=1024MB
TeraByte: 1 TB=1024GB
PetaByte: 1 PB=1024 TB
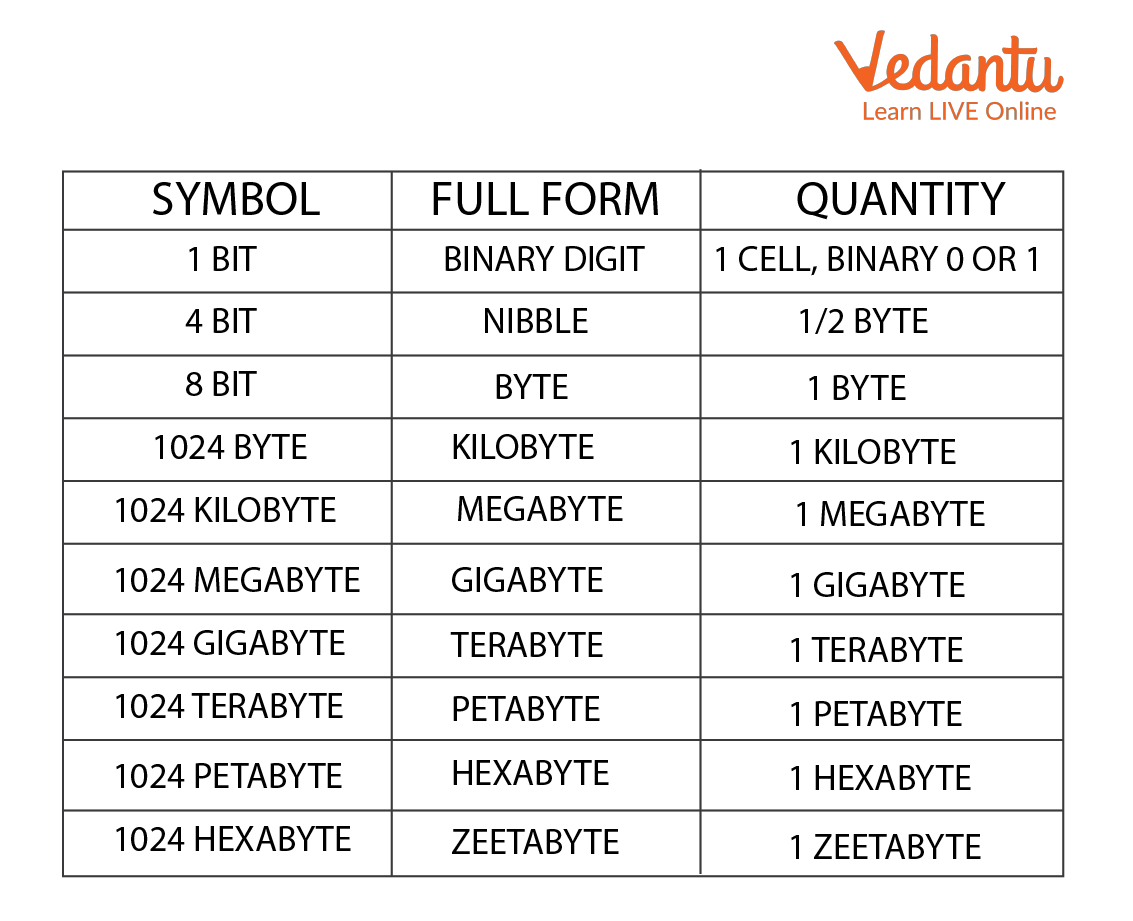

Computer Memory System
Computer Memory and Its Types
There are two main types of computer memory:
Primary Memory
Secondary Memory
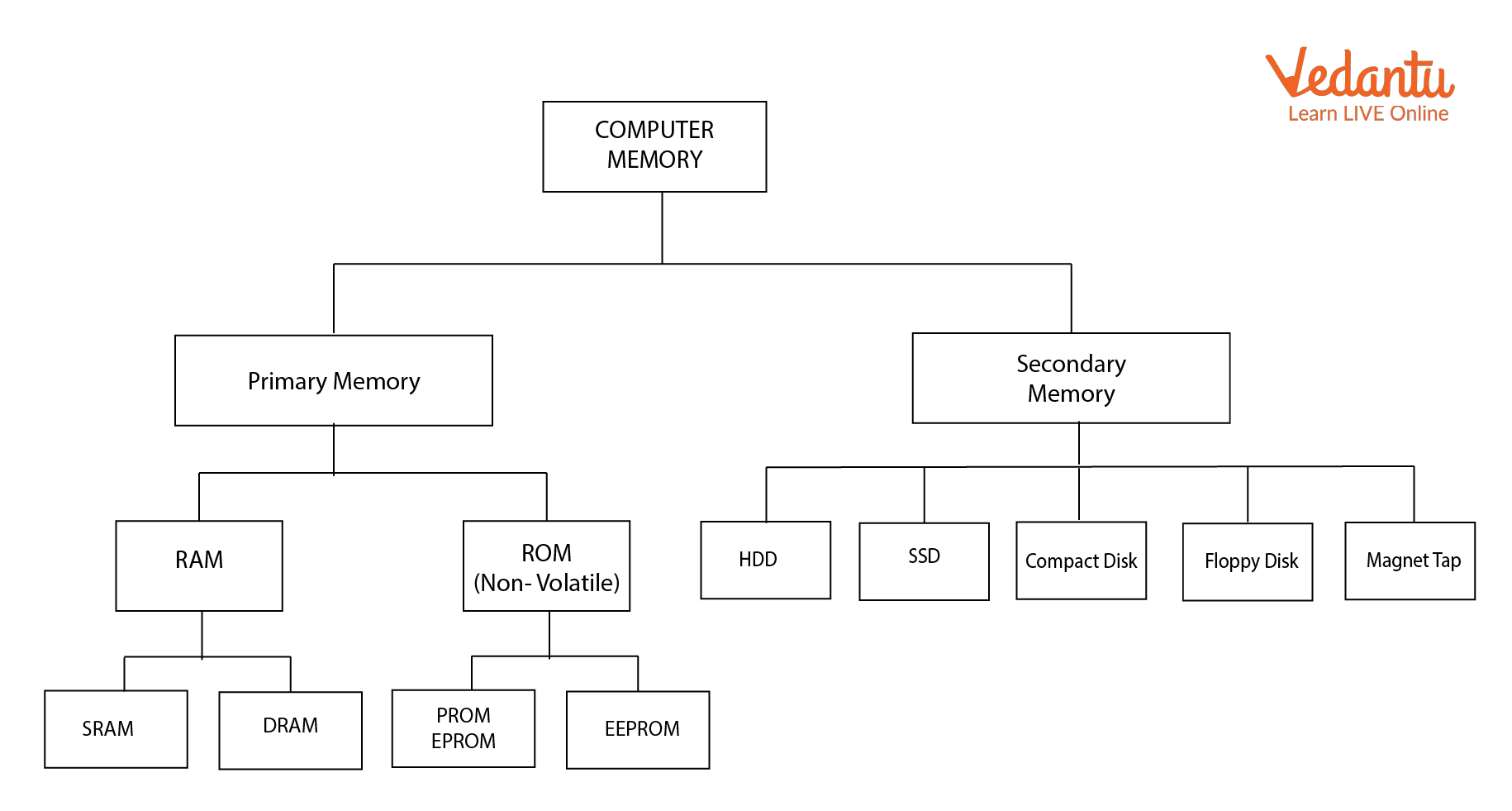
Types of Computer Memories
Types of Primary Memory
The Primary Memory is the internal memory of the computer, also known as Volatile Memory. However, it is lost as soon as the power of the device is cut off. Some features of Primary Memory are:
It is also known as Volatile Memory or the Main Memory.
It is lost once the power is cut off.
It provides the main working space for all the computer functions and processes.
Some subtypes of Primary Memory are:
RAM
ROM
RAM
It stands for Random Access Memory. It is the internal memory of the CPU which stores most of the data and the instructions for the processing of the data. Since it is the internal memory, it can only be viewed but not modified by the user. RAM is lost once the power is cut off, and it also has limited storage. It, however, is faster than any other storage device.
RAM
In RAM, as the name suggests, any piece of data can be assessed randomly, that is, without touching the preceding or proceeding data.
There are two different types of RAM:
DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory)
SRAM (Static Random Access Memory)
ROM
It stands for Read Only Memory. It is responsible for storing data permanently, which cannot be changed or modified. The data stored in ROM is not rewritable as suggested by the name; it can only be read. ROM is also a Non Volatile Memory, which is not lost once the power is cut off.
ROM
Different Types of ROM are:
PROM (Programmable Read Only Memory)
EPROM( Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory)
EEPROM( Electrically Erasable Read Only Memory)
Flash EEPROM Memory
Memory That Cannot be Processed by the CPU
The memory that cannot be directly processed by the CPU is: Secondary Memory
Secondary Memory is the physical device used for storing data permanently. Some examples of Secondary Memory are:
Hard Disk
Flash Drive
Compact Disc
Floppy Disc
Digital Versatile Disk (DVD)
What is the Use of Memory in a Computer?
Some of the main uses of computer memory are:
It is one of the most important factors for determining the performance of the system.
RAM gives a place for applications to be processed on a short-term basis.
RAM is also responsible for storing the information, which the computer actively uses for accessing all the data and performing all the functions.
