




An Overview of Class 11 Chemistry Study Of The Shift Of Equilibrium Between Ferric Ions And Thiocyanate Ions By Increasing The Concentration Of Either Of Them Experiment
Concentration highly affects the shifting of equilibrium. Chemical equilibrium will shift or move towards the reactant when the concentration of the product increases, less product is formed and the concentration of the reactant increases as the concentration of the product decreases.
Some daily life examples of equilibrium are: A book kept on a desk at rest, a car moving on the road at a constant velocity, and also a chemical reaction where the rate of the forward reaction is exactly equal to the rate of the backward reaction. And in ionic equilibrium, the ionic substance dissociates into its constituent ions in the polar solvents.
Table of Content
Aim
Apparatus Required
Theory
Procedure
Observation
Result
Precautions
Lab Manual Questions
Viva Questions
Practical Based Questions
Aim
To study the shift of equilibrium between ferric ions and thiocyanate ions by increasing the concentration of either of them.
Materials Required
Test tubes
Test tube stand
Glass rod
Droppers
Beakers
Weight box
Measuring cylinders
Measuring flask
Ferric chloride (0.1 M)
Potassium thiocyanate (0.1 M)
Potassium chloride (0.1 M)
Theory
1. Effect of Increasing Concentration of Ferric Ions
When ferric chloride solution is added to the red solution containing ferric ions, thiocyanate ions and ferric-thiocyanate complex, the concentration of ferric ions increases, and therefore, the concentration of thiocyanate ions should decrease or that of [Fe(SCN)]2+ should increase to keep concentration quotient equal to the equilibrium constant at a given temperature. Therefore, an increase in the concentration of ferric ions results in more thiocyanate ions combining with ferric ions to give more of [Fe(SCN)]2+ complex, and therefore, the colour intensity of red-solution increases. Thus, an increase in the concentration of Fe3+ ions shifts the above equilibrium in the forward direction.
2. Effect of Increasing Concentration of Thiocyanate Ions
Since the thiocyanate ion is in the denominator in the equilibrium law equation, the addition of more and more of thiocyanate results in more ferric ions reacting with thiocyanate ions to give more of [Fe(SCN)]2+ complex. Hence, the colour intensity of red-solution increases. Thus, an increase in the concentration of SCN- ions shifts the above equilibrium in the forward direction.
3. Effect of Increasing the Concentration of Potassium Ions
An increase in the concentration of K+ ions shifts the equilibrium in the backward direction. This results in a decrease in the concentration of SCN- ions, which in turn shifts the equilibrium in the backward direction. In other words, some [Fe(SCN)]2+ complex dissociates to give Fe3+ ions and SCN- ions. Due to a decrease in the concentration of [Fe(SCN)]2+, the intensity of the red colour decreases. Thus, an increase in the concentration of K+ ions shifts the above equilibrium in the backward direction.
Procedure
Take a 250 ml (measure) beaker thoroughly or properly washed and cleaned.
Put 10 ml of 0.1 M FeCl3 solution (s) in it by using a measuring cylinder.
Add 10 ml of 0.1 M KSCN solution by using or with the help of a measuring cylinder.
A deep red colour is obtained or produced due to complex formation [Fe(SCN)]2+ (aq).
Dilute the above deep red solution by mixing or adding 50 ml of distilled water.
Take four test tubes and name or label them as A, B, C, and D. Add or mix 10 ml of the deep red solution to each of the four test tubes.
Arrange or place the test tubes in a test tube stand.
Add or mix 5 ml of distilled water to test tube labelled A; 5 ml of 0.1M FeCl3 solution to test tube labelled B; 5 ml of 0.1 M KSCN solution to test tube labelled C and 5 ml of 0.1 M KCl solution to test tube D.
Shake or mix all the tubes well.
Now compare the intensity (darkness) of the colours in test tubes, B, C, and D with the red colour in test tube A taken as a reference tube.
The intensity (darkness) of the red colour corresponds to the concentration (c) of the complex [Fe(SCN)]2+ and if the concentration (amount) of this ion increases, the colour intensity (darkness) will also increase.
