




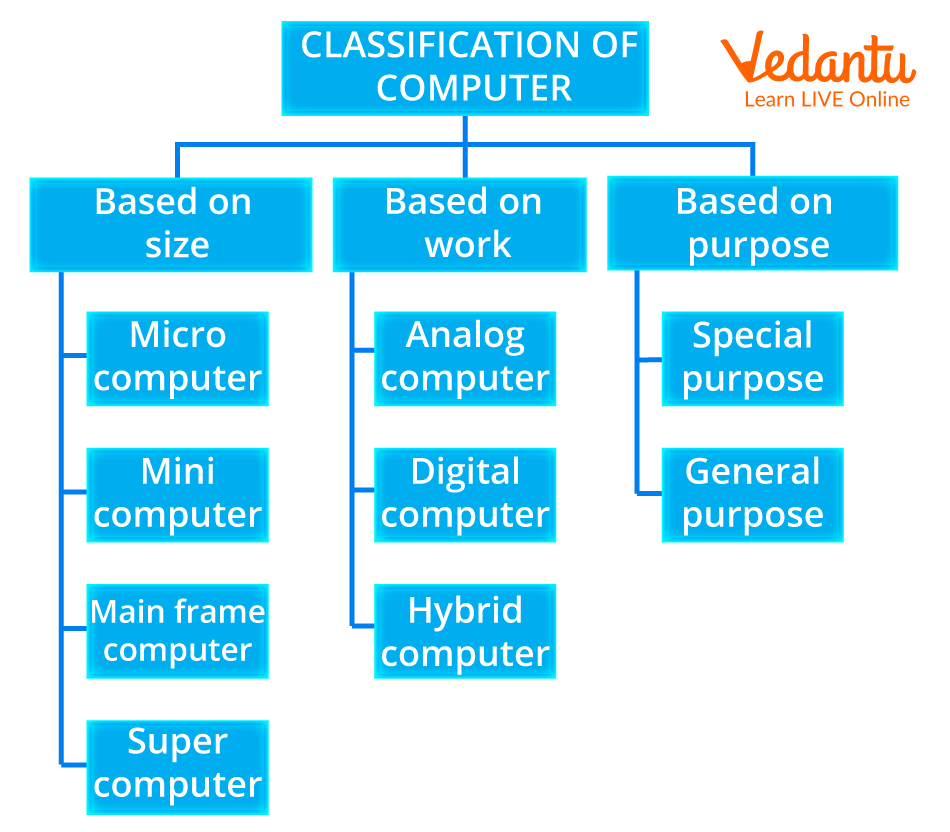
Computer Classification
A computer is a device that transforms unusable data into information. According to the set of instructions the user gives it, it processes the input and generates the desired outcome. Modern digital computers are classified on the basis of their size and capacity. The size and data handling capabilities of the various types of computers may be used to categorize them into two groups.
1. Computers according to Size:
Supercomputer.
Mainframe computer.
Personal computer.
Workstation.
Minicomputer.
2. Computers according to their Capacity to manage data:
Digital computer.
Hybrid computer.
Analog computer.
Classification of Computers
Classification of Computers with Examples
Different classifications of Computers are as follows.
Classification According to Size
There are four different sorts of computers based on their size and how they are configured to operate:
1. Supercomputers

