
The high boiling point of water is due to the presence of:
A. Dative bond
B. Covalent bond
C. Hydrogen bond
D. Vander Waals bond
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure of the liquid’s environment. At this temperature, liquid is converted into vapor. Moreover, hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole attraction between the molecules.
Complete step by step answer:
The boiling point of the liquid depends upon the pressure of the surrounding. So, when the liquid is at high pressure, then it has a higher boiling point than the boiling point at normal atmospheric pressure. Furthermore, the boiling point of a substance is dependent on the pressure of its surrounding.
Now, the high boiling point of water is due to the presence of Hydrogen bond. Multiple hydrogen bonds occur simultaneously in water because of its bent shape and the presence of two hydrogen atoms.
Moreover, in the liquid state, the hydrogen bonds of water can break and reform, as the molecules flow from one place to another. The electrostatic attraction between the partial positive charge between the hydrogen atoms and the partial negative charge close to the oxygen atom allows the formation of a hydrogen bond.
The hydrogen bonding in water molecule is as shown:
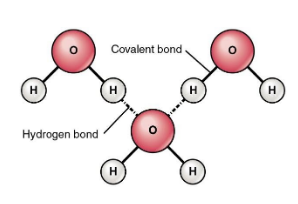
Hence, option C is correct.
Note: Hydrogen bonding also occurs due to the unique physical properties, low surface tension, high vaporization energy and high specific heat. Another unique property of water caused by hydrogen bonds is the hydrophobic effect or exclusion of compounds containing carbon and hydrogen. Further, the hydrophobic effect is also important in the formation of cell membranes.
Complete step by step answer:
The boiling point of the liquid depends upon the pressure of the surrounding. So, when the liquid is at high pressure, then it has a higher boiling point than the boiling point at normal atmospheric pressure. Furthermore, the boiling point of a substance is dependent on the pressure of its surrounding.
Now, the high boiling point of water is due to the presence of Hydrogen bond. Multiple hydrogen bonds occur simultaneously in water because of its bent shape and the presence of two hydrogen atoms.
Moreover, in the liquid state, the hydrogen bonds of water can break and reform, as the molecules flow from one place to another. The electrostatic attraction between the partial positive charge between the hydrogen atoms and the partial negative charge close to the oxygen atom allows the formation of a hydrogen bond.
The hydrogen bonding in water molecule is as shown:

Hence, option C is correct.
Note: Hydrogen bonding also occurs due to the unique physical properties, low surface tension, high vaporization energy and high specific heat. Another unique property of water caused by hydrogen bonds is the hydrophobic effect or exclusion of compounds containing carbon and hydrogen. Further, the hydrophobic effect is also important in the formation of cell membranes.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




