
A potential divider consists of two resistors of resistances \[{{R}_{1}}\] and \[{{R}_{2}}\]connected in series across a source of potential difference \[{{V}_{in}}\]. The potential difference across \[{{R}_{1}}\] is \[{{V}_{out}}\]. Which charges to \[{{R}_{1}}\And {{R}_{2}}\]will increase the value of \[{{V}_{out}}\]?
\[{{R}_{1}}\] \[{{R}_{2}}\] A- Doubled Doubled B- Doubled Halved C- Halved Doubled D- Halved halved
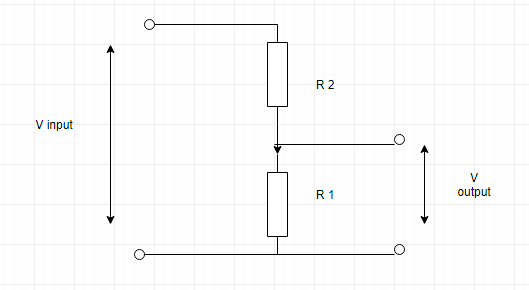
| \[{{R}_{1}}\] | \[{{R}_{2}}\] |
| A- Doubled | Doubled |
| B- Doubled | Halved |
| C- Halved | Doubled |
| D- Halved | halved |

Answer
570.9k+ views
Hint: A potential divider is a simple circuit that uses resistors or a combination of resistors to supply a variable potential difference as per the need of the output circuit. In this circuit both the given resistances are in series combination but the output is obtained only across the first resistor.
Complete step by step answer:
As per the given question, potential difference across the given resistor can be found by using ohm’s law. The total resistance of the circuit is \[{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}\] and the input voltage fed to the circuit is \[{{V}_{in}}\].
$ {{V}_{in}}=I({{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}) \\ $
$\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{{{V}_{in}}}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}} \\ $
Now, again using ohm’s law to find the potential difference across first resistor,
$ V=I{{R}_{1}} \\ $
$ \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{{{V}_{in}}{{R}_{1}}}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}} \\ $
We can see that the output voltage is directly proportional to the value of first resistor, thus we can write as
$ \Rightarrow {{V}_{out}}\propto {{R}_{1}} \\ $
$\therefore {{V}_{out}}\propto \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}} \\ $
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Ohm’s law holds for all ohmic conductors and it is one of the most important laws in electricity and magnetism. The combination was in series so we directly added the two resistances, had they been in parallel combination we would have to add them in another way as we use to add the resistances in parallel combination.
Complete step by step answer:
As per the given question, potential difference across the given resistor can be found by using ohm’s law. The total resistance of the circuit is \[{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}\] and the input voltage fed to the circuit is \[{{V}_{in}}\].
$ {{V}_{in}}=I({{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}) \\ $
$\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{{{V}_{in}}}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}} \\ $
Now, again using ohm’s law to find the potential difference across first resistor,
$ V=I{{R}_{1}} \\ $
$ \Rightarrow V=\dfrac{{{V}_{in}}{{R}_{1}}}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}} \\ $
We can see that the output voltage is directly proportional to the value of first resistor, thus we can write as
$ \Rightarrow {{V}_{out}}\propto {{R}_{1}} \\ $
$\therefore {{V}_{out}}\propto \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}} \\ $
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Ohm’s law holds for all ohmic conductors and it is one of the most important laws in electricity and magnetism. The combination was in series so we directly added the two resistances, had they been in parallel combination we would have to add them in another way as we use to add the resistances in parallel combination.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




