Download Free PDF with Solutions of Heredity and Evolution Class 10, Chapter 1
Heredity and Evolution is an essential chapter for Class 10 students in the Maharashtra Board. The chapter introduces students to the concept of Heredity and Evolution and follows with solved examples and practice questions. In this chapter, students will be able to learn all the methods to solve questions on Heredity and Evolution. In order to understand the chapter in detail, refer to the PDF where solutions can be downloaded for the chapter.
These solutions for Maharashtra Board Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 Heredity and Evolution have been carefully designed by the subject matter experts at Vedantu who are completely well-versed with the essential topics and sub-topics included in the chapter. Downloading the Heredity and Evolution Chapter 1 solutions will help students gain a better understanding of the chapter.
Access Maharashtra Board solutions for Biology Class X Chapter 1 Heredity and Evolution
1. Complete the following diagram.
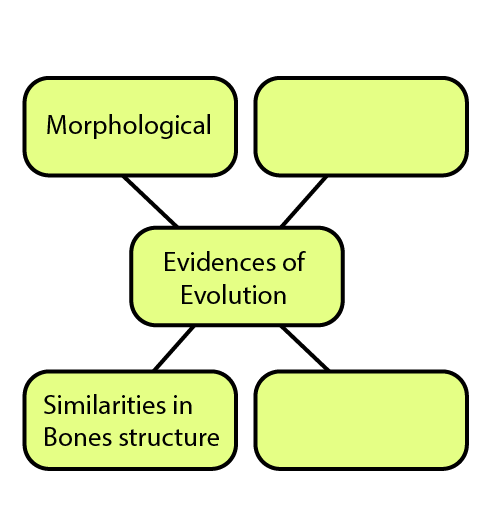
Ans: Evidence of Evolution has the part of Palaeontological and Embryological findings along with Morphological and anatomical.
2. Read the following statements and justify the same in your own words with the help of suitable examples.
a. Human evolution began approximately 7 crore years ago.
Ans: The ice era on earth started roughly 7 billion years ago. Dinosaurs perished under such circumstances. During this time, animals began to evolve and diversify. The forest cover also drastically decreased as a result of climate change.
Lemur-like animals originated during this epoch and are the ancestors of monkey-like creatures.
Around 4 billion years ago, these monkey-like creatures' tails began to slowly disappear.
The size of the body and the brain both grew, creating the first ape-like animals. Two evolutionary connections to apes and human-like creatures were created by the monkey-like predecessors.
Later, the size of the brain changed, along with our capacity to stand up straight and our propensity to manipulate objects with our hands.
Seven billion years ago, the human evolution process started. However, the truly knowledgeable and learned man only appeared some 50,000 years ago.
b. The geographical and reproductive isolation of organisms gradually leads to speciation.
Ans: Every species can only exist in certain geographical regions. Each species has unique needs in terms of food and habitat. Additionally, their cycles and capacities for reproduction differ.
As a result, members of one species cannot procreate with members of another species.
They are considered to be geographically isolated when they are separated by a distance or other physical obstacles.
Although both of these subspecies may descend from the same parent species, there is genetic differentiation between them as a result of their extended periods of isolation. As a result, speciation results from isolation.
c. The study of fossils is an important aspect of the study of evolution.
Ans: Paleontological proof of evolution is provided by fossils.
In earlier times, the organisms became buried as a result of natural disasters.
Such species' imprints and remains are still preserved underground. In addition, certain organisms or their imprints are trapped in the heated lava. Such formations all produce fossils.
The study of fossils enables the researcher to comprehend the traits of ancient organisms.
The carbon dating method also aids in determining the fossil's precise age. The fossils are discovered at particular depths based on the crustal structure of the planet.
The most recent ones are found on the surface, while the oldest ones are found in depth. Invertebrate fossils were thus discovered in the extremely old Palaeozoic epoch. Fossils of Pisces, Amphibia, and Reptilia were later discovered. While mammals were present during the Cenozoic era, reptiles dominated the Mesozoic era.
In this way, studying fossils reveals the mysteries of evolution.
d. There is evidence of fatal Science among chordates.
Ans: Fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals all exhibit remarkably similar early structural characteristics in their very immature embryos.
They develop new patterns as they continue to grow.
The earliest resemblance of vertebrate embryos is proof that all vertebrate classes shared a common ancestor during evolution.
This is referred to as embryological proof of the evolution of vertebrates.
1. Complete the statements by choosing the correct options from brackets.
(Gene, Mutation, Translocation, Transcription, Gradual development, Appendix)
a. The causality behind the sudden changes was understood due to -- – the principle of Hugo de Vries.
