
Hunsdiecker reaction is first notated by _ _ _ _ _ _ in 1961.
A.Borodin
B.Hunsdiecker
C.Clare
D. None of these
Answer
593.1k+ views
HintHunsdiecker reaction is a decarboxylation and halogenation reaction in which silver salts of carboxylic acids are used to form alkyl halides by reacting them with a halogen.
Complete step by step answer
-Hunsdiecker reaction is also known as Borodin reaction.
-It is a name reaction where the silver salts of carboxylic acids are reacted with a halogen to produce an organic halide. In this reaction both decarboxylation (removal of $C{O_2}$) and halogenations (addition of halogen) takes place at the same time.
This reaction is as follows:
$RCO{O^ - }A{g^ + }\xrightarrow[{CC{l_4}}]{{B{r_2}}}R - Br$
-In 1861, Alexander Borodin was the first one to demonstrate this reaction, when he prepared methyl bromide ($C{H_3}Br$) using silver acetate ($C{H_3}CO{O^ - }A{g^ + }$).
$C{H_3}COOAg + B{r_2} \to C{H_3}Br + C{O_2} + AgBr$
But now it is known as Hunsdiecker reaction because this process was developed into a general method for preparation of organic halide by Clare Hunsdiecker and her husband Heinz Hunsdiecker.
-We can say that this is a decarboxylation reaction because the product has 1 less carbon in it as compared to the parent molecules and a carbon dioxide molecule is released. Since a halogen atom is added to it, it is a halogenations reaction.
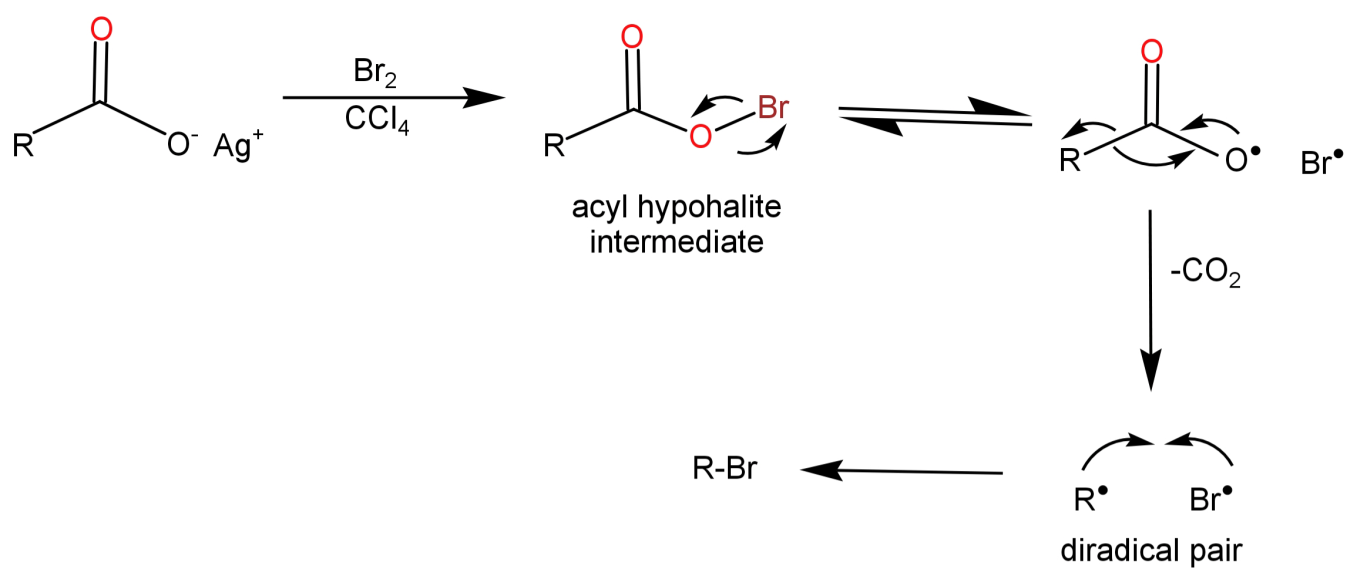
-In this reaction radical intermediates are formed. When the silver salt of carboxylic acid reacts with bromine an acyl hypohalite intermediate is formed. Then the O and Br in this hypohalite intermediate leave each other keeping their own electrons to themselves to form a diradical pair. This is followed by decarboxylation resulting in the formation of R free radical (${R^ \bullet }$) and Br free radical ($B{r^ \bullet }$), which combine quickly with each other to form alkyl halide.
This mechanism is shown below:
So, the correct option is: (A) Borodin.
Note:
Although the reaction is named after Hunsdiecker, they were not the first one to demonstrate this reaction. They made it a general reaction but it was first demonstrated by Borodin. Also if we take carboxylate to iodine (as a halide) ratio of 1:1 then we obtain alkyl halide as product, but if we take them in a ratio of 2:1 we obtain an ester product and for a 3:1 ratio we obtain a mixture of both alkyl halide and an ester.
Complete step by step answer
-Hunsdiecker reaction is also known as Borodin reaction.
-It is a name reaction where the silver salts of carboxylic acids are reacted with a halogen to produce an organic halide. In this reaction both decarboxylation (removal of $C{O_2}$) and halogenations (addition of halogen) takes place at the same time.
This reaction is as follows:
$RCO{O^ - }A{g^ + }\xrightarrow[{CC{l_4}}]{{B{r_2}}}R - Br$
-In 1861, Alexander Borodin was the first one to demonstrate this reaction, when he prepared methyl bromide ($C{H_3}Br$) using silver acetate ($C{H_3}CO{O^ - }A{g^ + }$).
$C{H_3}COOAg + B{r_2} \to C{H_3}Br + C{O_2} + AgBr$
But now it is known as Hunsdiecker reaction because this process was developed into a general method for preparation of organic halide by Clare Hunsdiecker and her husband Heinz Hunsdiecker.
-We can say that this is a decarboxylation reaction because the product has 1 less carbon in it as compared to the parent molecules and a carbon dioxide molecule is released. Since a halogen atom is added to it, it is a halogenations reaction.
-In this reaction radical intermediates are formed. When the silver salt of carboxylic acid reacts with bromine an acyl hypohalite intermediate is formed. Then the O and Br in this hypohalite intermediate leave each other keeping their own electrons to themselves to form a diradical pair. This is followed by decarboxylation resulting in the formation of R free radical (${R^ \bullet }$) and Br free radical ($B{r^ \bullet }$), which combine quickly with each other to form alkyl halide.
This mechanism is shown below:

So, the correct option is: (A) Borodin.
Note:
Although the reaction is named after Hunsdiecker, they were not the first one to demonstrate this reaction. They made it a general reaction but it was first demonstrated by Borodin. Also if we take carboxylate to iodine (as a halide) ratio of 1:1 then we obtain alkyl halide as product, but if we take them in a ratio of 2:1 we obtain an ester product and for a 3:1 ratio we obtain a mixture of both alkyl halide and an ester.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




