




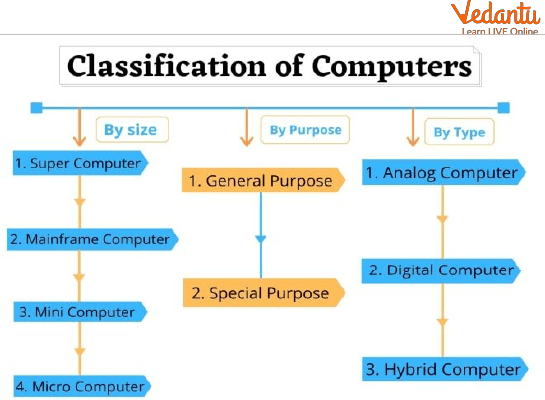
Types of Computers
A computer is a tool that turns raw data into information that can be used. It processes the input in accordance with the set of instructions the user provides it and produces the intended result. There are many different kinds of computers, and they may be divided into two groups based on their size and their ability to handle data.
There are therefore five different sorts of computers based on size:
Supercomputer
Mainframe Computer
Minicomputer
Workstation
PC (Personal Computer)
Additionally, there are three different kinds of computers based on their ability to handle data:
Analogue Computer
Digital Computer
Hybrid computer
Classification of Computers
Classification of Computers
Based on Operations:
According to fundamental operating principles, there are three different kinds of computers. They are as follows:
1. Analogous Computers
Analog data is processed by analog computers. Examples of this kind of data include temperature, pressure, weight, depth, and voltage. These are continuous quantities with an unlimited range of values.
The early computers were analog, and they served as the foundation for the creation of current digital computers.

Analogous Computers
2. Digital Computers
Digits are used in digital computers to represent letters, numbers, and other unique symbols. Digital computers use inputs that are of the ON-OFF kind, and they also produce signals that are of the ON-OFF variety.
Typically, an ON is denoted by a 1 and an OFF is denoted by a 0. Both numerical and non-numerical data may be processed by a digital computer. It can carry out logical operations in addition to basic arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.

Digital Computer
3. Hybrid Computers
Digital and analogue computers are combined to create hybrid computers. It has the speed of an analogue computer and the memory and precision of a digital computer, combining the best aspects of both types. In specialized applications where both types of data need to be handled, hybrid computers are mostly employed.For instance, a gas pump has a processor that transforms measurements of fuel flow into quality and pricing data.

Hybrid Computer
Classification According to Configuration
There are four different sorts of computers based on how they are configured to operate.
1. Supercomputers
Supercomputer
Supercomputers are the most effective computers in terms of performance and data processing. These computers are employed for investigational and research reasons. Supercomputers are both incredibly costly and very big. It can only fit in big rooms with air conditioning.
Supercomputers are employed in a variety of applications, including nuclear weapons testing, earthquake research, and space exploration.
Supercomputer Features
They make use of AI (Artificial intelligence).
They are the fastest and strongest.
They are very costly.
They are enormous in size.
They are employed by companies that manufacture goods.
They process information at a rapid rate.
2. Mainframe Computers

Mainframe Computers
Despite the fact that mainframe computers are less powerful than supercomputers, they are nevertheless fairly pricey. Mainframe computers are widely used by big businesses and government agencies to manage daily operations. They have the capacity to analyze and store plenty of data. They are used by banks, colleges, and insurance businesses to keep information about their clients, students, and insurance policyholders. They are also capable of serving as a server in a network setting. They may also manage hundreds of users at once.
Mainframe Computer Features
They have enormous amounts of memory.
They are capable of running several different operating systems.
They have a significant number of CPUs with powerful processing speeds.
Tightly Coupled Clustering Technology is employed.
3. Minicomputers

Mini Computer
Small companies and enterprises employ minicomputers. They go by the name "Midrange Computers." Often these minicomputers are multi-user systems, much like mainframe computers. Compared to mainframe computers, they are a tad slower.
Minicomputers can be used, for instance, by the manufacturing department to monitor certain production procedures.
Features of Minicomputers:
It is smaller than mainframes or supercomputers in terms of size.
In comparison to a mainframe or supercomputer, it is less costly.
It is able to perform many jobs at once.
It may be utilized by several users simultaneously.
It is utilized by small businesses.
4. Microcomputers

