NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology - Microbes in Human Welfare - Free PDF Download
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 - Microbes in Human Welfare solved by expert Biology teachers on Vedantu.com as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter 10 - Microbes in Human Welfare exercise questions with solutions to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Access NCERT Exemplar Solutions for CBSE Class 12 Science (Biology) Chapter 10 - Microbes in Human Welfare
Multiple-Choice Questions
1. The vitamin whose content increases following the conversion of milk into curd by lactic acid bacteria is
a. vitamin C
b. vitamin D
c. vitamin B12
d. vitamin E.
Ans: Option (c) is the answer. Lactic acid bacteria are used to transform milk into curd. Lactic acid bacteria and casein combine to produce this reaction. The bacteria employ enzymes to manufacture energy from ATP during this process, which also boosts the nutritional value of the food by raising vitamin B12 concentration.
2. Wastewater treatment generates a large quantity of sludge, which can be treated by:
a. anaerobic digesters
b. floc
c. chemicals
d. oxidation pond.
Ans: Option (a) is the answer. During secondary treatment, a large amount of activated sludge is generated, which is utilized as an inoculum. A small portion of this sludge is piped back to the massive aeration tanks, while the rest is treated anaerobically using anaerobic sludge digesters. Bacteria generate a combination of gases known as biogas during this digestion.
3. Methanogenic bacteria are not found in:
a. rumen of cattle
b. gobar gas plant
c. bottom of water-logged paddy fields
d. activated sludge
Ans: Option (d) is the answer. Inactivated sludge, methanogenic bacteria (bacteria that create methane) are not detected. Microorganisms that produce methane are anaerobic bacteria. Aerobic bacteria that proliferate quickly are seen in activated sludge microorganisms.
4. Match the following list of bacteria and their commercially important products:
Bacterium | Product |
A. Aspergillus niger | i. Lactic acid |
B. Acetobacter acetic | ii. Butyric acid |
C. Clostridium bretylium | iii. Acetic acid |
D. Lactobacillus | iv. Citric acid |
Choose the correct match:
a. A-ii, B-iii, C-iv, D-i
b. A-ii, B-iv, C-iii, D-i
c. A-iv, B-iii, C-ii, D-i
d. A-iv, B-i, C-iii, D-ii
Ans: Option (c) is the answer.
Bacterium | Product |
(i) Aspergillus niger | (D) Citric acid |
(ii) Acetobacter aceti | (C) Acetic acid |
(iii) Clostridium butylicum | (B) Butyric acid |
(iv) Lactobacillus | (A) Lactic acid |
5. Match the following list of bioactive substances and their roles:
Bioactive Substance | Role |
A. Statin | i. Removal of oil stains |
B. Cyclosporin A | ii. Removal of clots from blood vessels |
C. Streptokinase | iii. Lowering of blood cholesterol |
D. Lipase | iv. Immuno-suppressive agent |
Choose the correct match:
a. A-ii, B-iii, C-i, D-iv
b. A-iv, B-ii, C-i, D-iii
c. A-iv, B-i, C-ii, D-iii
d. A-iii, B-iv, C-ii, D-i
Ans: Option (d) is the answer
Bioactive Substance | Role |
(i) Statin | (C) Statins produced by yeast Monascus purpureus and used as a blood cholesterol lowering agents. |
(ii) Cyclosporin A | (D) It is used as an immunosuppressive agents produced by fungus Trichoderma polysporum. |
(iii) Streptokinase | (B) It is produced by bacteria Streptococcus and used as clot bluster for removing clots from blood vessels of patients which undergo myocardial infarction leading to heart attack. |
(iv) Lipase | (A) used in detergent formulations and remove oil stains from the laundry. |
6. The primary treatment of wastewater involves the removal of:
a. dissolved impurities
b. stable particles
c. toxic substances
d. harmful bacteria.
Ans: Option (b) is the answer. Filtration and sedimentation are used in the initial treatment to physically remove particles from the sewage. These are removed first by sequential filtering, which eliminates floating debris, and then by sedimentation, which removes grit.
7. BOD of wastewater is estimated by measuring the amount of:
a. total organic matter
b. biodegradable organic matter
c. oxygen evolution
d. oxygen consumption.
Ans: Option (d) is the answer. The quantity of oxygen consumed when all the organic matter in one litre is oxidized by bacteria is known as biological oxygen demand (BOD). Thus, the quantity of oxygen used is used to calculate the BOD of wastewater.