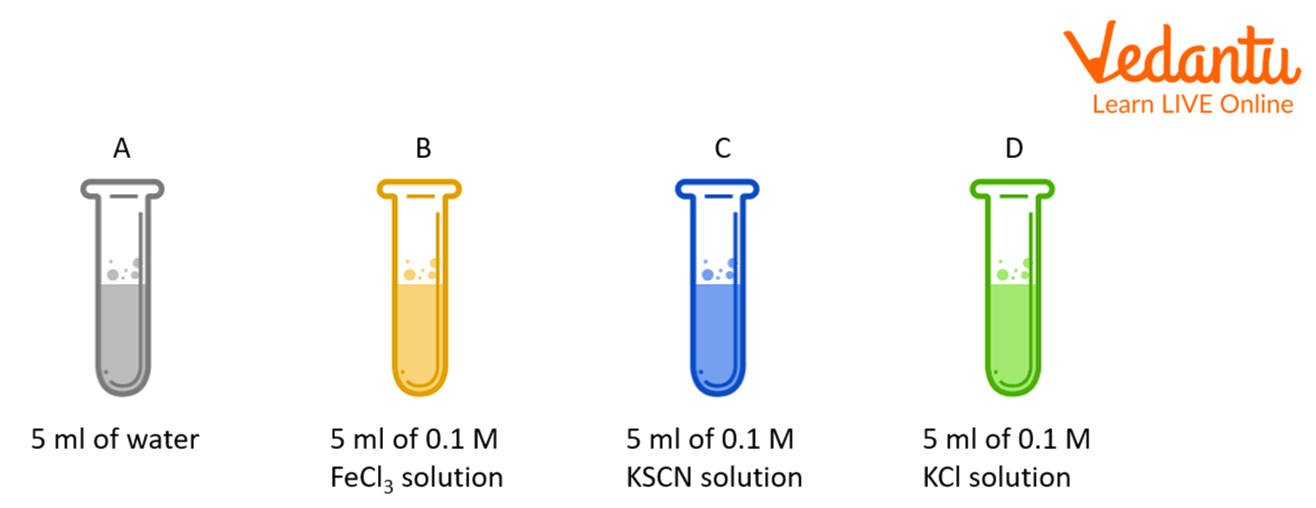
The Process of the Shift in Equilibrium between Ferric Ions and Thiocyanate Ions
Observations
The Process of the shift in Equilibrium between Ferric Ions and Thiocyanate Ions
Result
An increase in the concentration of either of the reactants (Fe3+ ions or SCN- ions) shifts the equilibrium in the right or forward direction.
A decrease in the concentration of the reactants shifts the equilibrium towards the left or in the backward direction.
Precautions
Use tubes of almost identical diameter.
Dilute solutions of thiocyanate should be used.
The intensity of the colour of a solution should be compared by keeping it and reference side by side and then observing from the top.
Lab Manual Questions
1. What is a thiocyanate ion?
Ans: Thiocyanate is a pseudohalide anion obtained by deprotonation of the thiol group of thiocyanic acid.
2. What is potassium sulphocyanide?
Ans: Potassium sulphocyanide or potassium thiocyanate is one of the known chemical compounds with the molecular formula KSCN. It is a potassium salt, which is the monopotassium salt of thiocyanic acid.
3. What is the colour of ferrous ions?
Ans: Ferrous ions have a light green colour.
4. What is the colour of ferric thiocyanate?
Ans: The colour of ferric thiocyanate is red.
Viva Questions
1. Define a reversible reaction.
Ans: The reaction in which the products formed react back to give the reactant molecules is called a reversible reaction.
2. State the law of chemical equilibrium.
Ans: For a reversible reaction in equilibrium, the product of the molar concentration of products, divided by the product of the molar concentrations of the reactants, each concentration raised to the power equal to its coefficients is constant at a particular temperature. This constant is called the equilibrium constant.
3. What is chemical equilibrium?
Ans: In a chemical reaction when the rate of the forward reaction becomes equal to the rate of the backward reaction, that state is known as a chemical equilibrium.
4. How does the concentration of reactants affect the equilibrium?
Ans: If the concentration of the reactants is increased, the equilibrium shifts in the forward direction.
5. Does the constancy of colour intensity indicate the dynamic nature of equilibrium? Explain your answer with appropriate reasons.
Ans: No, because the colour would become constant even if the reaction stops altogether at equilibrium.
6. Does temperature affect equilibrium?
Ans: Yes.
7. What will be the effect of increasing the temperature of the reaction mixture at equilibrium?
Ans: On increasing the temperature, the equilibrium shifts in favour of the endothermic direction.
8. What is the colour of [Co (H2O)6]2+ ions?
Ans: Pink.
9. What is the formula of the complex ion formed when a solution containing [Co (H2O)6]2+ ions is treated with hydrochloric acid?
Ans: [CoCl4]2-
Practical Questions
In a reversible chemical reaction at equilibrium, if the concentration of any one of the reactants is doubled, then the equilibrium constant will
Be doubled
Become one-fourth
Be halved
Remain the same
Ans: The equilibrium constant will remain the same.
When a neutral atom undergoes oxidation, the atom's oxidation state
Decreases as it loses electrons
Increases as it gains electrons
Decreases as it gains electrons
Increases as it loses electrons
Ans: Increases as it loses electrons.
If a system is at equilibrium, the rate of forwarding to the reverse reaction is
Less
High
Equal
none
Ans: If a system is at equilibrium, the rate of forward-to-reverse reaction is equal.
On doubling P and V with constant temperature, the equilibrium constant will
Become double
Remain constant
Become one-fourth
none
Ans: The equilibrium constant will remain constant.
What happens when an inert gas is added to an equilibrium, keeping volume unchanged?
Less product will form
More products will form
More reactants will form
Equilibrium will remain unchanged
Ans: When an inert gas is added to an equilibrium keeping volume unchanged, more product will form.
What is the formula of potassium sulphocyanide?
K2SO4
KSCN
KCN
none
Ans: KSCN is the formula of potassium sulphocyanide.
