Open Economy Macroeconomics Class 12 Extra Questions and Answers Free PDF Download


FAQs on CBSE Important Questions for Class 12 Economics Open Economy Macroeconomics - 2025-26
1. What are the most expected 3-mark and 5-mark important questions in CBSE Class 12 Macro-Economics Chapter 6: Open Economy Macroeconomics for 2025–26?
Key questions tend to focus on balance of payments (BOP), distinguishing between fixed and flexible exchange rates, sources of foreign exchange, and the impact of currency appreciation or depreciation. Application-based problems involving BOP deficit/surplus and scenario-based analysis of foreign exchange rate changes often appear as 3-mark or 5-mark questions in board exams.
2. How should students structure answers for high-weightage questions on exchange rates and balance of payments in board exams?
To score well on 5-mark or HOTS questions, start with precise definitions, illustrate with suitable examples or diagrams, and conclude with implications or differences. Use headings such as 'Definition', 'Example', and 'Conclusion' for clarity. For distinctions or merits/demerits, use comparative tables or bulleted points for better organization.
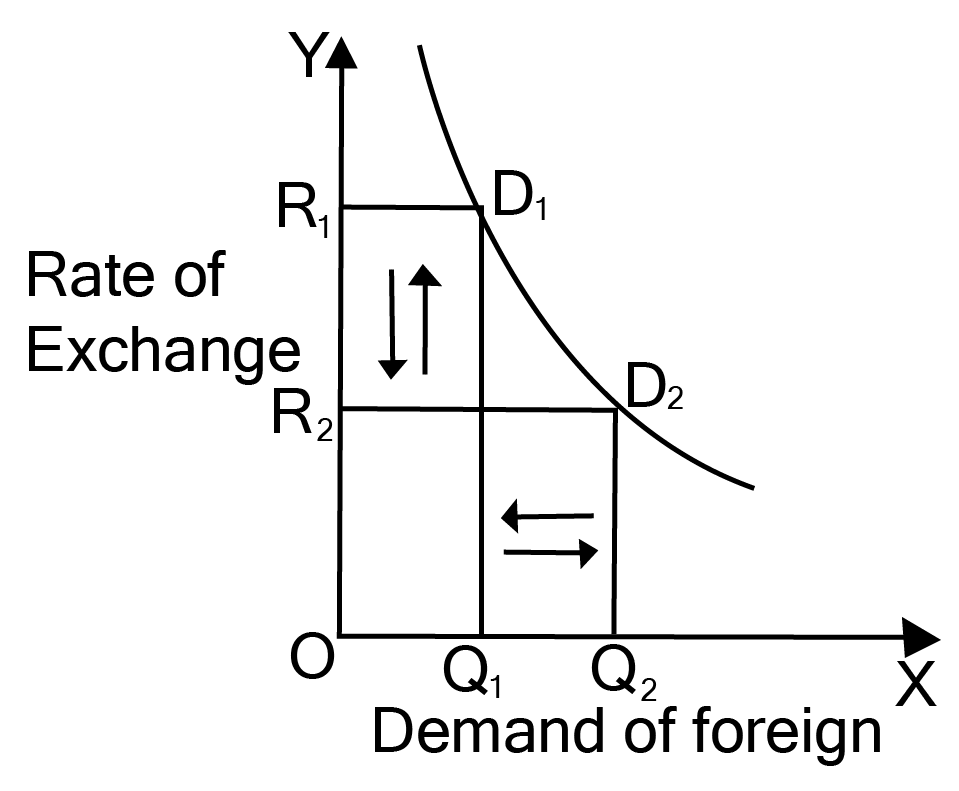
3. Why does the demand for foreign currency generally rise when its price falls?
When the foreign exchange rate declines (i.e., the domestic currency appreciates), imports become cheaper for domestic consumers. This leads to:
- Increased demand for imported goods and services
- More domestic tourists able to afford foreign travel
- Businesses finding foreign machinery or technology less expensive
This increased purchasing triggers higher demand for foreign currency in the market.