8. Which one of the following alcoholic drinks are produced without distillation?
a. Wine
b. Whisky
c. Rum
d. Brandy
Ans: Option (a) is the answer. Wine is an alcoholic drink produced without distillation whereas whisky, rum, and brandy are produced by the distillation of the fermented broth. The alcoholic drinks are formed either by distillation or without distillation depending on the type of raw material used for fermentation.
9. The technology of biogas production from cow dung was developed in India largely due to the efforts of:
a. Gas Authority of India
b. Oil and Natural Gas Commission
c. Indian Agricultural Research Institute and Khadi & Village Industries Commission
d. Indian Oil Corporation
Ans: Option (c) is the answer. The technology of biogas production from cow dung was developed in India largely due to the efforts of the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) and Khadi & Village Industries Commission (KVIC).
10. The free-living fungus Trichoderma can be used for:
a. killing insects
b. biological control of plant diseases
c. controlling butterfly caterpillars
d. producing antibiotics
Ans: Option (b) is the answer. The fungus Trichoderma is a biological control being developed for use in the treatment of plant disease. Trichoderma fungi are free-living fungi found in abundance in root habitats.
11. What would happen if oxygen availability to activated sludge flocs is reduced?
a. It will slow down the rate of degradation of organic matter
b. The centre of flocs will become anoxic, which would cause the death of bacteria and eventually breakage of flocs.
c. Flocs would increase in size as anaerobic bacteria would grow around flocs.
d. Protozoa would grow in large numbers
Ans: Option (b) is the answer. Flocs are bacterial swarms that bind together with fungal filaments to produce a mesh-like structure. The rate of breakdown of organic materials in activated sludge flocs will be slowed if oxygen availability is restricted. As the centre of the flocs becomes anoxic, the bacterial cells die, resulting in floc rupture.
12. Mycorrhiza does not help the host plant in:
a. Enhancing its phosphorus uptake capacity
b. Increasing its tolerance to drought
c. Enhancing its resistance to root pathogens
d. Increasing its resistance to insects.
Ans: Option (d) is the answer. Mycorrhizae aids the host plant in increasing its phosphorus absorption capability and drought tolerance. Mycorrhiza generates compounds that protect against pathogens such as Fusarium. As a result, the correct answer is 'increasing its insect resistance.'
13. Which one of the following is not a nitrogen-fixing organism?
a. Anabaena
b. Nostoc
c. Azotobacter
d. Pseudomonas
Ans: Option (d) is the answer. Pseudomonas is a bacterium that does not fix nitrogen. Pseudomonas is a bacterium that lives in the soil as a saprophyte. Pseudomonas is utilized to degrade organic pollutants such as petroleum spills.
14. Big holes in Swiss cheese are made by a:
a. a machine
b. a bacterium that produces methane gas
c. a bacterium producing a large amount of carbon dioxide
d. a fungus that releases a lot of gases during its metabolic activities.
Ans: Option (c) is the answer. During fermentation, a bacteria called Propionibacterium sharmanii creates a lot of carbon dioxide. This is why Swiss cheese has many holes.
15. The residue left after methane production from cattle dung is:
a. burnt
b. buried in landfills
c. used as manure
d. used in civil construction.
Ans: Option (c) is the answer. The residue left after methane production from cattle dung is used as manure. Biogas is a methane-rich fuel gas generated by anaerobic digestion of biomass using methanogenic bacteria.
16. Methanogens do not produce:
a. oxygen
b. methane
c. hydrogen sulfide
d. carbon dioxide.
Ans: Option (a) is the answer. Methanogens are obligate anaerobes, meaning that they create methane, hydrogen sulphide, and carbon dioxide but not oxygen.
17. Activated sludge should have the ability to settle quickly so that it can:
a. be rapidly pumped back from sedimentation tank to aeration tank
b. absorb pathogenic bacteria present in wastewater while sinking
to the bottom of the settling tank
c. be discarded and anaerobically digested
d. absorb colloidal organic matter.
Ans: Option (a) is the answer. To be pumped back to the aeration tank, the activated sludge must settle quickly. 'Be rapidly pumped back from the sedimentation tank to the aeration tank' is the proper choice.