Supercomputer
The most efficient computers in terms of processing data and performance are supercomputers. These computers are used for research and exploratory purposes. Supercomputers are exceedingly large and highly expensive. It can only fit in large, air-conditioned spaces.
Supercomputers are used for a range of tasks, such as space exploration, seismic research, and the testing of nuclear weapons.
Supercomputer Features:
They make use of AI (Artificial intelligence)
They are the fastest and strongest;
They are very costly.
They are enormous in size.
They are employed by companies that manufacture goods.
They process information at a rapid rate.
Examples:
Fugaku (Japan)
IBM Blue Gene
Cray XT5
2. Mainframe Computers
Mainframe Computers
Despite being less efficient than supercomputers, mainframe computers are nevertheless extremely expensive. Large corporations and governmental organizations frequently employ mainframe computers to run everyday operations. They have the ability to store and analyze a lot of data. To maintain information on their customers, students, and insurance policyholders, banks, colleges, and insurance companies utilize them. They may also act as a server in a network environment. Hundreds of users may be managed simultaneously by them.
Mainframe Computer Features:
They have enormous amounts of memory.
They are capable of running several different operating systems.
They have a significant number of CPUs with powerful processing speeds.
Tightly Coupled Clustering Technology is employed.
Examples:
IBM Z Series
Unisys ClearPath
3. Minicomputers

Mini Computer
Minicomputers are used by small businesses and industries. They go by the term "Midrange Computers." These minicomputers frequently have several users, just as mainframe computers. They are a bit slower than mainframe computers.
For example, the manufacturing department may employ minicomputers to keep an eye on specific production processes.
Features of Minicomputers:
It is smaller than mainframes or supercomputers in terms of size.
In comparison to a mainframe or supercomputer, it is less costly.
It is able to perform many jobs at once.
It may be utilized by several users simultaneously.
It is utilized by small businesses.
Examples:
DEC PDP-11
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC)
VAX Systems
4. Microcomputers.

Micro Computer
A microcomputer, sometimes referred to as a personal computer (PC), is a type of computer that runs on a smaller scale than traditional computers (Personal Computer). A component that is commonly referred to as a motherboard houses the central processing unit (CPU), a microprocessor, memory in the form of ROM (Read Only Memory), RAM (Random Access Memory), I/O ports, and a bus system of connecting wires. They are the most affordable.
Features of Microcomputers:
They are extensively employed for personal usage.
They are smaller and comparably less expensive.
Multi-user functionality is not supported.
It has a limited computational capacity.
They are quite simple to use.
Examples:
Desktop PCs
Laptops
Smartphones
Tablets
Raspberry Pi
Based on Capacity
According to fundamental operating principles, there are three different kinds of computers. They are as follows:
1. Analogous Computers
Analog computers process analog data. Temperature, pressure, weight, depth, and voltage are a few examples of this type of data. These have an infinite range of values and are continuous quantities.
The first computers were analog, and they laid the groundwork for today's digital computers.
Examples:
Analog thermometers
Speedometers
Flight simulators

Analogous Computers
2. Digital Computers
In digital computers, letters, numbers, and other special symbols are represented by digits. On-off (ON-OFF) inputs are used by digital computers, and ON-OFF signals are also generated by them.
An ON is often represented by a 1 and an OFF by a 0, respectively. A digital computer is capable of processing both numerical and non-numerical data. In addition to doing fundamental arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, it can also perform logical operations.
Examples:
Personal computers
Laptops
Smartphones
Servers

Digital Computer
3. Hybrid Computers
Computers that combine digital and analog components are called hybrid computers. It combines the best features of both types, having the speed of an analog computer with the memory and precision of a digital computer. Hybrid computers are typically used in specific applications where both forms of data need to be processed. As an example, a gas pump contains a processor that converts measurements of fuel flow into information about quality and cost.
Examples:
Hospital patient monitoring systems
Control systems in factories