4. What are the main sources of demand and supply of foreign exchange as per CBSE board trends?
Sources of supply include:
- Exports of goods and services
- Foreign direct investment (FDI) and portfolio investments
- Foreign tourists spending domestically
- Remittances received from abroad
- Imports of goods and services
- Indian citizens investing overseas
- Payment of interest or dividends abroad
- Indian tourists traveling internationally
5. What distinguishes autonomous from accommodating transactions in the Balance of Payments, and why is this distinction important for 5-mark answers?
Autonomous transactions (above the line) occur for economic motives like trade or investment and directly influence the BOP balance. Accommodating transactions (below the line) are undertaken to finance imbalances from autonomous flows—such as borrowing or using reserves. Correctly differentiating these helps avoid marks loss in analytical questions.
6. How do examiners typically assess application-based knowledge about BOP deficits or surpluses in board papers?
Students are often given scenarios—for example, where payments exceed receipts in India's BOP—and asked to:
- Calculate deficit or surplus with provided figures
- Identify economic causes and consequences
- Suggest corrective measures, such as RBI interventions or policy changes
Strong answers link causes, calculation, and policy responses clearly.
7. What is a managed floating exchange rate and how is it different from other exchange rate systems?
A managed floating exchange rate combines elements of both fixed and flexible systems. The central bank intervenes periodically to stabilize or influence the rate, but does not maintain a strict peg. By contrast, fixed rates are government-set and flexible rates are purely market-driven without official intervention.
8. How can a prolonged BOP deficit affect India's economy, and what topics are likely to be tested around this?
A prolonged BOP deficit may lead to:
- Depletion of foreign exchange reserves
- Pressure on currency value (depreciation of the rupee)
- Inevitability of borrowing or seeking foreign aid
Boards may ask students to analyze these effects, link to case studies, or connect with policy interventions by authorities like RBI.
9. What are the most common conceptual traps for students answering 5-mark questions related to open economy macroeconomics?
Common traps include:
- Confusing Balance of Trade (BOT) with Balance of Payments (BOP)
- Omitting the inverse relationship between exchange rate and foreign currency demand
- Misclassifying transactions as autonomous/accommodating based on account type instead of economic motive
- Ignoring implications of currency appreciation/depreciation on exports and imports
10. What strategies can help students prioritize and revise important questions for Chapter 6 effectively before the CBSE board exams?
Effective strategies include:
- Practicing previous years’ important questions and board trends
- Creating summary tables for differences (e.g., fixed vs flexible exchange rate, BOT vs BOP)
- Focusing on source-based HOTS questions
- Time-managing long answer practice and peer-discussion of scenario questions
11. How can the RBI intervene if the Indian rupee is rapidly depreciating, and why are such interventions emphasized in important board questions?
The RBI may:
- Sell foreign exchange reserves (like US dollars) to buy rupees and support its value
- Implement capital controls or alter interest rates to stabilize the market
Such interventions are exam-relevant because they directly relate to policy-level impacts on BOP and currency stability, a recurring theme in high-weightage board questions.
12. Compare two key merits and two demerits of the fixed exchange rate system as per the Class 12 syllabus.
Merits:
- Ensures stability in international prices
- Reduces uncertainty for traders and investors
- Limits flexibility of monetary policy
- Contradicts objectives of a free market system
13. In what ways is distinguishing between Balance of Trade and Balance of Payments critical for scoring in Class 12 Economics?
Being accurate allows students to answer both objective and long-answer questions effectively. The Balance of Trade reflects only goods exported and imported, while Balance of Payments is broader, covering goods, services, capital and transfer payments. Examiners look for precise and comprehensive distinctions in these areas.
14. What is meant by appreciation of currency, and how does it influence a country's exports?
Currency appreciation is an increase in the value of the domestic currency relative to others. This makes exports more expensive for foreign buyers, potentially reducing demand for the country’s goods abroad and impacting its trade balance.
15. How does understanding autonomous and accommodating transactions help in evaluating a country’s BOP position in high-order application questions?
Recognizing these transaction types enables students to analyze the factors creating BOP deficits or surpluses and to explain how governments address imbalances. Such insights are essential for scoring full marks in application and reasoning-based board questions.