18. Match the items in Columns ‘A’ and Column ‘B’ and choose the correct answer.
Column I | Column II |
A. Ladybird | i. Methane bacterium |
B. Mycorrhiza | ii. Trichoderma |
C. Biological control | iii. Aphids |
D. Biogas | iv. Glomus |
The correct answer is:
a. A-ii, B-iv, C-iii, D-i
b. A-iii, B-iv, C-ii, D-i
c. A-iv, B-i, C-ii, D-iii
d. A-iii, B-ii, C-i, D-iv
Ans: Option (b) is the answer. The ladybird beetle is a biological pest control agent for aphids. Glomus is a genus of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus that creates a mycorrhizal symbiotic association with plant roots. Trichoderma is a biological control agent used to combat pathogenic fungus of several species. Biogas is made up of methane, which is produced by methanobacterium.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
1. Why does ‘Swiss cheese’ have big holes?
Ans: The big holes in ‘swiss cheese’ are made by a bacterium known as Penicillium Sherman which consumes the lactose protein in the cheese to form lactic acid
2. What are fermentors?
Ans: Fermentors are large vessels that are used for the commercial production of fermented products. It is used for fermentation by growing microorganisms.
3. Name a microbe used for statin production. How do statins lower blood cholesterol levels?
Ans: A microbe that is used in the production of statin is Monascus purpureus. Statins function by reducing the rate at which LDL cholesterol is produced in the liver. Because your liver isn't producing as much cholesterol, it absorbs cholesterol from your blood to utilize in the production of bile, lowering your blood cholesterol levels.
4. Why do we prefer to call secondary wastewater treatment a biological treatment?
Ans: Secondary wastewater treatment is more commonly referred to as biological treatment since it includes the employment of microorganisms to treat wastewater.
5. What Nucleopolyhydro viruses are being used nowadays?
Ans: Nucleopolyhydroviruses (NPVs) are currently being utilized as a biological insecticide to kill insects that cause harm to plants and crops, such as caterpillars and butterflies.
6. How has the discovery of antibiotics helped mankind in the field of medicine?
Ans: Antibiotics were discovered to aid humans in the realm of medicine by offering resistance to bacterial illnesses.
7. Why is distillation required for producing certain alcoholic drinks?
Ans: Distillation is required for producing certain alcoholic drinks because it increases the overall alcohol content in alcoholic drinks.
8. Write the most important characteristic that Aspergillus niger, Clostridium bretylium, and Lactobacillus share.
Ans: The most important characteristic that Aspergillus niger, Clostridium butylicum, and Lactobacillus share are that they all are micro-organisms that are involved in the production of various acids. Aspergillus niger is used for the production of citric acid, Clostridium butylicum is used for the production of butyric acid, and Lactobacillus is used for the production of lactic acid.
9. What would happen if our intestine harbours microbial flora exactly similar to that found in the rumen of cattle?
Ans: If our intestine harbours microbial flora exactly similar to that found in the rumen of cattle then our digestive system would be able to digest cellulose and methane can be produced in our digestive system.
10. Give any two microbes that are useful in biotechnology.
Ans: E. Coli and agrobacterium are the two microbes that are useful in biotechnology.
11. What is the source organism for ECORI, restriction endonuclease?
Ans: ECORI's source organism is Escherichia coli restriction endonucleases (e.g., E.Coli). It's a rod-shaped, gram-negative bacterium found in the intestines of warm-blooded mammals.
12. Name any genetically modified crop.
Ans: Bt cotton is a genetically modified (GM) crop that produces an insecticide that makes the plant resistant to bollworm.
13. Why are blue-green algae not popular as biofertilizers?
Ans: Blue-green algae are not widely used as biofertilizers because they create a slippery mucus and induce an algal bloom.
14. Which species of Penicillium produces Roquefort cheese?
Ans: The species of Penicillium that produces Roquefort cheese is Penicillium roqueforti.
15. Name the states involved in the Ganga action plan.
Ans: The states which are involved in the Ganga action plan are Jharkhand, UP, Bihar, West Bengal.
16. Name any two industrially important enzymes.
Ans: The two industrially important enzymes are-
i) Lipase: It is used for the removal of oily stains from clothes and it is used widely in detergents.
ii) Amylase: It is used in the food and fermentation industry.
17. Name an immune immunosuppressive agent?
Ans: Cyclosporin A is an immune-suppressive agent produced by the Trichodermapolysporum fungus.
