
Compare the acidic strength of acetic acid, Chloroacetic acid, Benzoic acid and Phenol.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The strength of the acid can be compared by the stability of its conjugate bases. Conjugated bases can be stabilized by inductive effect as well as resonance effect. The EWG group attached to the acid makes it stronger.
Complete step by step answer:
We will see the stability of the conjugate base formed by all the given acids in order to compare their acidity. We can say the more stable the conjugate base, more acidic the compound will be.
i) Phenol:
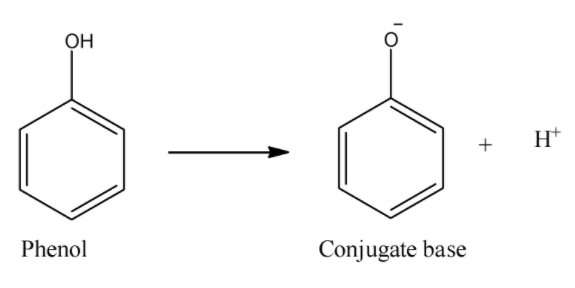
Here, in the dissociation reaction, we can see that phenol forms phenoxide ion. Now, this ion can be stabilized only by the resonance of double bonds in which in some structures, the negative charge will be on carbon atoms. So, this and absence of carbonyl groups makes phenols less acidic than carboxylic acids. So, phenol will be the least acidic compound from all of the given.
ii) Acetic acid:
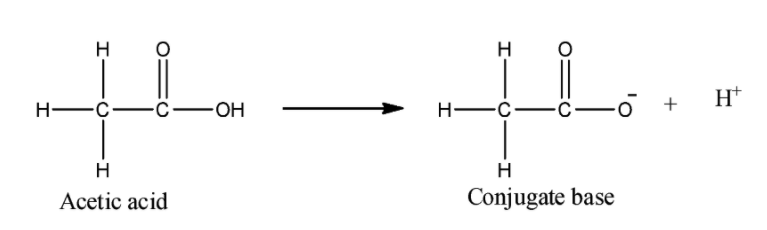
We can see that the negative charge on the oxygen atom can be stabilized by the inductive effect of the carbonyl group. Methyl group here is an electron donating group, so it will increase the electron density on the oxygen. Still it will be more acidic than phenol.
iii) Benzoic acid:
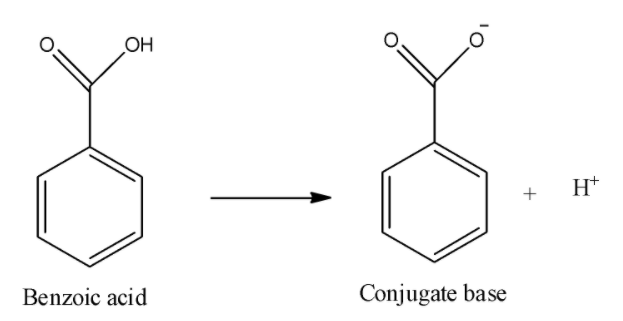
Here, in this dissociation reaction, we can see that carboxylate anion will be formed and it can be stabilized by inductive effect of the carbonyl group as well as by resonance of double bond of carbonyl oxygen. Thus, it will be more acidic than acetic acid because the phenyl ring will decrease the electron density on the negatively charged oxygen because it is an electron withdrawing group.
iv) Chloroacetic acid:
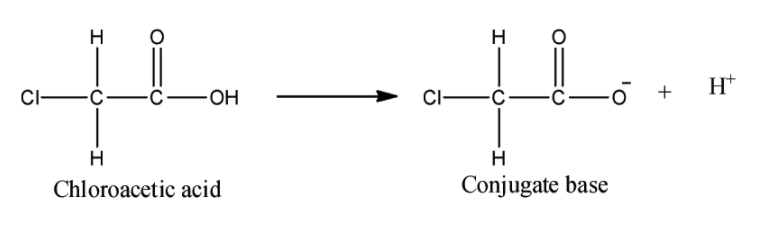
Here, one chlorine atom in place of the hydrogen atom is the only difference between chloroacetic acid and acetic acid. Chlorine atom is a highly electron withdrawing group, so it will withdraw the electron density form the negatively charged oxygen atom and hence the conjugate base will get stabilized. Now, this chlorine atom is stronger EWG than the phenyl ring. Hence we can say that chloroacetic acid will be a stronger acid than benzoic acid.
Thus, from the above discussion, we can conclude that the order of acidity of these compounds is as below:
Phenol < Acetic acid < Benzoic acid < Chloroacetic acid
Note:
Remember that if Electron withdrawing group is there in the structure of the conjugate base, then it will decrease the electron density on the negatively charged oxygen atom and that will stabilize it. If EDG is attached there, then it will increase the electron density there and that will destabilize the conjugate base and the acid will be weaker.
Complete step by step answer:
We will see the stability of the conjugate base formed by all the given acids in order to compare their acidity. We can say the more stable the conjugate base, more acidic the compound will be.
i) Phenol:

Here, in the dissociation reaction, we can see that phenol forms phenoxide ion. Now, this ion can be stabilized only by the resonance of double bonds in which in some structures, the negative charge will be on carbon atoms. So, this and absence of carbonyl groups makes phenols less acidic than carboxylic acids. So, phenol will be the least acidic compound from all of the given.
ii) Acetic acid:

We can see that the negative charge on the oxygen atom can be stabilized by the inductive effect of the carbonyl group. Methyl group here is an electron donating group, so it will increase the electron density on the oxygen. Still it will be more acidic than phenol.
iii) Benzoic acid:

Here, in this dissociation reaction, we can see that carboxylate anion will be formed and it can be stabilized by inductive effect of the carbonyl group as well as by resonance of double bond of carbonyl oxygen. Thus, it will be more acidic than acetic acid because the phenyl ring will decrease the electron density on the negatively charged oxygen because it is an electron withdrawing group.
iv) Chloroacetic acid:

Here, one chlorine atom in place of the hydrogen atom is the only difference between chloroacetic acid and acetic acid. Chlorine atom is a highly electron withdrawing group, so it will withdraw the electron density form the negatively charged oxygen atom and hence the conjugate base will get stabilized. Now, this chlorine atom is stronger EWG than the phenyl ring. Hence we can say that chloroacetic acid will be a stronger acid than benzoic acid.
Thus, from the above discussion, we can conclude that the order of acidity of these compounds is as below:
Phenol < Acetic acid < Benzoic acid < Chloroacetic acid
Note:
Remember that if Electron withdrawing group is there in the structure of the conjugate base, then it will decrease the electron density on the negatively charged oxygen atom and that will stabilize it. If EDG is attached there, then it will increase the electron density there and that will destabilize the conjugate base and the acid will be weaker.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