What is the colour of ferric thiocyanate?
Red
Blue
Green
yellow
Ans: The colour of ferric thiocyanate is red.
What is the colour of ferrous ions?
Dark red
Light green
Black
None
Ans: The colour of ferrous ions is light green.
An aqueous solution of sodium cyanide is
Acidic
Basic
Neutral
Amphoteric
Ans: An aqueous solution of sodium cyanide is basic.
Conclusion
From the above experiment, we can conclude that the increase in the concentration of either of the reactants (Fe3+ ions or SCN- ions) shifts the equilibrium in the forward direction (towards the right); on the other hand, a decrease in the concentration of the reactants shifts the equilibrium in the backward direction (towards left).
FAQs on Class 11 Chemistry Study Of The Shift Of Equilibrium Between Ferric Ions And Thiocyanate Ions By Increasing The Concentration Of Either Of Them Experiment
1. What is the fundamental principle demonstrated in the Class 11 experiment involving ferric ions and thiocyanate ions?
This important experiment for the CBSE 2025-26 syllabus demonstrates Le Chatelier's Principle. It states that if a change in concentration, temperature, or pressure is applied to a system at equilibrium, the system will shift in a direction that counteracts the change to re-establish a new equilibrium.
2. For 2 marks, write the balanced net ionic equation for the equilibrium between ferric ions and thiocyanate ions and state the colours of the key species involved.
The balanced net ionic equation for this reversible reaction is:
Fe³⁺(aq) + SCN⁻(aq) ⇌ [Fe(SCN)]²⁺(aq)
The colours of the ions are as follows:
- Fe³⁺ (ferric ion): Pale yellow
- SCN⁻ (thiocyanate ion): Colourless
- [Fe(SCN)]²⁺ (ferric thiocyanate ion): Blood-red
3. What observable change is expected when more ferric chloride (FeCl₃) is added to the equilibrium mixture? Explain this shift based on Le Chatelier's Principle.
When more ferric chloride is added, the concentration of ferric ions (Fe³⁺) increases. According to Le Chatelier's Principle, the system will counteract this stress by consuming the added Fe³⁺ ions. This causes the equilibrium to shift to the right (forward direction). The expected observable change is the intensification of the blood-red colour due to the formation of more [Fe(SCN)]²⁺ complex ions.
4. What are two key precautions a student must take while performing the experiment on equilibrium shifts between ferric and thiocyanate ions for the practical exam?
Two important precautions for this experiment are:
- Use very dilute solutions of both ferric chloride and potassium thiocyanate. If the initial solution is too dark, the subsequent colour changes upon shifting the equilibrium will not be clearly visible.
- Handle chemicals like ferric chloride carefully, as it is corrosive. Always add reactants slowly and mix thoroughly to ensure the change is uniform and properly observed.
5. How can the equilibrium in the ferric-thiocyanate reaction be forced to shift in the backward direction? Describe a method and the expected visual result.
To shift the equilibrium backward, you must decrease the concentration of a reactant. A common method is to add a substance that removes Fe³⁺ ions from the solution. For instance, adding a few drops of oxalic acid (H₂C₂O₄). The oxalate ions form a stable, colourless complex with Fe³⁺ ions, reducing their concentration. This causes the equilibrium to shift to the left (backward direction) to replenish the Fe³⁺ ions, leading to the fading of the blood-red colour, making the solution appear more yellow or even colourless.
6. Why is it so important to establish an initial equilibrium mixture that is not too dark red in colour?
It is crucial to start with a moderately coloured solution to ensure that any changes are easily observable. If the initial solution is too dark, the equilibrium is already positioned far to the right. This makes it very difficult to visually detect a further intensification of colour when a forward shift is induced. Similarly, a very pale initial solution would make it hard to notice the fading of colour during a backward shift. A medium intensity allows for clear observation of shifts in both directions, which is a key objective of this important experiment.
7. What is a likely Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) question for 3 marks related to the ferric-thiocyanate equilibrium?
A typical HOTS question could be: "If a small amount of solid KCl (potassium chloride) is added to the blood-red equilibrium mixture, what effect will it have on the position of the equilibrium and the colour of the solution? Justify your answer."
Answer: Adding KCl, an inert electrolyte, does not change the molar concentration of the reacting species (Fe³⁺ or SCN⁻). Therefore, according to Le Chatelier's principle, it will have no significant effect on the position of the equilibrium. The intensity of the blood-red colour will remain unchanged.
8. How does a change in temperature affect the ferric-thiocyanate equilibrium, and what does this imply about the reaction's enthalpy?
The formation of the [Fe(SCN)]²⁺ complex is an exothermic reaction (ΔH is negative). Based on Le Chatelier's Principle:
- Increasing the temperature (e.g., in a hot water bath) adds heat, causing the equilibrium to shift left to absorb the heat. The blood-red colour fades.
- Decreasing the temperature (e.g., in an ice bath) removes heat, causing the equilibrium to shift right to produce more heat. The blood-red colour intensifies.
