18. Give an example of a rod-shaped virus.
Ans: An example of the rod-shaped virus is the Tobacco Mosaic virus which causes a disease known as a mosaic disease in tobacco leaves
19. What is the group of bacteria found in both the rumen of cattle and the stage of sewage treatment?
Ans: Methanogens are the group of bacteria found in both the rumen of cattle and sludge of sewage treatment. Methanogens release methane gas.
20. Name a microbe used for the production of Swiss cheese.
Ans: A microbe that is used for the production of Swiss cheese is Penicillium sherman which consumes the lactose protein in the cheese to form lactic acid
Short Answer Type Questions
1. Why are flocs important in the biological treatment of wastewater?
Ans: Flocs are crucial in biological wastewater treatment because they aid to lower biological oxygen demand (B.O.D) in the water, making it less polluted and livable for aquatic species, as well as reducing pathogens and decomposing organic waste.
2. How has the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis helped us in controlling caterpillars of insect pests?
Ans: The bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis aids in the management of insect pest caterpillars by creating an endotoxin in the caterpillar's midgut when it is consumed by the pest. The endotoxin discharged will kill the insects' midgut lining.
3. How do mycorrhizal fungi help the plants harbouring them?
Ans: Mycorrhiza is a fungus that aids plants in taking additional nutrients from the soil, such as phosphorus, and transferring them to the host plant. This also aids ion in pulling more water from the soil, allowing plants to better endure environmental circumstances such as drought.
4. Why are cyanobacteria considered useful in paddy fields?
Ans: Cyanobacteria are thought to be beneficial in rice fields because they fix nitrogen from the air and provide organic matter, which improves soil fertility.
5. How was penicillin discovered?
Ans: Alexander Fleming discovered penicillin by accident in 1921. When he returned from a trip, he discovered that one of his staphylococcus culture plates had been infected with mold. The mold stopped staphylococcus culture from growing. As a result, he came to the conclusion that the antibiotic was isolated from the fungus Penicillium notatum.
6. Name the scientists who were credited for showing the role of Penicillin as an antibiotic?
Ans: Alexander Fleming discovered penicillin in 1921 but he was not credited for showing its role as an antibiotic.
7. How do bioactive molecules of fungal origin help in restoring good health of humans?
Ans: As a variety of bioactive molecules are important in the medical treatment of people, bioactive molecules of fungal origin aid in the restoration of human health.
a) A statin is a drug that helps to decrease cholesterol levels in the blood.
b) Cyclosporin A, an immunosuppressive medication.
c) Lipase is an enzyme that digests lipids in our digestive system as well as removes oil stains.
8. What roles do enzymes play in detergents that we use for washing clothes? Are these enzymes produced from some unique microorganisms?
Ans: Enzymes such as lipases are employed in detergent formulas to stimulate oil breakdown and so aid in the removal of oily and greasy stains from laundry clothing. Candida lipolytica and Geotrichum candidum are used to make these.
9. What is the chemical nature of biogas? Name an organism which is involved in biogas production?
Ans: Biogas is made up of three different gases. Methane (\[CH_{3}\]) makes up roughly 60-70 percent of the overall volume, carbon dioxide (\[CO_{2}\]) makes up about 30-40 percent, and hydrogen sulphide makes up about 0.1 percent. The organisms involved in biogas generation are known as methanogens.
10. How do microbes reduce the environmental degradation caused by chemicals?
Ans: Microbes aid in the reduction of chemical-induced environmental damage. Agriculture is a good example of bioremediation. Bio fertilizers are made up of bacteria that enrich the soil by removing nitrogen from the air. Pesticides that produce an endotoxin that is absorbed by the bug and destroys the midgut lining are also used to kill pests.
11. What is a broad-spectrum antibiotic? Name one such antibiotic.
Ans: Broad-spectrum antibiotics are a class of antibiotics that can be used for treating multiple bacterial infections. An example of such an antibiotic is Ampicillin.
12. What are viruses parasitizing bacteria called? Draw a well-labeled diagram of the same.
Ans: The viruses parasitizing are known as bacteriophages.
