
A vicinal diol has two alcoholic groups present:
A.on the same carbon
B.on adjacent carbon
C.anywhere along with the carbon
D.none of the above
Answer
232.5k+ views
Hint: We know that there are two types of groups one is vicinal and one is a geminal diol. One group has two hydroxyl groups on the same carbon and the other has two hydroxyl groups on different carbon.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the vicinal meaning is adjacent or neighboring.
Let us see the example of vicinal diol:
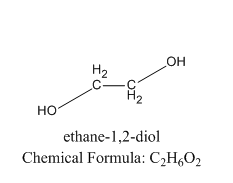
As we can see that the two alcoholic groups are present on the adjacent carbon in vicinal diol.
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option B.
Additional Information:
Let us see the structure of geminal diol to understand the difference between vicinal alcohol and geminal alcohol.
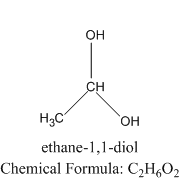
As we can see that the two alcoholic groups are present on the same carbon in geminal diol.
We know that in a vicinal diol, the two hydroxyl groups occupy neighboring positions, that is, they are attached to adjacent atoms and these compounds are called glycols. Examples include 1,2-ethanediol or ethylene glycol \[HO - {(C{H_2})_2} - OH\], a common ingredient of antifreeze products. Another example is propane-1,2-diol, or alpha propylene glycol, \[HO - C{H_2} - CH\left( {OH} \right) - C{H_3}\], used in the food and medicine industry, as well as a relatively non-poisonous antifreeze product.
We most know that on commercial scales, the main route to vicinal diols is the hydrolysis of epoxides and the epoxides are prepared by epoxidation of the alkene.
Note: We can get confused between the vicinal and geminal alcohol and we must know the placement of the alcoholic group on the adjacent carbon atom and same carbon atom respectively. So, option A and option C can be neglected.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the vicinal meaning is adjacent or neighboring.
Let us see the example of vicinal diol:

As we can see that the two alcoholic groups are present on the adjacent carbon in vicinal diol.
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option B.
Additional Information:
Let us see the structure of geminal diol to understand the difference between vicinal alcohol and geminal alcohol.

As we can see that the two alcoholic groups are present on the same carbon in geminal diol.
We know that in a vicinal diol, the two hydroxyl groups occupy neighboring positions, that is, they are attached to adjacent atoms and these compounds are called glycols. Examples include 1,2-ethanediol or ethylene glycol \[HO - {(C{H_2})_2} - OH\], a common ingredient of antifreeze products. Another example is propane-1,2-diol, or alpha propylene glycol, \[HO - C{H_2} - CH\left( {OH} \right) - C{H_3}\], used in the food and medicine industry, as well as a relatively non-poisonous antifreeze product.
We most know that on commercial scales, the main route to vicinal diols is the hydrolysis of epoxides and the epoxides are prepared by epoxidation of the alkene.
Note: We can get confused between the vicinal and geminal alcohol and we must know the placement of the alcoholic group on the adjacent carbon atom and same carbon atom respectively. So, option A and option C can be neglected.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