Ans: Mutation
Explanation: Hugo de Vries (1848–1935), a Dutch botanist and one of the independent discoverers of Mendelism put forward his views on the formation of new species in 1901. According to him, new species arise not through continuous change, but through the sudden appearance of changes, which he calls mutations.
b. The proof for the fact that protein synthesis occurs through -- --- was given by George Beadle and Edward Tatum.
Ans: Genes
Explanation: Evidence that protein synthesis occurs enzymatically was provided by George Beadle and Edward Tatum. They proposed the one-gene-one-enzyme theory. According to this theory, genes are involved in protein production.
c. The transfer of information from a molecule of DNA to mRNA is called as -- -- -- process.
Ans: Transcription
Explanation: The transcription process is one of the parts of the central dogma. In this process, DNA segment changes into RNA. Segments of DNA that are transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are designed to produce messenger RNA (mRNA).
d. Evolution means -- -- -- --.
Ans: Gradual development
Explanation: Evolution is the change in traits of a species over several generations and is based on the process of natural selection. This process by which a particular situation or thing develops gradually over some time.
e. The vestigial organ -- -- -- the present inhuman body is proof of evolution.
Ans: Appendix
Explanation: The immature, useless organs of an organism are called vestigial organs. Such organs are useless in some organisms, but these organs are useful in others. The appendix is useless in humans but works in cows. The auricular muscle is useless in humans, but useful in monkeys.
1. Write short notes based on the information known to you.
a. Lamarckism
Ans: Jean Baptiste Lamarck put out two hypotheses that make up Lamarckism. These are listed below: Use and abuse of organs (a) (b) The passing on of acquired traits.
According to Lamarck's theory of organ use and abuse, organ characteristics emerge as a result of particular tasks that organisms must carry out. Such an organ degenerates if it is not used. Therefore, morphological changes result from an organism's activity or inactivity.
He used the instances below to illustrate this principle. The giraffe's neck lengthened as a result of constant neck extension to eat vegetation from the tops of the trees. Similar to how blacksmiths, who work constantly, have powerful arms. Ostriches and emus that were unable to fly lost the use of their wings. Swans and ducks are aquatic birds that evolved their feet to be capable of swimming by subsisting in water. Snake sought to burrow but lost limbs in the process.
Such acquired traits are handed down through one generation of parents to the kids. This is referred to as character inheritance.
Since there is no such transmission of acquired character, the notion of heredity of acquired traits is rejected. Only genetic traits are passed on.
b. Darwin’s theory of natural selection
Ans: Following extensive research on several specimens, Charles Darwin put out the hypothesis of natural selection. He released the idea of "survival of the fittest."
Darwin explains this idea by saying that all organisms reproduce a lot. As a result, rivalry for food, partners, etc. is constant. Only modifications to endure this struggle.
Natural selection contributes significantly by choosing only species that can survive. Those who lack more effective adaptations perish. Then, over a very long time, a few selected sustaining creatures carry out reproduction and create new species.
Darwin wrote forth his ideas in the book "Origin of Species."
c. Embryology
Ans: The study of growing embryos is known as embryology.
These embryos are quite similar to one another while they are first developing.
Later in the development, these similarities get less prominent.
These animals likely descended from a common ancestor because of their similarities in the early developmental phases.
Comparative analysis of the embryos of diverse vertebrate species provides proof of evolution in evolutionary science.
d. Evolution
Ans: Evolution is the name given to the series of relatively slow changes that occur in groups of living things.
The emergence of new species as a result of natural selection is another definition of evolution.
For the development and speciation of many organisms, evolution takes millions of years.
The study of evolution encompasses both the evolution of stars, planets and other celestial bodies as well as the evolution of the biosphere on Earth.
Evolution makes organisms more fit, boosts biodiversity, and produces new species.
To explain how evolution works, various scientists have proposed hypotheses. The hypothesis of natural selection and speciation advanced by Charles Darwin is among those that are widely accepted.
e. Connecting link
Ans: Some living things have characteristics that are the defining characteristics of various groups or phyla. Such people serve as connective ties between these two groups since they exhibit traits common to both.
Examples: (1) Peripatus, which serves as the link between Annelida and Arthropoda. Both animal phyla are represented by their characters. It exhibits a segmented body, a thin cuticle, and parapodia similar to an annelid worm. It exhibits an open circulatory system and a tracheal system for breathing, much like an arthropod.
Duck-billed platypus: This animal serves as a connection between reptiles and mammals. It has hairy skin and mammary glands like mammals, yet it also lays eggs like reptiles.
Lungfish: Fish and amphibians are connected by lungfish. Despite being a fish, it exhibits lungs for breathing like amphibian species.
Interconnecting links show the hierarchy and direction of progression.