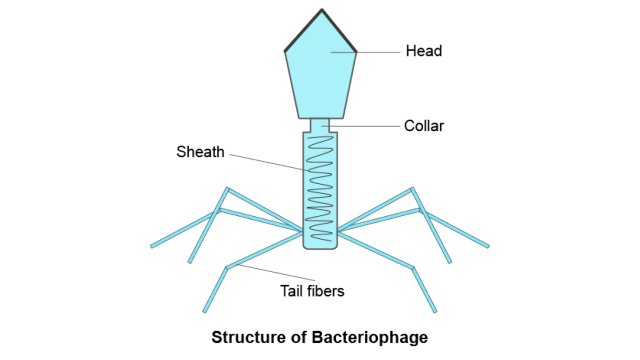
13. Which bacterium has been used as a clot-buster? What is its mode of action?
Ans: Bacterium Streptococcus produces an enzyme known as streptokinase is widely used as an anti-clotting agent. It can break down clots and prevent clot associated diseases like heart attacks.
14. What are biofertilizers? Give two examples.
Ans: Biofertilizers are used to enrich the soil by boosting the nutrient content, which aids in the general development and growth of the plants. Rhizobium and nostoc are examples of biofertilizers.
Long Answer Type Questions
1. Why is aerobic degradation more important than anaerobic degradation for the treatment of large volumes of wastewaters rich in organic matter? Discuss.
Ans: Aerobic degradation is more significant than anaerobic degradation for the treatment of large volumes of organic-rich wastewaters because:
i) The majority of the organic sludge is digested in the wastewater during aerobic degradation.
ii) The decomposers are removed from the organic waste, which is rich in nutrients, after aerobic decomposition.
iii) During aerobic degradation, the biological oxygen demand (BOD) is lowered, making the water more favorable for aquatic species.
iv) Activated sludge is formed during aerobic decomposition, which creates gases such as methane and carbon dioxide, which are the major components of biogas.
2. (a) Discuss the major programs that the Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India, has initiated for saving major Indian rivers from pollution.
Ans: (a) The Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India has initiated two plAns:
i. Ganga Action Plan
ii. Yamuna Action Plan
These plans were planned to involve a large number of sewage treatment plants. Ganga and Yamuna are very important rivers in terms of flora, fauna and as a tourist and religious attraction spot.
(b) Ganga has recently been declared the national river. Discuss the implication with respect to the pollution of this river.
Ans: (b) The Ganga is India's greatest river, flowing across India and Bangladesh for around 2520 kilometres and providing home for more than 140 different species of fish, 90 different species of frogs, and numerous endangered species. As a result, the Ganga is considered the world's greatest river and must be pollution-free.
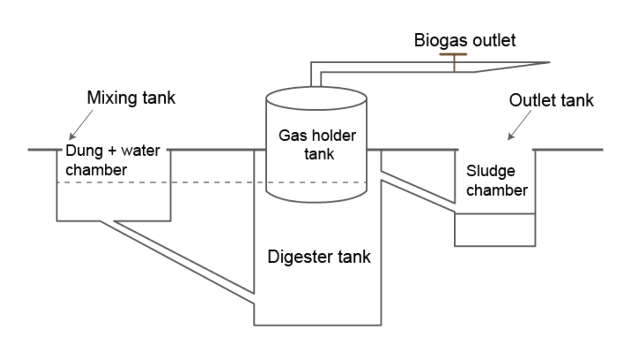
3. Draw a diagrammatic sketch of the biogas plant, and label its various components given below: Gas Holder, Sludge Chamber, Digester, Dung + water chamber.
Ans:
4. Describe the main ideas behind the biological control of pests and diseases.
Ans:
The primary concepts underlying biological pest and disease control are to reduce the population of pests by introducing natural predators into the ecosystem.
Examples are:
i) The Ladybird beetle is used to control the population of insects like Aphids.
ii. Nucleopolyhydro viruses (NPVs) are being used to kill insects such as caterpillars and butterflies which damage the plants and crops. This virus will damage the insect’s midguts.
5. (a) What would happen if a large volume of untreated sewage is discharged into a river?
Ans: The Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) will increase, resulting in the mortality of species like fish owing to a lack of oxygen in the water. As people drink water directly from the river, illnesses like cholera and dysentery will spread.
(b) In what way anaerobic sludge digestion is important in sewage treatments?
Ans: Anaerobic sludge digestion is important in sewage treatment because it reduces Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD). Sludge digestion occurs in the presence of anaerobic bacteria, and when the sludge is digested, the anaerobic bacteria release a mixture of gases such as methane (\[CH_{3}\]), carbon dioxide (\[CO_{2}\]), and hydrogen sulphide (\[H_{2}S\]). Biogas is made up mostly of these components.