RAM also dictates the speed of the computer, which is directly correlated to the amount of RAM attached to the device.
Summary
The Computer Memory System is the ability to store all the data and the instructions related to them; it is one of the most important factors in determining the overall functioning of the device. It is mainly of two types: Primary and Secondary Memory. The Primary Memory is the volatile memory but is the main memory of the device, whereas the Secondary Memory is generally detachable devices and is a non-volatile memory.
Learn by Doing
1. Give the full form for the following:
ROM
RAM
DRAM
SRAM
PROM
EPROM
EEPROM
Answers:
Read Only Memory
Random Access Memory
Dynamic Read Only Memory
Static Read Only Memory
Programmable Read Only Memory
Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory
Sample Questions
1. Give some examples of Primary Memory and Secondary Memory.
Ans: Primary Memory:
RAM
ROM
Secondary Memory:
Hard Disk
CD (Compact Disk)
DVD (Digital Versatile Disc)
Floppy Disc
Blu Ray Disc
Flash Drive
Magnetic tapes
SD Cards
2. What is computer memory made up of?
Ans: Any computer’s memory is made up of small bits (cells) arranged in a grid form. Mostly it follows the basic system of two digits (1 and 0). This system is known as the Binary System.
FAQs on Introduction to Computer Memory System
1. What is a computer memory system and what is its primary role?
A computer memory system is the set of electronic storage components that a computer uses to hold data and instructions. Its primary role is to provide the Central Processing Unit (CPU) with immediate access to the information it needs to execute programs and perform tasks. Without memory, a computer cannot even boot up, let alone run applications.
2. What are the main types of memory found in a computer?
Computer memory is broadly classified into two main types based on their function and proximity to the CPU:
- Primary Memory: This is the main memory directly accessible by the CPU. It is very fast but typically has less storage capacity. Examples include RAM (Random Access Memory) and ROM (Read-Only Memory).
- Secondary Memory: Also known as auxiliary or external memory, this is used for long-term storage of data and programs. It is slower than primary memory but offers much larger storage capacity. Examples include Hard Disk Drives (HDD), Solid-State Drives (SSD), CDs, and DVDs.
3. How is Primary Memory (RAM and ROM) different from Secondary Memory?
The key differences between primary and secondary memory are based on speed, volatility, capacity, and cost. Primary memory is significantly faster, directly accessed by the CPU, but is mostly volatile (loses data when power is off, like in RAM) and more expensive per byte. In contrast, secondary memory is slower, has a much larger storage capacity, is non-volatile (retains data without power), and is cheaper, making it ideal for permanent storage.
4. Why is RAM called 'volatile memory' while ROM is 'non-volatile'?
RAM (Random Access Memory) is called 'volatile' because it requires constant power to maintain the stored information. As soon as the power is turned off, all data in RAM is lost. This is why you lose unsaved work during a power cut. ROM (Read-Only Memory), on the other hand, is 'non-volatile' because it holds its data permanently, even without power. It contains essential startup instructions for the computer, which must be available every time the system boots up.
5. What is the function of Cache memory in the computer memory hierarchy?
Cache memory is a small, extremely fast type of volatile memory that sits between the CPU and the main memory (RAM). Its primary function is to store copies of frequently used data and instructions from RAM. Since the CPU can access the cache much faster than RAM, this significantly reduces the time the CPU has to wait for data, thereby improving the overall performance and speed of the computer.
6. What is the real-world difference between memory (RAM) and storage (like an SSD/HDD)?
A simple analogy helps explain this. Memory (RAM) is like your workbench or desk. It's where you keep the tools and papers you are actively working on right now for quick access. It's fast but has limited space. Storage (SSD/HDD) is like your filing cabinet or warehouse. It's where you keep all your files, applications, and the operating system for the long term. You pull items from storage onto your workbench to use them.
7. How are the different units of computer memory, like KB, MB, GB, and TB, related?
Computer memory is measured in bytes, with larger units representing multiples of 1024 bytes. The hierarchy is as follows:
- A Bit is the smallest unit (a 0 or 1).
- A Byte is a group of 8 bits.
- A Kilobyte (KB) is 1,024 Bytes.
- A Megabyte (MB) is 1,024 Kilobytes.
- A Gigabyte (GB) is 1,024 Megabytes.
- A Terabyte (TB) is 1,024 Gigabytes.
8. Can data be recovered after it is deleted from a storage device?
Yes, often it can be. When you 'delete' a file from a storage device like a hard drive, the operating system usually just removes the pointer or reference to that file in its index. The actual data (the 1s and 0s) remains on the disk in an area now marked as 'available'. Until that physical space is overwritten by new data, specialised data recovery software can scan the disk and retrieve the 'deleted' file.