1. Define heredity. Explain the mechanism of hereditary changes.
Ans: Heredity is the process through which genes are used to pass on biological traits from one generation of parents to the following.
The hereditary change's mechanism,
Mutation: Mutations can result from a sudden change in the parental DNA. The inherited traits are altered as a result.
The crossing-over takes place during meiosis. The genetic information gets recombined in novel ways as a result. As a result, the haploid gametes created have altered genetic traits.
2. Define vestigial organs. Write names of some vestigial organs in the human body and write the names of those animals in whom the same organs are functional.
Ans: Degenerated or undeveloped organs in living things that serve no purpose are known as vestigial organs.
Such organs are in danger of going extinct, following the natural selection theory. But it doesn't completely disappear for many millions of years.
As long as they continue to carry out their normal activities, an animal's vestige organs may still be useful to other species.
For humans, the appendix is merely a vestige that serves no purpose, but in ruminant animals, it plays an important role in digesting.
While they are useful in monkeys and cattle, our ear muscles are vestigial in humans.
Names of the human body's vestiges: the appendix, the tailbone or coccyx, the wisdom teeth, and body hair
3. Answer the following questions.
a. How are hereditary changes responsible for evolution?
Ans: Character traits are passed on from the parents to their children. Inheritance preserves these characteristics. However, a bigger percentage of the genes that help organisms adapt to their environment is passed on to the following generations. Because of natural selection, this occurs.
The evolution process proceeds quite slowly. Because they increase individual survival, advantageous genes are kept within the species. Such a person evolves and reproduces more successfully. Unfavorable gene carriers are not naturally selected for and are hence eliminated from the population through natural causes of death. Thus, genetic alterations provide the fuel for evolution.
b. Explain the process of formation of complex proteins.
Ans: The steps involved in synthesizing proteins are transcription, translation, and translocation. With the aid of RNA molecules, protein synthesis is carried out by the arrangement of nucleotides on the DNA molecule. This is referred to as the protein synthesis central dogma.
Transcription: mRNA is created during transcription following the DNA's nucleotide sequence. DNA's two strands are split for this. The creation of mRNA involves just one strand. On mRNA, the nucleotide sequence that is now present on DNA is duplicated. Uracil is added to the mRNA in place of the thymine found in DNA. Although transcription occurs in the nucleus, the genetic code is carried by the mRNA before it exits the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm. The triplet codon name refers to the fact that this genetic code always takes this form. Each amino acid has a unique code made up of three nucleotides.
Each mRNA could have thousands of codons. But just one amino acid is particular to each codon. According to the mRNA coding, the tRNA molecule transports the necessary amino acid. Each tRNA contains an anticodon that pairs with the corresponding codon in the mRNA. The translation is the term for this action.
c. Explain the theory of evolution and mention the proof supporting it.
Ans: According to this theory, the first organisms, the protoplasm, formed in the sea. Evolution is the gradual development of plants and animals with different structural and functional organizations from their ancestors. There is plenty of evidence to support the theory.
The earliest living substance, according to the theory of evolution, was protoplasm, which originated in the ocean.
It gradually led to the emergence of single-celled creatures. These unicellular organisms underwent changes that caused them to grow larger and more complex.
All evolutionary changes occurred over a 300 billion-year period and were relatively gradual.
As living beings changed and evolved, new forms of organisms emerged that was multifaceted and woven into all directions.
Thus, the terms organized and progressive are used to describe this entire evolutionary process.
During evolution, a variety of plants and animals evolved from predecessors with various structural and functional organizations.
Evidence of evolution:
1. Morphological Evidence: Similarities in morphology and physical structure prove that they share the same origin and common ancestor. For example, mouth structure, nostril position, auricles, and thick hair on the whole body of animals such as dogs, goats, and sheep.
2. Vestigial Organs as Evidence: The immature, useless organs of an organism are called vestigial organs. Such organs are useless in some organisms, but these organs are useful in others. For example, the appendix is useless in humans but works in cows. The auricular muscle is useless in humans, but useful in monkeys.
Also, there is more evidence as proof of evolution, which is listed below.
Morphological proof
Skeletal evidence
Remnant organs
Palaeontological proofs
Establishing links
Embryological proof.
d. Explain with suitable examples the importance of anatomical evidence in evolution. (July 2019)
Ans: The structure and anatomy of various animal groupings share some commonalities.
The internal anatomy of the human hand, a bull's forelimb, a bat's patagium, and a whale's flipper, for instance, is comparable.
All of these specimens' bones and joints are comparable.
There is no similarity in the external morphology. Each organ has a varied function in various animals. Structure-wise, they might not be connected.