6. Which type of food would have lactic acid bacteria? Discuss their useful application.
Ans: Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) is widely used to ferment or culture food products. Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) are found in curd. Its useful applications are:
i) Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) is a type of bacteria that can convert milk into curd by producing an enzyme called lactase.
ii) Some people will suffer from a condition called lactose tolerance which gets allergic to lactose. So the bacteria will help to remove or convert lactose.
iii) Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) increase the vitamin B12 content and they are present in our digestive system also.
NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology - Microbes in Human Welfare
Biology is one of the fundamental subjects for Class 12 students, especially those who want to get into the medical field. The Class 12 Biology consists of numerous Chapters that cover important topics and concepts that are vital for the education of students. If the students are preparing for the Class 12 Biology Exam then they must make it a point to study the NCERT Exemplar with solutions for a more in-depth study of the different concepts.
The NCERT Exemplar with solutions from Vedantu provides a comprehensive solution set with detailed answers and excellent as well as lucid explanations for the answers. This helps the students to learn about the different concepts more comprehensively and thus prepares them for tackling the different types and difficulties of questions that they are likely to face in the Exam.
Vedantu is one of the most trusted and reliable platforms for online learning resources for students. Vedantu provides wide-ranging resources including reference books, sample exercises, important formulae, practice questions, solved question papers, and related content. So if you are preparing for the Class 12 Biology Exam then it makes sense to refer to NCERT Exemplar solutions based on individual Chapters.
The students can find Chapter-wise solutions for the different topics that are included in the Class 12 Biology syllabus at Vedantu. The solution sets for the different Chapters are available in the form of PDF files which can be downloaded on your personal device. Once you have downloaded the file you can access it anytime based on your convenience.
The Benefits of Referring to NCERT Exemplar Solutions from Vedantu
At Vedantu you can find a comprehensive collection of solution sets for all the Chapters of specific subjects. While the NCERT textbook solutions educate about the basic concepts, the NCERT Exemplar includes more complex questions that further helps in developing an in-depth understanding of the Chapters.
The NCERT Exemplar solutions from Vedantu include detailed explanations and graphical illustrations wherever necessary.
The lucid explanations combined with accurate answers ensure that students get access to the best resource for learning about the different Chapters and subjects.
The easy access to the solution set via the PDF and incredibly responsive user interface means Vedantu is one of the most widely used platforms for different solution sets including the NCERT Exemplar solutions.
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology Chapter-10 (Book Solutions)
1. Why should I refer to the NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 from Vedantu?
The NCERT Exemplar solutions provide more in-depth knowledge of the concepts and help students with the polishing of their concepts. The NCERT Exemplar includes trickier questions with higher difficulty levels than the textbooks and referring to these solutions equips the students with the essential knowledge for scoring well in the Exams. The Exemplar questions are considered HOTS, which means higher order of thinking skills.
2. What are the different Chapters included in the NCERT Class 12 Biology solutions?
The NCERT Class 12 Biology solutions includes important and relevant Chapters that are important for the education of medical students. Some of the major Chapters and topics included in the book for Class 12 includes ‘Reproduction in organisms’, ‘Sexual reproduction in flowering plants’, ‘Human Reproduction’, ‘Reproductive health’, and ‘Microbes in human welfare’ amongst others. These Chapters provide a comprehensive education in different biological topics which is important in both Exams and future professional setup.
3. How can I download the NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 solutions from Vedantu?
If you want to access the NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 solutions from Vedantu then it is very simple. You need to go to the specific section on the Vedantu app or website and then click on the “Download PDF” option. Once the file is downloaded on your device, it can be accessed offline anytime based on your convenience.
4. How should I approach learning the NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10?
Before you proceed and refer to the NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10, you must be clear in your concepts and have a basic understanding of the Chapter that you have learned from the textbook. If you directly jump to the exemplar solution then learning can be difficult since these questions are built on the basic concepts and include more complex questions. Once you have learnt the basic concepts you can then proceed to study the NCERT Exemplar solutions from Vedantu.
5. What is the major difference between textbook solutions and NCERT Exemplar solutions?
The NCERT Exemplar solutions include questions that are based on the fundamental concepts that are included in the textbook. The textbook solutions provide a basic version of the specific Chapter and the NCERT Exemplar builds on that concept to provide a more complex set of solutions. This helps the students to develop an in-depth understanding of the topic which is beneficial in the Exams.

























