
Highest ionization potential in a period is shown by:
(A) Alkali metals
(B) Transition elements
(C) Halogens
(D) Noble gases
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The closer and more tightly bound an electron is to the nucleus, the more difficult it will be to remove and higher will be its ionization potential. The ionization potential or ionization energy decreases from top to bottom in groups and increases from left to right across a period.
Complete step by step solution:
The ionization energy or ionization energy of an atom is the amount of energy that is required to remove an electron from a mole of atoms in the gas phase. In a periodic table, the ionization potential decreases from top to bottom in groups while it increases when crossing from right to left in a period. It can be understood by the image shown below,
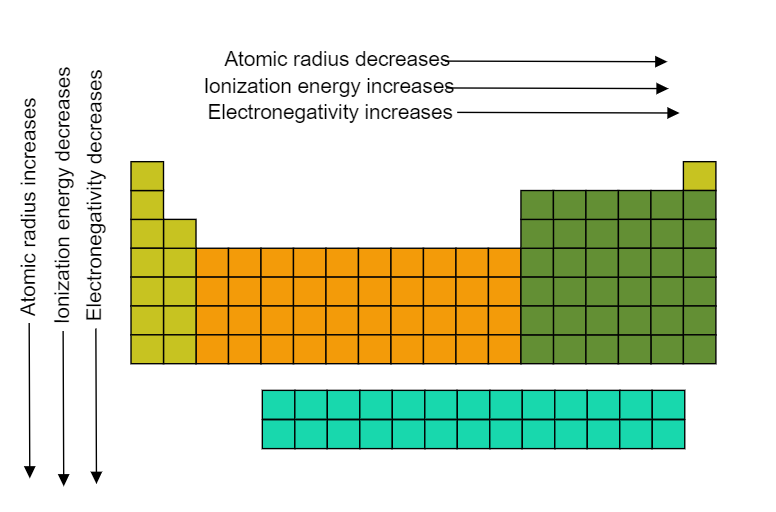
So, the groups further to the right of the periodic table would have greater ionization potential because they are more stable and they do not want to donate its electrons to other atoms and also there is the greater number of protons (positively charged) that attracts the electrons (negatively charged) which are present in the outer shell thereby requiring more energy to remove an electron from the shell.
Thus, concluding noble gases to be having the highest ionization potential. This is shown by the noble gases because an electron is to be removed from a completely filled orbital which further breaks the stable electronic configuration ns2np6 requiring a large amount of energy.
Hence, the correct option will be (D).
Note: Technically the noble gases have the largest ionization potential, but since they are special and it is not often seen that electrons would even be removed from these elements as they rarely react with other elements, you would usually get confused with halogens having the largest ionization potential as they are present before the noble gases in a period in the periodic table.
Complete step by step solution:
The ionization energy or ionization energy of an atom is the amount of energy that is required to remove an electron from a mole of atoms in the gas phase. In a periodic table, the ionization potential decreases from top to bottom in groups while it increases when crossing from right to left in a period. It can be understood by the image shown below,

So, the groups further to the right of the periodic table would have greater ionization potential because they are more stable and they do not want to donate its electrons to other atoms and also there is the greater number of protons (positively charged) that attracts the electrons (negatively charged) which are present in the outer shell thereby requiring more energy to remove an electron from the shell.
Thus, concluding noble gases to be having the highest ionization potential. This is shown by the noble gases because an electron is to be removed from a completely filled orbital which further breaks the stable electronic configuration ns2np6 requiring a large amount of energy.
Hence, the correct option will be (D).
Note: Technically the noble gases have the largest ionization potential, but since they are special and it is not often seen that electrons would even be removed from these elements as they rarely react with other elements, you would usually get confused with halogens having the largest ionization potential as they are present before the noble gases in a period in the periodic table.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