However, the anatomical similarities suggest that they may have shared an ancestor.
The anatomical data illuminates the evolutionary process in this way.
e. Define fossils. Explain the importance of fossils as proof of evolution.
Ans: Paleontological proof of evolution is provided by fossils.
In earlier times, the organisms became buried as a result of natural disasters.
Such species' imprints and remains are still preserved underground. In addition, certain organisms or their imprints are trapped in the heated lava. Such formations all produce fossils.
The study of fossils enables the researcher to comprehend the traits of ancient organisms.
The carbon dating method also aids in determining the fossil's precise age. The fossils are discovered at particular depths based on the crustal structure of the planet.
The most recent ones are found on the surface, while the oldest ones are found in depth. Invertebrate fossils were thus discovered in the extremely old Palaeozoic epoch. Fossils of Pisces, Amphibia, and Reptilia were later discovered. While mammals were present during the Cenozoic era, reptiles dominated the Mesozoic era.
In this way, studying fossils reveals the mysteries of evolution.
f. Write an evolutionary history of modern man.
Ans: Lemur-like animals were the ancestors of the animals that gave rise to modern humans.
Some of these lemur-like species went on to evolve into monkey-like creatures some seven billion years ago.
The tails of these monkey-like creatures slowly vanished in Africa around 4 billion years ago.
Their body and brain volume both increased at the same time. The hands also got better and got opposable thumbs. Animals that resemble apes have evolved in this way.
These ape-like creatures produced two distinct evolutionary lines, one of which produced apes like the gibbon and orangutan in South and North-East Asia and the other of which produced the gorilla and chimpanzee, which remained in Africa about 2.5 million years ago.
Around 2 billion years ago, the other branch of evolution gave rise to animals that are similar to humans.
As a result, the spinal column and pelvic girdle underwent modifications. Additionally freed from movement, the hands developed greater manipulating abilities.
In the future, hominoid species' voyage began some 2 billion years ago. The ape "Ramapithecus" from East Africa is the first example of a human-like animal.
The major stages in the evolution of humans are represented by Ramapithecus, Australopithecus, Neanderthal man, and Cro-Magnon.
The first smart man, according to legend, was a neanderthal. As his brain grew, man became a more intelligent and thought-provoking animal.
When man began farming and raising animals, cultural evolution overtook biological evolution. Civilizations, the arts, and science all developed. Man today governs the globe thanks to industrial inventions from about 200 years ago.
Importance of Maharashtra Board textbook solutions for Class 10 Biology Heredity and Evolution
The Chapter 1 of the Class 10 syllabus of Biology for the Maharashtra Board, Heredity and Evolution, is quite crucial. The chapter discusses all the important topics . They also get to learn the formulas and its application in real life.
1. Access to Solutions by Experts: Getting guidance and learning from experts who have curated the answers that focus on learning standards specific to the age group. It also provides well explained and easy to understand solutions for a student.
2. Beneficial for Resolving Doubts: Sometimes, questions asked in the chapter become challenging to comprehend, especially for students who find Biology difficult. The textbook solutions can present them with elaborative and comprehensive answers or solutions which will benefit them in case of doubts.
3. Learning Through Mistakes: When a student is trying to solve a question, it is often observed that they get the correct answers but do not follow the proper method. In such cases, textbook solutions can help them understand the experts' approach, which they can use while finding the answers.
4. Practice with the Right Approach: Practicing the questions by following correct methods and techniques becomes significant for a student. These practice questions become the building blocks for their further question-solving practice. Hence, it is crucial to solving many questions based on a concept with the right approach.
Benefits of using Vedantus' PDF Solutions for Class 10 Biology Maharashtra Board
The solutions for Class 10 Chapter 1 for the Maharashtra Board Students have been created by Vedantu experts. With amplified knowledge about the concepts, they have left no detail unexplained in the chapter. Students can use elaborate explanations, examples, etc., to gain further understanding of the chapter.
Solutions for Heredity and Evolution will help students understand how to solve complex problems related to the chapter. These solutions have been explained in a way that is easy to comprehend for students.
They can prepare properly for their examinations by solving the problems with the help of the solutions. All details about different ways to solve Heredity and Evolution have been explained. Students can build a strong foundation for the chapter with these solutions.
During revision, these solutions and practice sets can come in handy to revisit anything when you are having doubts about your answers.
Complete Your Practice With Maharashtra Board Class 10 Biology Chapter 1 Solutions
Download Maharashtra board Class 10 Biology solutions Chapter 1 Heredity and Evolution and start your practice today. With time, you can download more practice sets and solutions to strengthen your problem solving.





