Micro Computer
A microcomputer, sometimes known as a PC, is a computer that operates on a smaller scale than conventional computers (Personal Computer). Its central processing unit (CPU), a microprocessor, memory in the format of RAM (Read Only Memory) and ROM (Random Access Memory), I/O ports, and a bus system of linking cables are all contained in a component that is typically referred to as a motherboard. They are the least expensive of all.
Features of Microcomputers:
They are extensively employed for personal usage.
They are smaller and comparably less expensive.
Multi-user functionality is not supported.
It has a limited computational capacity.
They are quite simple to use.
Things to Remember
The term "generation" refers to a shift in the technology that is applied to computers.
The advent of the first computer generation occurred with the invention of the storage medium.
A different generation of computers is referred to as each stage of computer development.
There are many different kinds of computers, and they may be divided into two groups based on their size and their ability to handle data.
Digits are used in digital computers to represent letters, numbers, and other unique symbols.
Digital and analogue computers are combined to create hybrid computers.
Super computers are the most effective computers in terms of performance and data processing.
Mainframe computers are widely used by big businesses and government agencies to manage daily operations.
A microcomputer, sometimes known as a PC, is a computer that operates on a smaller scale than conventional computers (Personal Computer).
In addition, there are three distinct categories of computers according to how well they can manage data: Digital computer, hybrid computer, analogue computer
Solved Questions
1. Give a brief history of Computers?
Ans: The evolution of ancient calculating devices led to the growth of contemporary computers. The development of new components and techniques has led to an increase in the capabilities of various computer generations.
The first modern computer was constructed in the 1930s, which was followed by huge machines that took up entire rooms. Computers has grown by Five Generations (The First Computer Generation: (the 1940s-1950s), Second-generation computers: (the 1950s-1960s),The Third Computer Generation: (the 1960s-1970s), The Fourth Computer Generation: (1970s-present), The computer's fifth generation: (present and the future).
2. What are the types of Computers?
Ans: A computer is a device that transforms unusable data into information. According to the set of instructions the user gives it, it processes the input and generates the desired outcome. The size and data handling capabilities of the various types of computers may be used to categorize them into two groups.
As a result, there are five major categories of computers according to size:
Supercomputer
mainframe computer
Minicomputer
Workstation
PC (Personal Computer)
Additionally, there are three different kinds of computers based on their ability to handle data:
Analogue Computer
Digital Computer
hybrid computer
Learning by Doing
Choose the correct one:
1. Which of the following is Massive in size?
Supercomputers.
Mainframe computers.
Analog computers.
2. Which of the following are used as Personal computers?
Supercomputers.
Mainframe computers.
Microcomputers.
Summary
Today's generation is heavily reliant on computers and technology for everything from communication to research. In discussing the history of computers, the generations are frequently brought up. Computer technology has changed throughout the years, and this change is referred to as a "generation."The size and data handling capabilities of the various types of computers may be used to categorize them into two groups.
Based on the size, there are five major categories of computers: mainframe computer, supercomputer, mini computer, PC (Personal Computer).
FAQs on History and Briefing on Computers
1. What is a Computer?
A computer is an electronic device that can be used and programmed to accept data ( as input), process it, and generate required results (as output). A Computer contains various input and output devices like a Desktop, CPU, Speakers, Keyboard, and Mouse.
2. What are the features of Supercomputers?
The features of supercomputers are as follows:
They make use of AI (Artificial intelligence)
They are the fastest and strongest;
They are very costly.
They are enormous in size.
They are employed by companies that manufacture goods.
They process information at a rapid rate.
3. What issues are solved by supercomputers?
Supercomputers are used by climate scientists to predict global climate change, a difficult undertaking with many different factors. Although nuclear weapon testing has been prohibited in the US since 1992, supercomputer simulations guarantee that the country's nuclear arsenal is nonetheless secure and operational.























