
We feel blinded for a short while entering a dark room when coming from bright light. Why?
Answer
570.9k+ views
Hint: There are five senses that are associated with human beings. These senses are the sense of sight, hearing, smelling, touching, and tasting. Here we will concentrate on the sense of sight, and the organ related to this sense is the eye.
Complete answer:
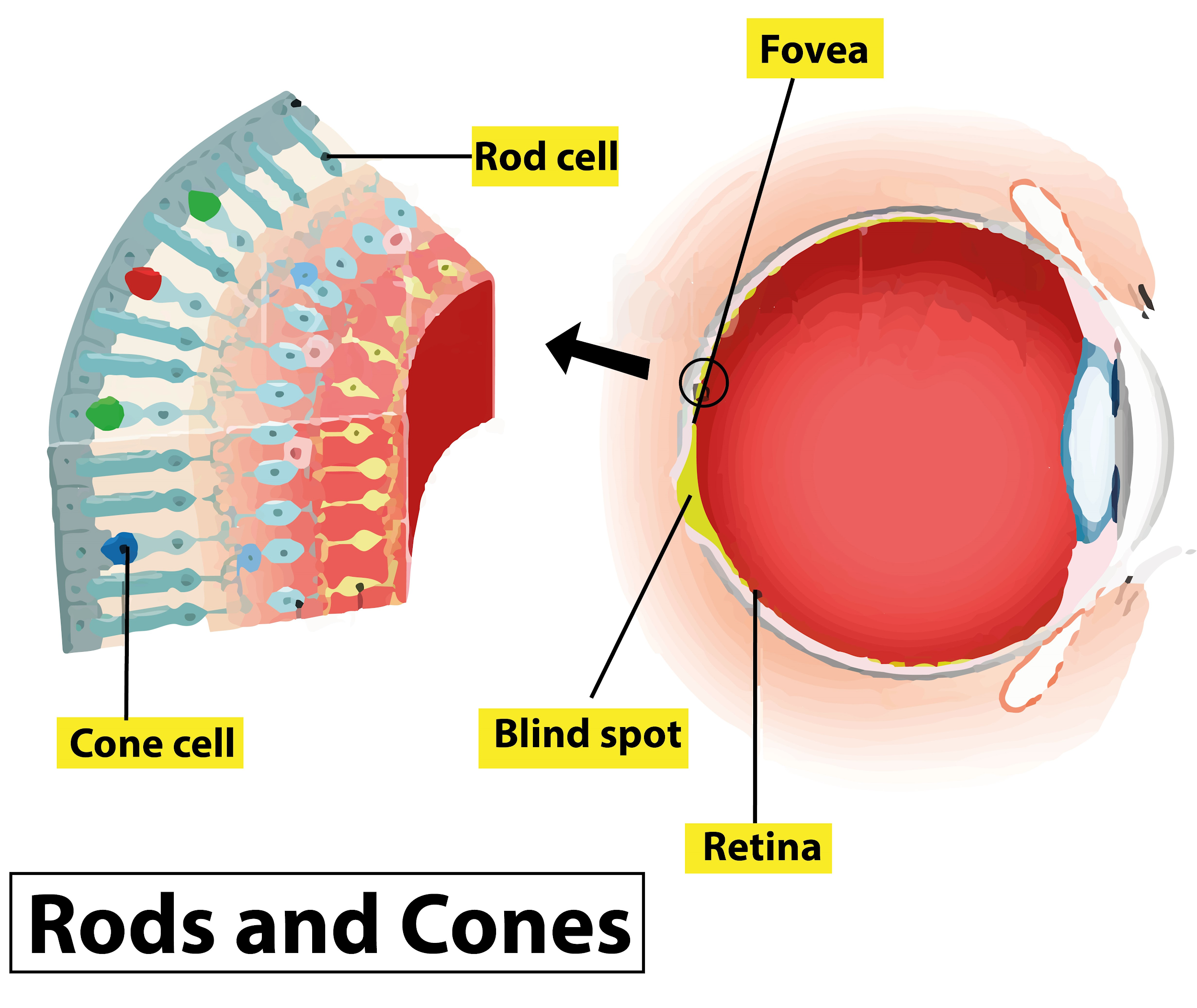
The eye muscles contain rods and cones, which enables a person to see in dim and bright light. When we were standing in bright light the muscles of the iris contract and the pupils constrict so that less light can pass into the eye. Then after moving from that bright area when we move into a dark room, the eyes need time to adjust and the iris muscles need time to dilate the pupils so that more light can enter the eye. So the duration of time taken by our eyes to adjust the eye to the received amount of light, that duration makes us feel blind. This is also called dark adaptation.
Additional Information: -The dark adaptation is a two-branched function; one for the cone receptors and the other for the rods.
-The receptors contain photopigments in their outer segment. When light is absorbed by these photopigments they undergo certain changes that stop them from helping to send visual signals to the brain.
-When the rod photopigments (rhodopsin) are exposed to light they undergo a process called bleaching. It is termed as bleaching because the photopigment color actually becomes almost transparent.
-Under bright light, all of our highly light-sensitive rod cells are bleached. Only cone cells remain to feed visual sensory information to our brain that is visual phototransduction.
-When you enter a dark environment, those cone cells are not very useful.
-They gradually become more sensitive to try to compensate, but this time our rod cells only work, which are the primary source of night vision that will unbleached and take over.
Note: -Rhodopsin is the technical name for the rod photopigment.
-When exposed to bright light the photopigments actually become almost transparent this is known as bleaching of photopigments.
-When exposed to light the photopigments in the cones also bleach.
Complete answer:
The eye muscles contain rods and cones, which enables a person to see in dim and bright light. When we were standing in bright light the muscles of the iris contract and the pupils constrict so that less light can pass into the eye. Then after moving from that bright area when we move into a dark room, the eyes need time to adjust and the iris muscles need time to dilate the pupils so that more light can enter the eye. So the duration of time taken by our eyes to adjust the eye to the received amount of light, that duration makes us feel blind. This is also called dark adaptation.
Additional Information: -The dark adaptation is a two-branched function; one for the cone receptors and the other for the rods.
-The receptors contain photopigments in their outer segment. When light is absorbed by these photopigments they undergo certain changes that stop them from helping to send visual signals to the brain.
-When the rod photopigments (rhodopsin) are exposed to light they undergo a process called bleaching. It is termed as bleaching because the photopigment color actually becomes almost transparent.
-Under bright light, all of our highly light-sensitive rod cells are bleached. Only cone cells remain to feed visual sensory information to our brain that is visual phototransduction.
-When you enter a dark environment, those cone cells are not very useful.
-They gradually become more sensitive to try to compensate, but this time our rod cells only work, which are the primary source of night vision that will unbleached and take over.
Note: -Rhodopsin is the technical name for the rod photopigment.
-When exposed to bright light the photopigments actually become almost transparent this is known as bleaching of photopigments.
-When exposed to light the photopigments in the cones also bleach.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




