Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Questions And Answers With Solutions
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure Of The Atom (2025-26)
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure Of The Atom (2025-26)
1. What are the three subatomic particles of an atom?
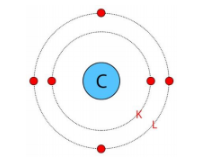
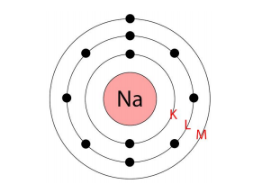
The three fundamental subatomic particles are protons (positively charged), neutrons (no charge), and electrons (negatively charged). Protons and neutrons are located in the atom's nucleus, while electrons revolve around the nucleus in distinct orbits or shells.
2. What was the major limitation of Rutherford's model of the atom?
Rutherford's model could not explain the stability of an atom. According to his model, an electron revolving in a circular orbit would undergo acceleration and radiate energy, eventually falling into the nucleus. This does not happen in stable atoms.
3. Where can I find the Structure of the Atom Class 9 questions and answers PDF?
You can download a Free PDF of the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 4 from the Vedantu website. This file contains solved answers for all exercise questions, allowing you to study the chapter offline at your convenience.
4. What is the difference between atomic number and mass number?
The atomic number (Z) is the number of protons in an atom's nucleus, defining the element. The mass number (A) is the total count of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. It represents the approximate mass of the atom.
5. What are valence electrons?
Valence electrons are the electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom. These electrons determine the chemical properties of an element, as they are the ones that participate in forming chemical bonds with other atoms.
6. How do Class 9 Science Chapter 4 NCERT Solutions help with exam preparation?
The NCERT Solutions for this chapter provide step-by-step explanations for every question. Practising with these solutions helps students understand the correct answering format, manage time effectively, and revise all key concepts before exams, ensuring better performance.
7. What are isotopes and isobars?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same atomic number but different mass numbers. Isobars are atoms of different elements having different atomic numbers but the same mass number.
8. What is covered in the NCERT Solution for Class 9 Science Chapter 4?
The NCERT Solution for Class 9 Science Chapter 4 covers all in-text and exercise questions. It provides detailed answers on atomic models, subatomic particles, valency, electronic configuration, atomic number, and mass number, aligning with the latest syllabus.
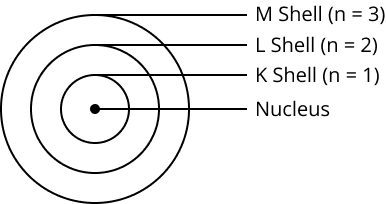
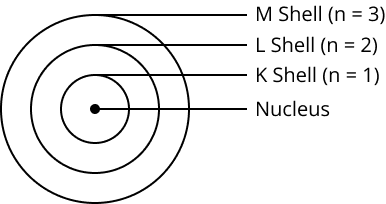
9. How did Bohr's model of the atom explain its stability?
Bohr's model proposed that electrons revolve in discrete, stable orbits called energy levels or shells. While in these specific orbits, electrons do not radiate energy. This postulate successfully explained the stability of the atom, a key drawback of Rutherford's model.
10. Are the Class 9 Science Chapter 4 question answers provided by Vedantu accurate?
Yes, all Class 9 Science Chapter 4 question answers are prepared by subject experts at Vedantu. The solutions are fact-checked and structured to be precise, easy to understand, and aligned with the NCERT curriculum and CBSE guidelines.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video