Hybrid Computer
Solved Questions
1. Comparison between micro and mini-computers?
2. What are the uses of Super Computers?
Ans: Supercomputers are employed in data-intensive and computation-intensive scientific and technical operations including quantum mechanics, meteorology, fossil fuel extraction, molecular dynamics, physical modeling, aerodynamics, nuclear fusion research, etc.
Practice Questions
Write True or False:
1. Supercomputers are the fastest and strongest. (T/F)
2. There is only one processing optimization in Minicomputers. (T/F)
3. Supercomputers are employed in data-intensive operations. (T/F)
4. Microcomputers are capable of running several different operating systems. (T/F)
Summary
Computers are divided into several categories based on their architecture, the speed at which commands or instructions are carried out, the peripherals they use, and the tasks for which they were designed.
The different computer types may be divided into two groups based on their size and capacity for handling data.
There are five main kinds of computers based on size: PC (Personal Computer), minicomputer, microcomputers, supercomputers, and mainframe.
Additionally, there are three different kinds of computers based on their capacity to manage data: A computer can be digital, hybrid, or analog.
FAQs on Classification of Computers Based on Size and Capacity
1. What are the main types of computers classified based on their size and processing capacity?
Computers are broadly classified into four primary types based on their physical size and processing capabilities: supercomputers, mainframe computers, minicomputers, and microcomputers. Each category is designed to meet different computational demands and serve various user needs, from individual tasks to complex scientific research.
2. What defines a supercomputer, and what are its primary applications?
A supercomputer represents the pinnacle of computing power, being the largest, fastest, and most expensive type of computer available. They are built to perform extremely complex calculations and process vast amounts of data at unparalleled speeds. Their primary applications include advanced scientific research, weather forecasting, climate modeling, nuclear simulations, and cryptography.
3. What are mainframe computers, and for what kind of large-scale operations are they primarily used?
Mainframe computers are robust, high-performance systems capable of handling and processing massive volumes of data and transactions concurrently. They are predominantly used by large organizations such as banks, airlines, insurance companies, and government agencies for mission-critical operations like financial transactions, enterprise resource planning, and large-scale data processing.
4. What are minicomputers, and where do they typically fit in the range of computer sizes and uses?
Minicomputers occupy an intermediate position between powerful mainframes and smaller microcomputers. They offer significant processing power, though less than mainframes, and are more affordable. They are commonly employed by small to medium-sized businesses, for specific departmental tasks, industrial control systems, and scientific laboratories where the demands exceed those of a microcomputer but do not require a full mainframe.
5. What defines a microcomputer, and why are they commonly used for personal and home tasks?
Microcomputers, often referred to as personal computers (PCs), are compact, relatively inexpensive, and designed for single-user operation. They are widely adopted for personal, educational, and small business tasks due to their affordability, user-friendliness, and ability to handle everyday activities such as word processing, internet browsing, multimedia consumption, and gaming.
6. How does the capacity of a computer, like its processing power and storage, influence its classification?
A computer's capacity—which includes its central processing unit (CPU) speed, random access memory (RAM), and storage capabilities—directly dictates its ability to perform tasks and process data. Higher capacity enables more complex computations and larger data handling, thus determining whether a system fits into classifications like supercomputers (highest capacity) or microcomputers (sufficient capacity for individual use).
7. Is there a direct relationship between a computer's physical size and its processing capacity?
Generally, there is a strong correlation: the larger a computer's physical size, the greater its potential for accommodating more powerful components and extensive cooling systems, leading to higher processing capacity. However, modern technological advancements have enabled significant miniaturization, meaning current smaller devices can often surpass the capacity of older, larger machines, showing that size isn't the only determining factor.
8. What exactly does computer capacity refer to, and why is it crucial for understanding different computer systems?
Computer capacity refers to the overall performance metrics of a system, including its computational speed (often measured in FLOPS for high-end systems or GHz for CPUs), memory (RAM in GB), and data storage space (in TB or PB). Understanding capacity is crucial because it helps identify the potential and limitations of different computer systems, aligning them with suitable applications from basic office work to highly demanding scientific calculations.
9. Can you provide examples of typical uses for each major classification of computers?
Certainly. Here are examples for each type of computer classification based on size and capacity:
- Supercomputers: Used in weather forecasting, drug discovery simulations, and complex physics research.
- Mainframe computers: Handle millions of daily transactions for credit card processing, airline reservations, and government databases.
- Minicomputers: Often found in manufacturing plants for process control, managing a university department's server, or in CAD/CAM applications.
- Microcomputers: Everyday use includes browsing the internet, writing documents, playing video games, and video conferencing.



































